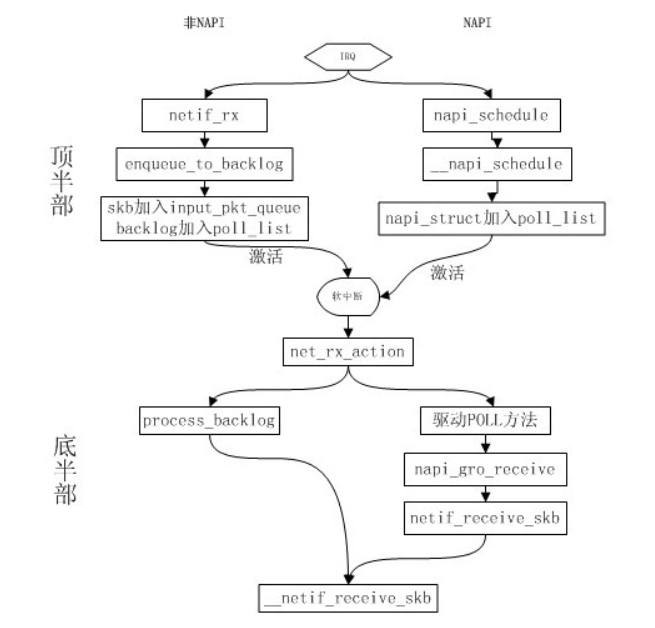
链路层收包2
1、网络层收包概述 NAPI
NAPI是综合中断方式与轮询方式的技术。
中断的好处是响应及时,如果数据量较小,则不会占用太多的CPU事件;缺点是数据量大时,会产生过多中断,
而每个中断都要消耗不少的CPU时间,从而导致效率反而不如轮询高。轮询方式与中断方式相反,它更适合处理
大量数据,因为每次轮询不需要消耗过多的CPU时间;缺点是即使只接收很少数据或不接收数据时,也要占用CPU
时间。
NAPI是两者的结合,数据量低时采用中断,数据量高时采用轮询。平时是中断方式,当有数据到达时,会触发中断
处理函数执行,中断处理函数关闭中断开始处理。如果此时有数据到达,则没必要再触发中断了,因为中断处理函
数中会轮询处理数据,直到没有新数据时才打开中断。
很明显,数据量很低与很高时,NAPI可以发挥中断与轮询方式的优点,性能较好。如果数据量不稳定,且说高不高
说低不低,则NAPI则会在两种方式切换上消耗不少时间,效率反而较低一些。
2.实现区别分析:
NAPI目前要求驱动设备提供poll 方法
非NAPI的内核接口为netif_rx(),NAPI的内核接口为napi_schedule()。
非NAPI使用共享的CPU队列softnet_data->input_pkt_queue
NAPI使用设备内存或者驱动程序的接受环
/*
* Structure for NAPI scheduling similar to tasklet but with weighting
*/
struct napi_struct {
/* The poll_list must only be managed by the entity which
* changes the state of the NAPI_STATE_SCHED bit. This means
* whoever atomically sets that bit can add this napi_struct
* to the per-CPU poll_list, and whoever clears that bit
* can remove from the list right before clearing the bit.
