微调
微调
步骤
下面将介绍迁移学习中的常见技巧:微调(fine-tuning)。如下图所示,微调包括以下四个步骤。
-
在源数据集(例如ImageNet数据集)上预训练神经网络模型,即源模型。
-
创建一个新的神经网络模型,即目标模型。这将复制源模型上的所有模型设计及其参数(输出层除外)。我们假定这些模型参数包含从源数据集中学到的知识,这些知识也将适用于目标数据集。我们还假设源模型的输出层与源数据集的标签密切相关;因此不在目标模型中使用该层。
-
向目标模型添加输出层,其输出数是目标数据集中的类别数。然后随机初始化该层的模型参数。
-
在目标数据集(如椅子数据集)上训练目标模型。输出层将从头开始进行训练,而所有其他层的参数将根据源模型的参数进行微调。
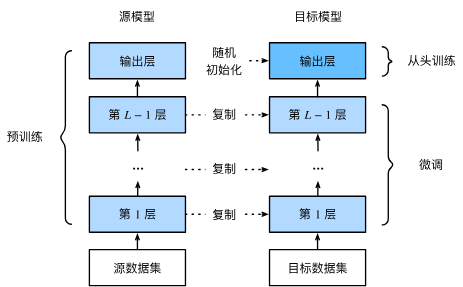
当目标数据集比源数据集小得多时,微调有助于提高模型的泛化能力。
热狗识别
让我们通过具体案例演示微调:热狗识别。 我们将在一个小型数据集上微调ResNet模型。该模型已在ImageNet数据集上进行了预训练。 这个小型数据集包含数千张包含热狗和不包含热狗的图像,我们将使用微调模型来识别图像中是否包含热狗。
%matplotlib inline
import os
import torch
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
获取数据集
我们使用的热狗数据集来源于网络。 该数据集包含1400张热狗的“正类”图像,以及包含尽可能多的其他食物的“负类”图像。 含着两个类别的1000张图片用于训练,其余的则用于测试。
解压下载的数据集,我们获得了两个文件夹hotdog/train和hotdog/test。 这两个文件夹都有hotdog(有热狗)和not-hotdog(无热狗)两个子文件夹, 子文件夹内都包含相应类的图像。
#@save
d2l.DATA_HUB['hotdog'] = (d2l.DATA_URL + 'hotdog.zip',
'fba480ffa8aa7e0febbb511d181409f899b9baa5')
data_dir = d2l.download_extract('hotdog')
Downloading ..\data\hotdog.zip from http://d2l-data.s3-accelerate.amazonaws.com/hotdog.zip...
我们创建两个实例来分别读取训练和测试数据集中的所有图像文件。
train_imgs = torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join(data_dir, 'train'))
test_imgs = torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join(data_dir, 'test'))
下面显示了前8个正类样本图片和最后8张负类样本图片。正如所看到的,图像的大小和纵横比各有不同。
hotdags = [train_imgs[i][0] for i in range(8)]
not_hotdags = [train_imgs[-i-1][0] for i in range(8)]
d2l.show_images(hotdags + not_hotdags, 2, 8, scale=1.4)
array([<AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>,
<AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>,
<AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>,
<AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>],
dtype=object)

在训练期间,我们首先从图像中裁切随机大小和随机长宽比的区域,然后将该区域缩放为\(224\times224\)的大小,并对其进行标准化。 然后,我们将裁剪的区域作为输入图像。 在测试过程中,我们将图像的高度和宽度都缩放到256像素,然后裁剪中央\(224\times224\)区域作为输入。 此外,对于RGB(红、绿和蓝)颜色通道,我们分别标准化每个通道。 具体而言,该通道的每个值减去该通道的平均值,然后将结果除以该通道的标准差。
# 使用RGB通道的均值和标准差,以标准化每个通道
normalize = torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# 定义训练时的数据增强操作
train_augs = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
normalize
])
# 定义测试时的数据增强操作
test_augs = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.Resize([256, 256]),
torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(224),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
normalize
])
定义和初始化模型
我们使用在ImageNet数据集上预训练的ResNet-18作为源模型。 在这里,我们指定pretrained=True以自动下载预训练的模型参数。 如果首次使用此模型,则需要连接互联网才能下载。
pretrain_net = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
d:\app_program\work\Anaconda3\envs\d2l\lib\site-packages\torchvision\models\_utils.py:208: UserWarning: The parameter 'pretrained' is deprecated since 0.13 and will be removed in 0.15, please use 'weights' instead.
