MySQL(单表查询、多表查询、Navicat软件使用、查询练习、pymysql模块)
一 单表操作
表准备和注意事项
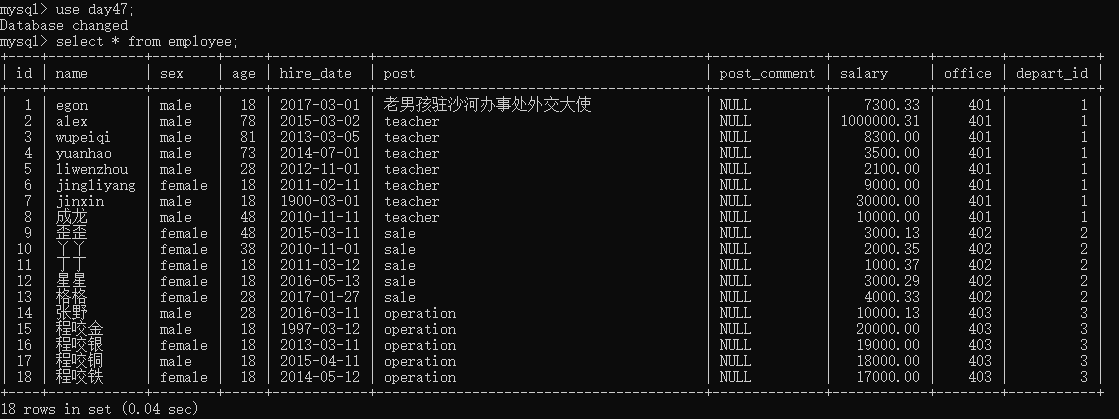
create table employee( id int not null unique auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null, sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', #大部分是男的 age int(3) unsigned not null default 28, hire_date date not null, post varchar(50), post_comment varchar(100), salary double(15,2), office int, #一个部门一个屋子 depart_id int ); insert into employee(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values ('egon','male',18,'20170301','老男孩驻沙河办事处外交大使',7300.33,401,1), #以下是教学部 ('alex','male',78,'20150302','teacher',1000000.31,401,1), ('wupeiqi','male',81,'20130305','teacher',8300,401,1), ('yuanhao','male',73,'20140701','teacher',3500,401,1), ('liwenzhou','male',28,'20121101','teacher',2100,401,1), ('jingliyang','female',18,'20110211','teacher',9000,401,1), ('jinxin','male',18,'19000301','teacher',30000,401,1), ('成龙','male',48,'20101111','teacher',10000,401,1), ('歪歪','female',48,'20150311','sale',3000.13,402,2),#以下是销售部门 ('丫丫','female',38,'20101101','sale',2000.35,402,2), ('丁丁','female',18,'20110312','sale',1000.37,402,2), ('星星','female',18,'20160513','sale',3000.29,402,2), ('格格','female',28,'20170127','sale',4000.33,402,2), ('张野','male',28,'20160311','operation',10000.13,403,3), #以下是运营部门 ('程咬金','male',18,'19970312','operation',20000,403,3), ('程咬银','female',18,'20130311','operation',19000,403,3), ('程咬铜','male',18,'20150411','operation',18000,403,3), ('程咬铁','female',18,'20140512','operation',17000,403,3) ; # 当表字段特别多,展示的时候错乱,可以使用\G分行展示 select * from employee\G; # 个别同学的电脑在插入中文的时候是会出现乱码或者空白的现象,可以将字符编码,统一设置成GBK
几个重要关键字的执行顺序
# 书写顺序 select id,name from employee where id > 3; # 执行顺序 from where select ''' 虽然执行顺序和书写顺序不一致,按照书写顺序的方式写sql select * 先用*占位 之后补全后面的sql语句 最后将*号替换后你想要的具体字段 '''
# 作用:是对整体数据的一个筛选操作 # 1、查询id大于等于3小于等于6的数据 select id,name,age from employee where id>=3 and id<=6; select id,name,age from employee where id between 3 and 6; 两者等价 # 2、查询薪资是20000或者18000或者17000的数据 select * from employee where salary=20000 or salary=18000 or salary=17000; select * from employee where salary in (20000,18000,17000); 两者等价 # 3、查询员工姓名中包含字母o的员工的姓名和薪资 ''' 模糊查询 like % 匹配任意多个字符 — 匹配任意单个字符 ''' select name,salary from employee where name like '%o%'; # 4、查询员工姓名是有四个字符组成的,姓名和薪资 select