*/
struct list_head poll_list; /* 用于加入处于轮询状态的设备队列 */
unsigned long state; /* 设备的状态 */
int weight; /* 每次处理的最大数量,非NAPI有默认值*/
unsigned int gro_count;
int (*poll)( struct napi_struct *, int ); /* 此设备的轮询方法,非NAPI为process_backlog() */
#ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
spinlock_t poll_lock;
int poll_owner;
#endif
struct net_device *dev;
struct sk_buff *gro_list;
struct sk_buff *skb;
struct hrtimer timer;
struct list_head dev_list;
struct hlist_node napi_hash_node;
unsigned int napi_id;
};
void netif_napi_add( struct net_device *dev, struct napi_struct *napi,
int (*poll)( struct napi_struct *, int ), int weight)
{
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&napi->poll_list);
hrtimer_init(&napi->timer, CLOCK_MONOTONIC, HRTIMER_MODE_REL_PINNED);
napi->timer.function = napi_watchdog;
napi->gro_count = 0;
napi->gro_list = NULL;
napi->skb = NULL;
napi->poll = poll;
if (weight > NAPI_POLL_WEIGHT)
pr_err_once( "netif_napi_add() called with weight %d on device %s\n" ,
weight, dev->name);
napi->weight = weight;
list_add(&napi->dev_list, &dev->napi_list);
napi->dev = dev;
#ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
spin_lock_init(&napi->poll_lock);
napi->poll_owner = -1;
#endif
set_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &napi->state);
napi_hash_add(napi);
}
NAPI 方式为在中断处理函数中调用napi_schedule 来获取数据报文
static irqreturn_t e100_intr(int irq, void *dev_id) { struct net_device *netdev = dev_id; struct nic *nic = netdev_priv(netdev); u8 stat_ack = ioread8(&nic->csr->scb.stat_ack); netif_printk(nic, intr, KERN_DEBUG, nic->netdev, "stat_ack = 0x%02X\n", stat_ack); if (stat_ack == stat_ack_not_ours || /* Not our interrupt */ stat_ack == stat_ack_not_present) /* Hardware is ejected */ return IRQ_NONE; /* Ack interrupt(s) */ iowrite8(stat_ack, &nic->csr->scb.stat_ack); /* We hit Receive No Resource (RNR); restart RU after cleaning */ if (stat_ack & stat_ack_rnr) nic->ru_running = RU_SUSPENDED; //napi_schedule if (likely(napi_schedule_prep(&nic->napi))) { e100_disable_irq(nic);//关闭中断 __napi_schedule(&nic->napi); } return IRQ_HANDLED;
此时napi 的poll初始化在驱动中注册如下

static int e100_probe(struct pci_dev *pdev, const struct pci_device_id *ent) { struct net_device *netdev; struct nic *nic; int err; if (!(netdev = alloc_etherdev(sizeof(struct nic)))) return -ENOMEM; netdev->hw_features |= NETIF_F_RXFCS; netdev->priv_flags |= IFF_SUPP_NOFCS; netdev->hw_features |= NETIF_F_RXALL; netdev->netdev_ops = &e100_netdev_ops; netdev->ethtool_ops = &e100_ethtool_ops; netdev->watchdog_timeo = E100_WATCHDOG_PERIOD; strncpy(netdev->name, pci_name(pdev), sizeof(netdev->name) - 1); nic = netdev_priv(netdev); netif_napi_add(netdev, &nic->napi, e100_poll, E100_NAPI_WEIGHT); ---------------- 未完