warnings.warn(
d:\app_program\work\Anaconda3\envs\d2l\lib\site-packages\torchvision\models\_utils.py:223: UserWarning: Arguments other than a weight enum or `None` for 'weights' are deprecated since 0.13 and will be removed in 0.15. The current behavior is equivalent to passing `weights=ResNet18_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1`. You can also use `weights=ResNet18_Weights.DEFAULT` to get the most up-to-date weights.
warnings.warn(msg)
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-f37072fd.pth" to C:\Users\石国亮/.cache\torch\hub\checkpoints\resnet18-f37072fd.pth
100.0%
预训练的源模型实例包含许多特征层和一个输出层fc。 此划分的主要目的是促进对除输出层以外所有层的模型参数进行微调。 下面给出了源模型的成员变量fc。
pretrain_net.fc
Linear(in_features=512, out_features=1000, bias=True)
在ResNet的全局平均汇聚层后,全连接层转换为ImageNet数据集的1000个类输出。 之后,我们构建一个新的神经网络作为目标模型。 它的定义方式与预训练源模型的定义方式相同,只是最终层中的输出数量被设置为目标数据集中的类数(而不是1000个)。
在下面的代码中,目标模型finetune_net中成员变量features的参数被初始化为源模型相应层的模型参数。 由于模型参数是在ImageNet数据集上预训练的,并且足够好,因此通常只需要较小的学习率即可微调这些参数。
成员变量output的参数是随机初始化的,通常需要更高的学习率才能从头开始训练。 假设Trainer实例中的学习率为\(\eta\),我们将成员变量output中参数的学习率设置为\(10\eta\)。
finetune_net = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
finetune_net.fc = nn.Linear(finetune_net.fc.in_features, 2)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(finetune_net.fc.weight)
d:\app_program\work\Anaconda3\envs\d2l\lib\site-packages\torchvision\models\_utils.py:208: UserWarning: The parameter 'pretrained' is deprecated since 0.13 and will be removed in 0.15, please use 'weights' instead.
warnings.warn(
d:\app_program\work\Anaconda3\envs\d2l\lib\site-packages\torchvision\models\_utils.py:223: UserWarning: Arguments other than a weight enum or `None` for 'weights' are deprecated since 0.13 and will be removed in 0.15. The current behavior is equivalent to passing `weights=ResNet18_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1`. You can also use `weights=ResNet18_Weights.DEFAULT` to get the most up-to-date weights.
warnings.warn(msg)
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.0186, -0.0469, -0.0044, ..., -0.0982, -0.0990, -0.0847],
[-0.0730, -0.0830, 0.0177, ..., 0.0903, -0.0229, 0.0668]],
requires_grad=True)
模型微调
首先,我们定义了一个训练函数train_fine_tuning,该函数使用微调,因此可以多次调用
# 如果parm_group=True,输出层的模型参数将使用10倍的学习率
def train_fine_tuning(net, learning_rate, batch_size=128, num_epochs=5, parm_group=True):
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join(data_dir, 'train'), transform=train_augs), batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join(data_dir, 'test'), transform=test_augs), batch_size=batch_size)
devices = d2l.try_all_gpus()
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
if parm_group:
params_1x = [param for name, param in net.named_parameters() if name not in ['fc.weight', 'fc.bias']]
trainer = torch.optim.SGD([{'params': params_1x}, {'params': net.fc.parameters(), 'lr': learning_rate * 10}], lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=0.001)
else:
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=0.001)
d2l.train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs, devices)
我们使用较小的学习率,通过微调预训练获得的模型参数
train_fine_tuning(finetune_net, 5e-5)
loss 0.177, train acc 0.928, test acc 0.941
296.9 examples/sec on [device(type='cuda', index=0)]
为了进行比较,我们定义了一个相同的模型,但是将其所有模型参数初始化为随机值。 由于整个模型需要从头开始训练,因此我们需要使用更大的学习率。
scratch_net = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
scratch_net.fc = nn.Linear(scratch_net.fc.in_features, 2)
train_fine_tuning(scratch_net, 5e-4, parm_group=False)
loss 0.111, train acc 0.959, test acc 0.940
381.5 examples/sec on [device(type='cuda', index=0)]
意料之中,微调模型往往表现更好,因为它的初始参数值更有效。
总结
-
迁移学习将从源数据集中学到的知识迁移到目标数据集,微调是迁移学习的常见技巧。
-
除输出层外,目标模型从源模型中复制所有模型设计及其参数,并根据目标数据集对这些参数进行微调。但是,目标模型的输出层需要从头开始训练。
-
通常,微调参数使用较小的学习率,而从头开始训练输出层可以使用更大的学习率。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义