Mybatis XML 映射器以及动态SQL
前言
老生常谈的一个框架Mybatis,以下是Mybatis Logo:

像不像一只奋斗的小鸡🐥🐱🏍,哈哈哈。小鸡都开始奋斗了,我们还有什么理由不学习。闲话少讲,上干货。
一、XML 映射器
MyBatis 的真正强大在于它的语句映射,这是它的魔力所在。由于它的异常强大,映射器的 XML 文件就显得相对简单。如果拿它跟具有相同功能的 JDBC 代码进行对比,你会立即发现省掉了将近 95% 的代码。MyBatis 致力于减少使用成本,让用户能更专注于 SQL 代码。
SQL 映射文件只有很少的几个顶级元素(按照应被定义的顺序列出):
- cache – 该命名空间的缓存配置。
- cache-ref – 引用其它命名空间的缓存配置。
- resultMap – 描述如何从数据库结果集中加载对象,是最复杂也是最强大的元素。
- insert – 映射插入语句。
- update – 映射更新语句。
- delete – 映射删除语句。
- select – 映射查询语句。
下一部分将从语句本身开始来描述每个元素的细节。
select标签
属性介绍:
- id:唯一的标识符,与dao层方法名一致。
- parameterType:传给此语句的参数的全路径名或别名 例:com.xxx.xxx.User 或 user
- resultType:期望从这条语句中返回结果的类全限定名或别名。 注意,如果返回的是集合,那应该设置为集合包含的类型,而不是集合本身的类型。 resultType 和 resultMap 之间只能同时使用一个。
- resultMap:对外部 resultMap 的命名引用。结果映射是 MyBatis 最强大的特性,如果你对其理解透彻,许多复杂的映射问题都能迎刃而解。 resultType 和 resultMap 之间只能同时使用一个。
<select id="findByUserId" parameterType="int" resultType="com.zhengwei.entity.User">
select * from n_User where userId= #{userId}
</select>
这个语句名为 findByUserId,接受一个 int(或 Integer)类型的参数,并返回一个或多个User对象,此处parameterType也可以省略。
注意参数符号:
#{userId}
这就告诉 MyBatis 创建一个预处理语句(PreparedStatement)参数,在 JDBC 中,这样的一个参数在 SQL 中会由一个“?”来标识,并被传递到一个新的预处理语句中,就像这样:
// 近似的 JDBC 代码,非 MyBatis 代码...
String selectPerson = "SELECT * FROM USER WHERE ID=?";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(selectPerson);
ps.setInt(1,id);
所以$和#的不同就在于一个$符号一般用来当作占位符,#{}是预编译处理,$ {}是字符串替换。mybatis在处理#{}时,会将sql中的#{}替换为?号,调用PreparedStatement的set方法来赋值;mybatis在处理 $ { } 时,就是把 ${ } 替换成变量的值。使用 #{} 可以有效的防止SQL注入,提高系统安全性。
insert 标签
属性介绍:
- id:唯一的标识符,与dao层方法名一致。
- parameterType:传给此语句的参数的全路径名或别名 例:com.xxx.xxx.User 或 user
- useGeneratedKeys:(仅适用于 insert 和 update)这会令 MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键(比如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系型数据库管理系统的自动递增字段),默认值:false。
useGeneratedKeys="true" 表示取出数据库内部生成的主键 - keyProperty:(仅适用于 insert 和 update)指定能够唯一识别对象的属性,MyBatis 会使用 getGeneratedKeys 的返回值或 insert 语句的 selectKey 子元素设置它的值,默认值:未设置(unset)。如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。
keyProperty="id" 绑定唯一标识 - useGeneratedKeys和keyProperty配合使用
主键回填
<insert id="addCow" parameterType="com.zhengwei.entity.Cow" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into n_cow
(userId,farmId,cowGroupId,status)
values
(#{userId},#{farmId},#{cowGroupId},#{status})
</insert>
update 标签
基本与insert一致,if标签表示判断是否更新这一个字段,userId!=0更新字段,=0不更新字段。
<update id="upadteCow" parameterType="com.zhengwei.entity.Cow">
update n_cow
<set>
<if test="userId!= 0">
userId=#{userId},
</if>
<if test="farmId!= 0">
farmId=#{farmId},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
AND status=0
</update>
delete 标签
<delete id="deleteCowById" parameterType="com.zhengwei.entity.Cow">
delete from n_cow where id=#{id}
</delete>
二、结果映射resultMap
resultMap 元素是 MyBatis 中最重要最强大的元素。它可以让你从 90% 的 JDBC ResultSets 数据提取代码中解放出来,并在一些情形下允许你进行一些 JDBC 不支持的操作。实际上,在为一些比如连接的复杂语句编写映射代码的时候,一份 resultMap 能够代替实现同等功能的数千行代码。ResultMap 的设计思想是,对简单的语句做到零配置,对于复杂一点的语句,只需要描述语句之间的关系就行了。
实体类与表字段映射
<resultMap id="authorResult" type="com.xxx.xxx.Author">
<id property="id" column="author_id"/>
<result property="username" column="author_username"/>
<result property="password" column="author_password"/>
<result property="email" column="author_email"/>
<result property="bio" column="author_bio"/>
</resultMap>
经典的一对一结果集映射
<resultMap type="order" id="orderUserResultMap">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="userId" column="user_id" />
<result property="number" column="number" />
<result property="createtime" column="createtime" />
<result property="note" column="note" />
<!-- association :配置一对一属性 -->
<!-- property:order里面的User属性名 -->
<!-- javaType:属性类型 -->
<association property="user" javaType="user">
<!-- id:声明主键,表示user_id是关联查询对象的唯一标识-->
<id property="id" column="user_id" />
<result property="username" column="username" />
<result property="address" column="address" />
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- 一对一关联,查询订单,订单内部包含用户属性 -->
<select id="queryOrderUserResultMap" resultMap="orderUserResultMap">
SELECT
o.id,
o.user_id,