/** * __napi_schedule - schedule for receive * @n: entry to schedule * * The entry's receive function will be scheduled to run. * Consider using __napi_schedule_irqoff() if hard irqs are masked. */ void __napi_schedule(struct napi_struct *n) { unsigned long flags; local_irq_save(flags); ____napi_schedule(this_cpu_ptr(&softnet_data), n); local_irq_restore(flags); } /* Called with irq disabled */ static inline void ____napi_schedule(struct softnet_data *sd, struct napi_struct *napi) { list_add_tail(&napi->poll_list, &sd->poll_list); __raise_softirq_irqoff(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ); } // 也就是 将 napi struct 加入到 cpu的sd list 中, 然后唤醒软中断, 软中断来处理
static int e100_poll(struct napi_struct *napi, int budget) { struct nic *nic = container_of(napi, struct nic, napi); unsigned int work_done = 0; e100_rx_clean(nic, &work_done, budget);//从网络设备中读取报文。并由netif_recieve_skb 接收报文到上层协议中去,work_done为已经读取的报文 e100_tx_clean(nic);//释放已经发送出去的报文 /* If budget not fully consumed, exit the polling mode */ if (work_done < budget) {//如果待输出 输入的报文已经处理完成,退出轮询模式,从网络轮询设备队列中删除网络设备,并打开网络设备中断。 napi_complete(napi); e100_enable_irq(nic); } return work_done; }
oid __napi_complete(struct napi_struct *n) { BUG_ON(!test_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state)); list_del_init(&n->poll_list);/从poll_list中删除 smp_mb__before_atomic(); clear_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state); } -- /* all work done, exit the polling mode */ void napi_complete_done(struct napi_struct *n, int work_done) { unsigned long flags; /* * don't let napi dequeue from the cpu poll list * just in case its running on a different cpu */ if (unlikely(test_bit(NAPI_STATE_NPSVC, &n->state))) return; if (n->gro_list) { ---------------------- napi_gro_flush(n, false);//gro 全部提交协议栈 }//对于gro 后续再看 --------------------------------- /* If n->poll_list is not empty, we need to mask irqs */ local_irq_save(flags); __napi_complete(n);/从poll_list中删除 local_irq_restore(flags); } }
NAPI方式中的POLL方法由驱动程序提供,在通过netif_napi_add()加入napi_struct时指定。
在驱动的poll()中,从自身的队列中获取sk_buff后,如果网卡开启了GRO,则会调用
napi_gro_receive()处理skb,否则直接调用netif_receive_skb()。
POLL方法应该和process_backlog()大体一致,多了一些具体设备相关的部分。

链路层收包下半部分析:
static int napi_poll(struct napi_struct *n, struct list_head *repoll) { void *have; int work, weight; list_del_init(&n->poll_list); have = netpoll_poll_lock(n); weight = n->weight; /* This NAPI_STATE_SCHED test is for avoiding a race * with netpoll's poll_napi(). Only the entity which * obtains the lock and sees NAPI_STATE_SCHED set will * actually make the ->poll() call. Therefore we avoid * accidentally calling ->poll() when NAPI is not scheduled. */ work = 0; /*如果取得的napi状态是被调度的,就执行napi的轮询处理函数*/ if (test_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state)) { /* NAPI的napi_struct是自己构造的,该结构上的poll钩子函数也是自己定义的。 