name,salary from employee where name like '____'; select name,salary from employee where char_length(name)=4; # 5、查询id小于3或者id大于6的数据 select * from employee where id not between 3 and 6; # 6、查询薪资不在20000,18000,17000范围的数据 select * from employee where salary not in (20000,18000,17000); # 7、查询岗位描述为空的员工姓名和岗位名,针对null不能用=,用is select name,post from employee where post_comment is null;
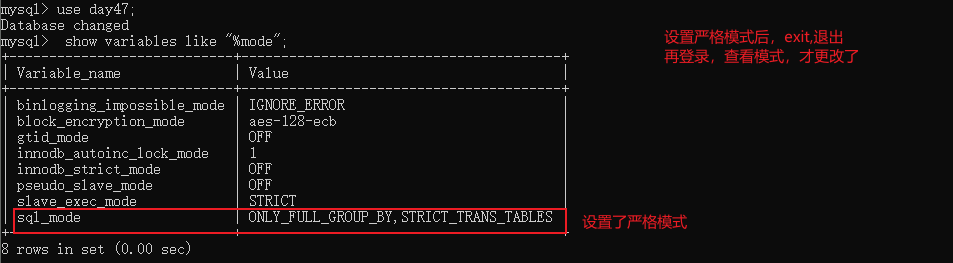
# 分组实际应用场景,分组应用场景非常多 男女比例 部门平均薪资 国家之间数据统计 # 1 按照部门分组 select * from employee group by post; ''' 分组后,最小可操作单元应该是组,还不在是组内的单个数据 上述命令在你没有设置严格模式的时候是可正常执行的,返回的是分组之后,每个组的第一条数据, 但是不符合分组的规范,分组后不应该考虑单个数据,而应该以组为操作单位(分组之后,没办法直接获取 组内单个数据) 如果设置了严格模式,那么上述命令会直接报错 ''' set global sql_mode='strict_trans_tables,only_full_group_by'; 设置严格模式之后,分组默认只能拿到分组的依据 select post from employee group by post; 按照什么分组就只能拿到分组,其他字段不能直接获取,需要借助于一些方法(聚合函数) ''' 什么时候需要分组 关键字 每个 平均 最高 最低 聚合函数 max min avg sum count '''
案例
# 1.获取每个部门的最高薪资 select post,max(salary) from employee group by post; select post as '部门', max(salary) as '最高薪资' from employee group by post; # as可以给字段起别名,也可以直接省略不写,但不推荐 select post '部门', max(salary) '最高薪资' from employee group by post; # 不推荐 # 2.获取每个部门的最低薪资 select post,min(salary) from employee group by post; # 3.获取每个部门的平均薪资 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post; # 4.获取每个部门的工资总和 select post,sum(salary) from employee group by post; # 5.获取每个部门的人数 select post,count(id) from employee group by post; # 常用,符合逻辑,count是计数的意思 # 6.查询分组之后的部门名称和每个部门下所有的员工姓名 # group_concat 不单单可以支持你获取分组之后的其他字段值,还支持拼接操作 select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post; select post,group_concat(name,'_yyds') from employee group by post; select post,group_concat(name,':',salary) from employee group by post; # concat 不分组的时候用 select concat('NAME:',name),concat('SAL:',salary) from employee; #concat_ws 如果多个字段之间的连接符号是相同的情况下,你可以直接使用concat_ws来完成 select concat_ws(':',name,age,sex) from employee; ''' 补充 as 语法不单单可以给字段起别名,还可以给表临时起别名 ''' select emp.id,emp.name from employee as emp; # 7.查询每个人的年薪,12薪 select name,salary*12 from employee;
group_concat()使用

