openCV - 3. Mat对象
Mat对象与IplImage对象、Mat对象使用、Mat定义数组
Mat对象与IplImage对象
- Mat对象OpenCV2.0之后引进的图像数据结构、自动分配内存、不存在内存泄漏的问题,是面向对象的数据结构。分了两个部分,头部与数据部分
- IplImage是从2001年OpenCV发布之后就一直存在,是C语言风格的数据结构,需要开发者自己分配与管理内存,对大的程序使用它容易导致内存泄漏问题
Mat对象构造函数与常用方法
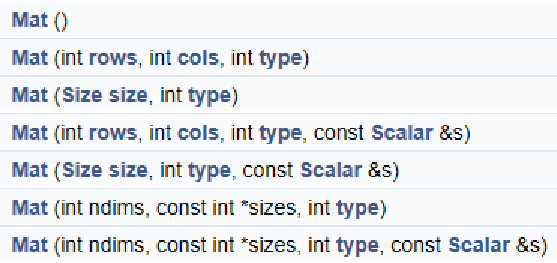
常用方法:
void copyTo(Mat mat)
void convertTo(Mat dst, int type)
Mat clone()
int channels()
int depth()
bool empty();
uchar* ptr(i=0)
Mat对象使用
-
部分复制:一般情况下只会复制Mat对象的头和指针部分,不会复制数据部分
Mat A = imread(imgFilePath); Mat B(A) // 只复制 -
完全复制:如果想把Mat对象的头部和数据部分一起复制,可以通过如下两个API实现
Mat F = A.clone(); 或 Mat G; A.copyTo(G);
Mat对象使用 - 四要点
- 输出图像的内存是自动分配的
- 使用OpenCV的C++接口,不需要考虑内存分配问题
- 赋值操作和拷贝构造函数只会复制头部分
- 使用
clone与copyTo两个函数实现数据完全复制
Mat对象创建
-
cv::Mat::Mat构造函数 例:Mat M(2,2,CV_8UC3, Scalar(0,0,255))
其中前两个参数分别表示 行(row) 跟 列(column);第三个CV_8UC3中的8表示每个通道占8位、U表示无符号、C表示Char类型、3表示通道数目是3; 第四个参数是向量表示初始化每个像素值是多少,向量长度对应通道数目一致 -
创建多维数组
cv::Mat::createint sz[3] = {2,2,2}; // 将一个长度为3、元素为2的数组当做第二个参数传入 Mat L(3,sz, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0)); -
cv::Mat::create实现Mat M; M.create(4, 3, CV_8UC2); M = Scalar(127,127); cout << "M = " << endl << " " << M << endl << endl; uchar* firstRow = M.ptr<uchar>(0); printf("%d", *firstRow);
定义小数组
Mat C = (Mat_<double>(3,3) << 0, -1, 0, -1, 5, -1, 0, -1, 0);
cout << "C = " << endl << " " << C << endl << endl;
演示代码
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** args) {
// 载入图片
Mat image = imread("D:/test.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (image.empty()) {
cout << "could not find the image resource..." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
namedWindow("My Image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("My Image", image);
Mat M;
M.create(4, 3, CV_8UC2);
M = Scalar(127,127);
cout << "M = " << endl << " " << M << endl << endl;
uchar* firstRow = M.ptr<uchar>(0);
printf("%d\n", *firstRow);
Mat C = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 0, -1, 0,
-1, 5, -1,
0, -1, 0);
cout << "C = " << endl << " " << C << endl << endl;
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号