非NAPI的napi_struct结构是默认的,也就是per cpu的softnet_data>backlog, 起poll钩子函数为process_backlog */ work = n->poll(n, weight);netif_napi_add trace_napi_poll(n); } WARN_ON_ONCE(work > weight); if (likely(work < weight)) goto out_unlock; /* Drivers must not modify the NAPI state if they * consume the entire weight. In such cases this code * still "owns" the NAPI instance and therefore can * move the instance around on the list at-will. */ if (unlikely(napi_disable_pending(n))) { napi_complete(n); goto out_unlock; } if (n->gro_list) { /* flush too old packets * If HZ < 1000, flush all packets. */ napi_gro_flush(n, HZ >= 1000); } /* Some drivers may have called napi_schedule * prior to exhausting their budget. */ if (unlikely(!list_empty(&n->poll_list))) { pr_warn_once("%s: Budget exhausted after napi rescheduled\n", n->dev ? n->dev->name : "backlog"); goto out_unlock; } list_add_tail(&n->poll_list, repoll); out_unlock: netpoll_poll_unlock(have); return work; }
static void net_rx_action(struct softirq_action *h) { struct softnet_data *sd = this_cpu_ptr(&softnet_data); /*设置软中断处理程序一次允许的最大执行时间为2个jiffies*/ unsigned long time_limit = jiffies + 2; /*设置软中断接收函数一次最多处理的报文个数为 300 */ int budget = netdev_budget; LIST_HEAD(list); LIST_HEAD(repoll); local_irq_disable();//关闭本cpu上的中断 后面napi中的poll 完成后有可能打开设备网卡的中中断 list_splice_init(&sd->poll_list, &list); local_irq_enable(); for (;;) { struct napi_struct *n; if (list_empty(&list)) { if (!sd_has_rps_ipi_waiting(sd) && list_empty(&repoll)) return; break; } /* 取得softnet_data pool_list 链表上的一个napi, 即使现在硬中断抢占软中断,会把一个napi挂到pool_list的尾端 软中断只会从pool_list 头部移除一个pool_list,这样不存在临界区*/ n = list_first_entry(&list, struct napi_struct, poll_list); /*执行napi poll*/
/*
NAPI的napi_struct是自己构造的,该结构上的poll钩子函数也是自己定义的。
非NAPI的napi_struct结构是默认的,也就是per cpu的softnet_data>backlog,起poll钩子函数为process_backlog
*/ budget -= napi_poll(n, &repoll);/*总额度递减*/ /* If softirq window is exhausted then punt. * Allow this to run for 2 jiffies since which will allow * an average latency of 1.5/HZ. */ if (unlikely(budget <= 0 || time_after_eq(jiffies, time_limit))) { sd->time_squeeze++; break; } } __kfree_skb_flush(); local_irq_disable(); /*禁止本地CPU 的中断,下面会有把没执行完的NAPI挂到softnet_data
尾部的操作,和硬中断存在临界区。同时while循环时判断list是否为空时也要禁止硬中断抢占* list_splice_tail_init(&sd->poll_list, &list); list_splice_tail(&repoll, &list); list_splice(&list, &sd->poll_list); if (!list_empty(&sd->poll_list))// 还有数据需要处理 就打开软中断 __raise_softirq_irqoff(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ);// 设置softirq bitmask 等待 执行软中断回调 net_rps_action_and_irq_enable(sd); }
这里有处理方式比较直观,直接遍历poll_list链表,处理之前设置了两个限制:budget和time_limit。前者限制本次处理数据包的总量,后者限制本次处理总时间。只有二者均有剩余的情况下,才会继续处理。处理期间同样是开中断的,每次总是从链表表头取设备进行处理,如果设备被调度,其实就是检查NAPI_STATE_SCHED位,则调用 napi_struct的poll函数,处理结束如果没有处理完,则把设备移动到链表尾部,否则从链表删除
/*
* process_backlog()在非NAPI方式下,虚拟网络设备的
* 轮询函数。当虚拟网络设备backlog_dev添加到
* 网络设备轮询队列后,在数据包输入软中断
* 中会调用process_backlog()进行数据包的输入。
* @napi:进行轮询的虚拟的网络设备对应的结构
* @budget:在数据包输入软中断中,网络设备读取
* 报文的配额。
*/
/*
接收数据包的下半部处理流程为:
net_rx_action // 软中断
|--> process_backlog() // 默认poll
|--> __netif_receive_skb() // L2处理函数
|--> ip_rcv() // L3入口
*/