# 关键字where和group by 同时出现的时候group by必须在where的后面 where先对整体数据进行过滤之后再分组操作 where筛选条件不能使用聚合函数 select id,name,age from employee where max(salary)>3000; # 报错 select max(salary) from employee; # 不分组,默认整体就是一组 # 8.统计各部门年龄在30岁以上的员工平均薪资 1)先求所有年龄大于30岁的员工 select * from employee where age>30; 2)再对结果进行分组 select * from employee where age>30 group by post; 3)整合 select post,avg(salary) from employee where age>30 group by post;
''' having的语法跟where是一致的 只不过having是在分组之后进行的过滤操作 既having是可以直接使用聚合函数的 ''' # 统计各部门年龄在30岁以上的员工平均工资并且保留平均薪资大于10000的部门 select post,avg(salary) from employee where age>30 group by post having avg(salary)>10000; # 先对各部门年龄在30岁以上的员工平均工资进行分组的基础上,再用having进行过滤
''' 一定要注意,必须是完全一样的数据才可以去重!!! 一定不要将主键忽视,有主键存在的情况下,是不可能去重的 ORM 对象关系映射,让不懂SQL语句的人也能够很好的操作数据 表 类 一条条数据 对象 字段对应的值 对象的属性 写类 创建表 用类生成对象 创建数据 对象点属性 获取数据字段对应的值 目的让懂python面向对象的人也可以操作MySQL ''' select distinct id,age from employee; # 有id主键,去不了重 select distinct age from employee;
select * from employee order by salary; select * from employee order by salary asc; # 升序 select * from employee order by salary desc; # 降序 ''' order by默认是升序 asc可以省略不写 也可以改成降序 desc ''' select * from employee order by age desc,salary asc; # 先按照age降序排,如果碰到age相同,则再按照salary升序排 # 统计各部门年龄在10岁以上的员工平均工资并且保留平均薪资大于1000的部门,然后对平均工资降序排序 select post,avg(salary) from employee where age>10 group by post having avg(salary)>1000 order by avg(salary) desc;
select * from employee; '''针对数据过多的情况,通常做分页处''' select * from employee limit 3; # 只展示三条数据 select * from employee limit 0,5; select * from employee limit 5,5; ''' 第一个参数是起始位置 第二个参数是展示条数 '''
select * from employee where name regexp '^j.*(n|y)$'; # 匹配以j开头,n或y结尾的所有字符,.*贪婪匹配 ''' 正则是一门独立的语言 在python中使用re模块 1.re模块中常用的方法 findall:分组优先展示 ^j.*(n|y)$ 不会展示所有正则表达式匹配到的内容 仅仅展示括号内正则表达式匹配到的内容 math:从头匹配 search:从整体匹配 2.贪婪匹配与非贪婪匹配 正则表达式默认都是贪婪匹配的 将贪婪变成非贪婪只需要在正则表达式后面加? .* 贪婪 .*? 非贪婪 '''
二 多表操作
前期表准备
# 建表 create table department( id int, name varchar(20) ); create table employee1( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', age int, dep_id int ); # 插入数据 insert into department values (200,'技术'), (201,'人力资源'), (202,'销售'), (203,'运营'); insert into employee1(name,sex,age,dep_id) values ('egon','male',18,200), ('alex','female',48,201), ('wupeiqi','male',38,201), ('yuanhao','female',28,202), ('liwenzhou','male',18,200), ('jingliyang','female',18,204) ;

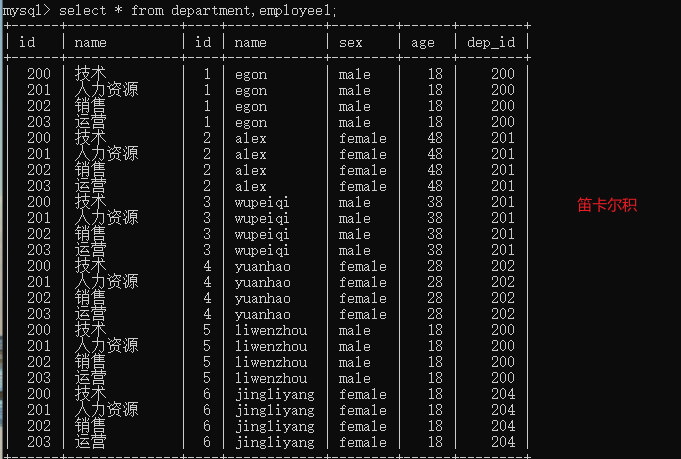