o.number,
o.createtime,
o.note,
u.username,
u.address
FROM
`order` o
LEFT JOIN `user` u ON o.user_id = u.id
</select>
经典的一对多结果集映射
User类:
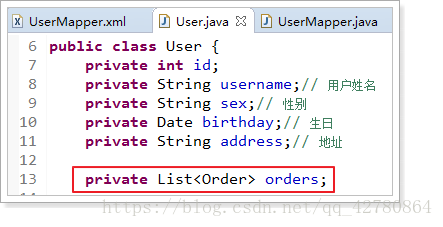
<resultMap type="user" id="userOrderResultMap">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="username" column="username" />
<result property="birthday" column="birthday" />
<result property="sex" column="sex" />
<result property="address" column="address" />
<!-- 配置一对多的关系
property:填写pojo类中集合类类属性的名称
javaType:填写集合类型的名称
-->
<collection property="orders" javaType="list" ofType="order">
<!-- 配置主键,是关联Order的唯一标识 -->
<id property="id" column="oid" />
<result property="number" column="number" />
<result property="createtime" column="createtime" />
<result property="note" column="note" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- 一对多关联,查询订单同时查询该用户下的订单 -->
<select id="queryUserOrder" resultMap="userOrderResultMap">
SELECT
u.id,
u.username,
u.birthday,
u.sex,
u.address,
o.id oid,
o.number,
o.createtime,
o.note
FROM
`user` u
LEFT JOIN `order` o ON u.id = o.user_id
</select>
三、动态 SQL
动态 SQL 是 MyBatis 的强大特性之一。如果你使用过 JDBC 或其它类似的框架,你应该能理解根据不同条件拼接 SQL 语句有多痛苦,例如拼接时要确保不能忘记添加必要的空格,还要注意去掉列表最后一个列名的逗号。利用动态 SQL,可以彻底摆脱这种痛苦。
使用动态 SQL 并非一件易事,但借助可用于任何 SQL 映射语句中的强大的动态 SQL 语言,MyBatis 显著地提升了这一特性的易用性。
if
使用动态 SQL 最常见情景是根据条件包含 where 子句的一部分。比如:
<select id="findActiveBlogWithTitleLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
</select>
choose、when、otherwise
有时候,我们不想使用所有的条件,而只是想从多个条件中选择一个使用。针对这种情况,MyBatis 提供了 choose 元素,它有点像 Java 中的 switch 语句。
还是上面的例子,但是策略变为:传入了 title 就按 title 查找,传入了 author 就按 author 查找的情形。若两者都没有传入,就返回标记为 featured=1的数据。
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND featured = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
trim、where、set
where
前面几个例子已经合宜地解决了一个臭名昭著的动态 SQL 问题。现在回到之前的 if 示例,这次我们将 state = ‘ACTIVE’ 设置成动态条件,看看会发生什么。
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE
<if test="state != null">
state = #{state}
</if>
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</if>
</select>
如果没有匹配的条件会怎么样?最终这条 SQL 会变成这样:
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE
这会导致查询失败。如果匹配的只是第二个条件又会怎样?这条 SQL 会是这样:
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE
AND title like ‘someTitle’
MyBatis 有一个简单且适合大多数场景的解决办法。而在其他场景中,可以对其进行自定义以符合需求。而这,只需要一处简单的改动:
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
<where>
<if test="state != null">
state = #{state}
</if>
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</if>
</where>
</select>
where 元素只会在子元素返回任何内容的情况下才插入 WHERE 子句。而且,若子句的开头为 AND 或 OR,where 元素也会将它们去除。
trim
使用
<sql id="sql-title-author-views">
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
AND author = #{author}
</if>
<if test="views != null">
AND views = #{views}
</if>
</sql>
<select id="queryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from blog
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="AND">
<include refid="sql-title-author-views"></include>
</trim>
</select>
set
set 元素可以用于动态包含需要更新的列,忽略其它不更新的列。
<update id="updateAuthorIfNecessary">
update Author
<set>
<if test="username != null">username=#{username},</if>
<if test="password != null">password=#{password},</if>
<if test="email != null">email=#{email},</if>
<if test="bio != null">bio=#{bio}</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
foreach
动态 SQL 的另一个常见使用场景是对集合进行遍历(尤其是在构建 IN 条件语句的时候)。比如:
<select id="selectPostIn" resultType="domain.blog.Post">
SELECT *
FROM POST P
WHERE ID in
<foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</select>
你可以将任何可迭代对象(如 List、Set 等)、Map 对象或者数组对象作为集合参数传递给 foreach。当使用可迭代对象或者数组时,index 是当前迭代的序号,item 的值是本次迭代获取到的元素。当使用 Map 对象(或者 Map.Entry 对象的集合)时,index 是键,item 是值。
sql语句查询条件的动态拼接
<sql id="if-title-author-views">
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
<if test="views != null">
and views = #{views}
</if>
</sql>
<!--where标签 if-->
<select id="queryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<include refid="if-title-author-views"></include>
</where>
</select>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号