static int process_backlog(struct napi_struct *napi, int quota) { int work = 0; struct softnet_data *sd = container_of(napi, struct softnet_data, backlog); /* Check if we have pending ipi, its better to send them now, * not waiting net_rx_action() end. */ if (sd_has_rps_ipi_waiting(sd)) { local_irq_disable(); net_rps_action_and_irq_enable(sd); } napi->weight = weight_p; local_irq_disable(); while (1) { struct sk_buff *skb; while ((skb = __skb_dequeue(&sd->process_queue))) { //在下面的skb_queue_splice_tail_init中,被放到了process_queue中 rcu_read_lock(); local_irq_enable(); /* * 分析分组类型,以便根据分组 * 类型将分组传递给网络层的接收函数, * 即传递到网络系统的更高一层.为此, * 该函数遍历有可能负责当前分组类型的所有 * 网络层函数,一一调用deliver_skb * * update: * 将当前报文传递到上层协议栈 */ __netif_receive_skb(skb); rcu_read_unlock(); local_irq_disable(); input_queue_head_incr(sd); if (++work >= quota) { local_irq_enable(); return work; } } rps_lock(sd); if (skb_queue_empty(&sd->input_pkt_queue)) { /* * Inline a custom version of __napi_complete(). * only current cpu owns and manipulates this napi, * and NAPI_STATE_SCHED is the only possible flag set * on backlog. * We can use a plain write instead of clear_bit(), * and we dont need an smp_mb() memory barrier. */ napi->state = 0; rps_unlock(sd); break; } /* 把sd->input_pkt_queue链表中的节点添加到sd->process_queue的尾部。 然后初始化sd->input_pkt_queue链表 */ skb_queue_splice_tail_init(&sd->input_pkt_queue, &sd->process_queue); rps_unlock(sd); } local_irq_enable(); return work; }
对于napi的状态:NAPI_STATE_SCHED ----解决了什么问题:
A:
- 初始化时:netif_napi_add 会将 napi->state 设置set为调度状态。
- open网卡时,会注册中断函数,然后配置网卡TX/RX信息(DMA等) 然后 enable napi,此时会clear 掉标志 也就是非调度状态
- 发生中断时, 调用napi_schedule ;其会检查是否为调度状态NAPI_STATE_SCHED ,如果不是调度状态,则将list_add_tail(&napi->poll_list, &sd->poll_list),添加到 队列。唤醒soft_irq。
- 如果是调度状态,这直接返回;也就是次队列不会加入到sd->list 里面去。
- 后续 net_rx_action 会处理报文,如果报文处理完了,就回调用napi_complete,此时会将状态设置位非调度状态,同时enable 网卡中断。
也就是NAPI_STATE_SCHED 和 enable 网卡中断互斥。。。。。
在软中断操作sd->list时,需要考虑硬件中断打断软中断 操作list的可能性
Softirq 收包预算:netdev_budget 和 netdev_budget_usecs
(新内核中变为:time_limit = jiffies + usecs_to_jiffies(netdev_budget_usecs);)
time_limit = jiffies + usecs_to_jiffies(netdev_budget_usecs);)这俩参数控制每次 softirq 线程的收包预算,
- budget:最多可以收包的数量
- time_limit:最长可以占用的 CPU 时间
softnet_data.time_squeeze 字段记录的是满足如下条件的次数: ring buffer 中还有包等待接收,但本次 softirq 的 budget 已经用完了。 这对理解网络处理的瓶颈至关重要。
在数据链路层接受数据并传递给上层的步骤如下所示:
1、一个 package 到达机器的物理网络适配器,当它接收到数据帧时,就会触发一个中断,并将通过 DMA 传送到位于 linux kernel 内存中的 rx_ring。
2、网卡发出中断,通知 CPU 有个 package 需要它处理。中断处理程序主要进行以下一些操作,包括分配 skb_buff 数据结构,并将接收到的数据帧从网络适配器I/O端口拷贝到skb_buff 缓冲区中;从数据帧中提取出一些信息,并设置 skb_buff相应的参数,这些参数将被上层的网络协议使用,例如skb->protocol;
3、终端处理程序经过简单处理后,发出一个软中断(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ),通知内核接收到新的数据帧。
4、内核 2.5 中引入一组新的 API 来处理接收的数据帧,即 NAPI。所以,驱动有两种方式通知内核:(1) 通过以前的函数netif_rx;(2)通过NAPI机制。该中断处理程序调用 Network device的 netif_rx_schedule函数,进入软中断处理流程,再调用net_rx_action函数。
5、该函数关闭中断,获取每个 Network device 的 rx_ring 中的所有 package,最终 pacakage 从 rx_ring 中被删除,进入netif _receive_skb处理流程。
6、netif_receive_skb是链路层接收数据报的最后一站。它根据注册在全局数组 ptype_all 和 ptype_base 里的网络层数据报类型,把数据报递交给不同的网络层协议的接收函数(INET域中主要是ip_rcv和arp_rcv)。该函数主要就是调用第三层协议的接收函数处理该skb包,进入第三层网络层处理。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号