select * from department,employee1; # 笛卡尔积 select * from employee1,department where employee1.dep_id=department.id; ''' MySQL也知道,你在后面查询数据过程中,肯定会经常用到拼表操作 所以特地给你开设了对应的方法 inner join 内连接 left join 左连接 right join 右连接 union 全连接 ''' # inner join 内连接 select * from employee1 inner join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id; # 只拼接两张表中公有的数据部分 # left join 左连接 select * from employee1 left join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id; # 左表所有的数据都展示出来,没有对应的项就用NULL # right join 右连接 select * from employee1 right join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id; # 右表所有的数据都展示出来,没有对应的项就用NULL # union 全连接 select * from employee1 left join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id union select * from employee1 right join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id;
''' 子查询就是我们平时解决问题的思路 分步骤解决问题 第一步 第二部 ... 将一个查询语句的结果当做另外一个查询语句的条件去用 ''' # 查询部门是技术或者人力资源的员工信息 1.先获取部门的id号 2.再去员工表里面筛选出对应的员工 select id from department where name='技术' or name='人力资源'; select name from employee1 where dep_id in (200,201); 两个条语句合起来 select * from employee1 where dep_id in ( select id from department where name='技术' or name='人力资源');
表的查询结果可以作为其他表的查询条件 也可以通过起别名的方式把它作为一张虚拟表跟其他表关联 ''' 多表查询两种方式 先拼接表再查询 子查询,一步一步来 ''' # 书写sql语句的时候,select后面先用*占位,之后写完再改 # 在写较为复杂的sql语句的时候,不要想着一口气写完,写一点查一点看一点再写(涉及到数据查询相关的语法都不应该一次性写完,不现实) # 在做多表查询的时候,联表操作和子查询可能会结合使用
# 查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名称 ''' 只要是多表查询,就有两种思路 联表 子查询 ''' # 联表操作 1 先拿到部门和员工表拼接之后的结果 2 分析语义,得出需要进行分组 select department.name from employee1 inner join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id group by department.name having avg (age)>25; '''涉及到多表操作的时候,一定要加上表的前缀 department.name''' # 子查询 1 拿到平均年龄25岁的dep_id 2 以dep_id为条件,到部门表中筛选名字 select name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age)>25); # 关键字exists(了解) 只返回布尔值 True False 返回True的时候外层查询语句执行 返回False的时候外层查询语句不再执行 select * from employee1 where exists (select id from department where id>3); select * from employee1 where exists (select id from department where id>300); # 不执行
https://www.cr173.com/soft/126934.html
navicat图形化界面有时候反应速度较慢,你可以选择刷新或者关闭当前窗口再次打开即可
当你有一些需求该软件无法满足的时候,就自己动手写sql



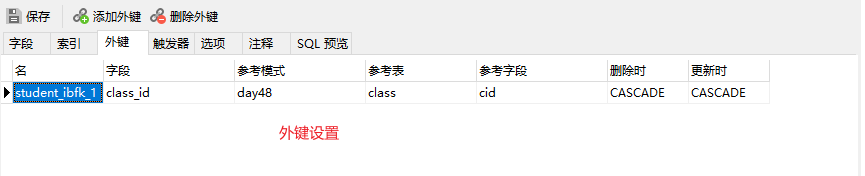
''' 1.MySQL是不区分大小写 2.MySQL建议所有的关键字写大写(也可以不) 3.MySQL中的注释,有两种 -- # 4.再navicat中快手添加注释和Pycharmy一样 ctr + ? '''
student表和course表是 多对多,第三张表是score表
teacher表和course表是一对多
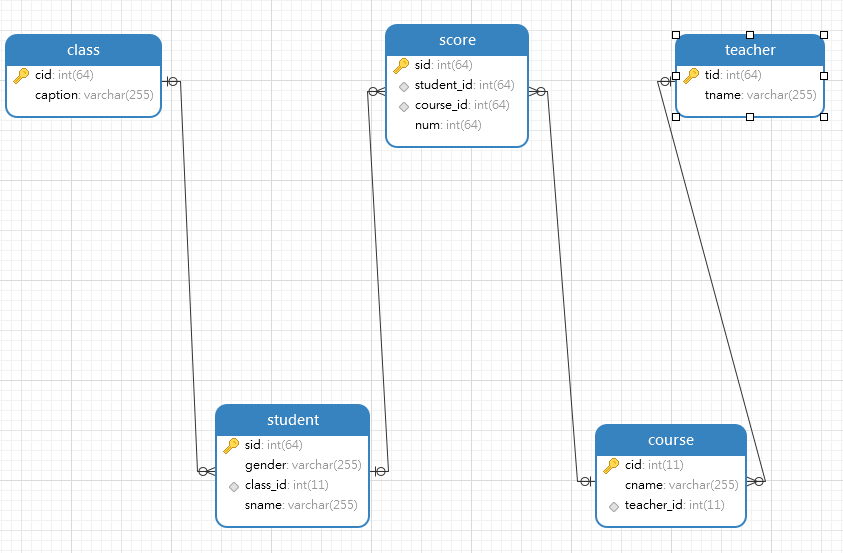
# 1、查询所有的课程的名称以及对应的任课老师名 SELECT course.cname, teacher.tname FROM course INNER JOIN teacher ON course.teacher_id = teacher.tid; # 2、查询平均成绩大于八十分的同学的姓名和平均成绩 ''' 分析 1.成绩表和学生表联表操作 2.按照学生id分组 3.avg(num)>80过滤,取值学生id及对应的平均值 4.上述生成的虚拟表取名为t1,再跟学生表进行连表操作 5.去学生姓名及对应的平均成绩 ''' SELECT student.sname, t1.avg_num FROM student INNER JOIN ( SELECT score.student_id, avg( num ) AS avg_num FROM score INNER JOIN student ON score.student_id = student.sid GROUP BY score.student_id HAVING AVG( num ) > 80 ) AS t1 ON student.sid = t1.student_id; # 3、查询没有报李平老师课的学生姓名 # 分步操作 # 1)先找到李平老师教授的课程id SELECT course.cid FROM teacher inner JOIN course on course.teacher_id=teacher.tid WHERE teacher.tname='李平老师'; # 2)再找所有报了李平老师课程的学生id(去重) SELECT DISTINCT student_id FROM score WHERE course_id in (SELECT course.cid FROM teacher inner JOIN course on course.teacher_id=teacher.tid WHERE teacher.tname='李平老师'); # 3)之后去学生表里面去反,就可以取到没有报李平老师课程的学生姓名 SELECT student.sname FROM student WHERE sid NOT IN ( SELECT DISTINCT student_id FROM score WHERE course_id IN ( SELECT course.cid FROM teacher INNER JOIN course ON course.teacher_id = teacher.tid WHERE teacher.tname = '李平老师' ) ); # 4、查询没有同时选修物理课程和体育课程的学生姓名 # (只要选了一门的,选了两门和没有选的都不要) # 1)先查物理和体育课程的id SELECT course.cid FROM course WHERE course.cname in ('物理','体育'); # 2)再去获取所有选了物理和体育的学生数据 SELECT * from score WHERE score.course_id in (SELECT course.cid FROM course WHERE course.cname in ('物理','体育')); # 3)按照学生分组,利用聚合函数count筛选出只选了一门的学生id SELECT score.student_id FROM score WHERE score.course_id in (SELECT course.cid FROM course WHERE course.cname in ('物理','体育')) GROUP BY score.student_id HAVING count(score.student_id)=1; # 4)依照id获取学生姓名 SELECT student.sname FROM student WHERE student.sid IN ( SELECT score.student_id FROM score WHERE score.course_id IN ( SELECT course.cid FROM course WHERE course.cname IN ( '物理', '体育' ) ) GROUP BY score.student_id HAVING count( score.student_id ) = 1 ); # 5、查询挂科超过两门(包括两门)的学生姓名和班级 # 1)先筛选出分数小于60的数据 SELECT score.student_id FROM score WHERE score.num<60 GROUP BY score.student_id HAVING count(score.student_id)>=2; # 2)按照学生分组,对数据进行计数获取大于等于2的数据 SELECT student.sname, class.caption FROM class INNER JOIN student ON student.class_id = class.cid WHERE student.sid IN ( SELECT score.student_id FROM score WHERE score.num < 60 GROUP BY score.student_id HAVING count( score.student_id ) >= 2 );
在解决sql查询问题的时候,不要慌
一步一步慢慢来,最终能够东拼西凑就过关
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='123', database='day47', charset='utf8' # 编码不要加- ) # 链接数据库 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 产生一个游标对象(用来帮助执行命令) ''' DictCursor,查询结果以字典形式返回 ''' sql = 'select * from employee;' res = cursor.execute(sql) # print(res) # 18,返回的数据条数 # execute返回的是你当前sql语句所影响的行数 # 获取命令执行的查询结果 print(cursor.fetchone()) # 只拿一条 print(cursor.fetchall()) # 拿所有 # print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) # 指定拿几条 # print(cursor.fetchone()) # 读取数据类似于文件光标的移动 # cursor.scroll(1, 'relative') # 相对于光标所在的位置继续往后移动1位 # cursor.scroll(1, 'absolute') # 相对于数据的开头往后继续移动1位 # print(cursor.fetchall())
select * from user where name='xxx' or 1=1 -- skkdjkdjkd' and password=''
日常生活中很多软件的注册的时候都不能含有特殊符号 因为怕你构造出特定的语句入侵数据库,不安全
敏感的数据不要自己拼接,交给execute帮你即可
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', database='day48', charset='utf8' ) # 链接数据库 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) username = input('>>>') password = input('>>>') # sql = "select * from user where name='{}' and password='{}'".format(username, password) sql = "select * from user where name=%s and password=%s" # 解决sql注入的问题,不要手动拼接数据,先用%s占位,之后将需要拼接的数据直接交个excute方法即可 print(sql) rows = cursor.execute(sql, (username, password)) # 自动识别sql里面的%s用后面元组里面的数据替换 if rows: print('登录成功') print(cursor.fetchall()) else: print('用户名密码错误')
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='123', database='day48', charset='utf8', autocommit=True # 完整配置 ) cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 建表 # sql = '''create table user( # id int primary key auto_increment, # name char(16), # password int(32) # )''' # res = cursor.execute(sql) # 建表 # 增 sql = 'insert into user(name,password) values(%s,%s)' rows = cursor.execute(sql, ('cy', 123)) rows = cursor.executemany(sql, [('zd', 123), ('dkj', 123), ('xiaobao', 123)]) # 一次性插入N多条数据 # print(rows) # conn.commit() # # 删除 # sql = 'delete from user where id=1' # rows = cursor.execute(sql) # print(rows) # conn.commit() # # # 改 # sql = 'update user set name="lr" where id=1' # rows = cursor.execute(sql) # print(rows) # conn.commit() # # # 查 # sql = 'select * from user ' # cursor.execute(sql) # print(cursor.fetchall()) ''' 增删改查中 删改增的操作设计到数据的修改 需要二次确认conn.commit(),或者autocommit修改成True 也可以一次性插入N多条数据 '''




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号