Spring系列之多个数据源配置
前言
在上篇文章讲到了如何配置单数据源,但是在实际场景中,会有需要配置多个数据源的场景,比如说,我们在支付系统中,单笔操作(包含查询、插入、新增)中需要操作主库,在批量查询或者对账单查询等对实时性要求不高的场景,需要使用读库来操作,依次来减轻数据库的压力。那么我们如何配置多数据源?
这里还是基于springboot应用的情况下,我们看一下怎么配置。
因为SpringBoot会实现自动配置,但是SpringBoot并不知道我们的业务场景分别要使用哪一个数据源,因此我们需要把相关的自动配置关闭。
首先,生成项目骨架,引入相应的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
```
**然后,在Application排除自动装配类**
```java
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class,DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class,JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration.class})
@Slf4j
public class MultiDataSourceDemoApplication {
}
上面代码中,我们排除了DataSourceAutoConfiguration、DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration、JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration三个类,然后就可以自己定义DataSource了。
配置数据源
//第一个数据源
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("first.datasource")
public DataSource firstDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate firstJdbcTemplate() {
return new JdbcTemplate(firstDataSource());
}
@Bean
@Resource
public PlatformTransactionManager firstTxManager(DataSource firstDataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(firstDataSource);
}
//第二个数据源
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("second.datasource")
public DataSource secondDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate secondJdbcTemplate() {
return new JdbcTemplate(secondDataSource());
}
@Bean
@Resource
public PlatformTransactionManager secondTxManager(DataSource secondDataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(secondDataSource);
}
application.properties的配置项信息
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
spring.output.ansi.enabled=ALWAYS
first.datasource.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/first
first.datasource.username=root
first.datasource.password=xxx
second.datasource.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/second
second.datasource.username=root
second.datasource.password=xxx
看一下表结构和数据
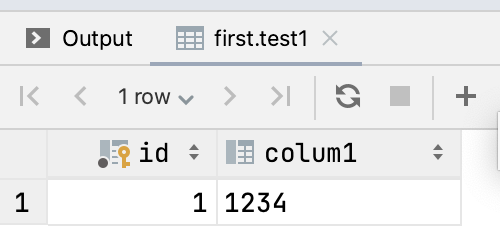
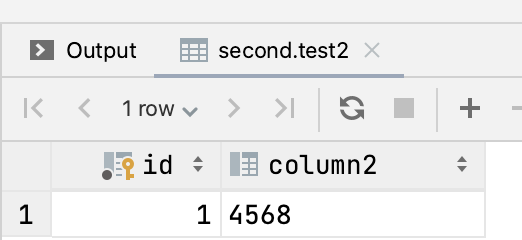
运行测试代码:
@Test
public void testMutilDataSource(){
firstJdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT * FROM test1")
.forEach(row -> log.info("记录:"+row.toString()));
secondJdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT * FROM test2")
.forEach(row -> log.info("记录:"+row.toString()));
}
我们看一下运行效果:
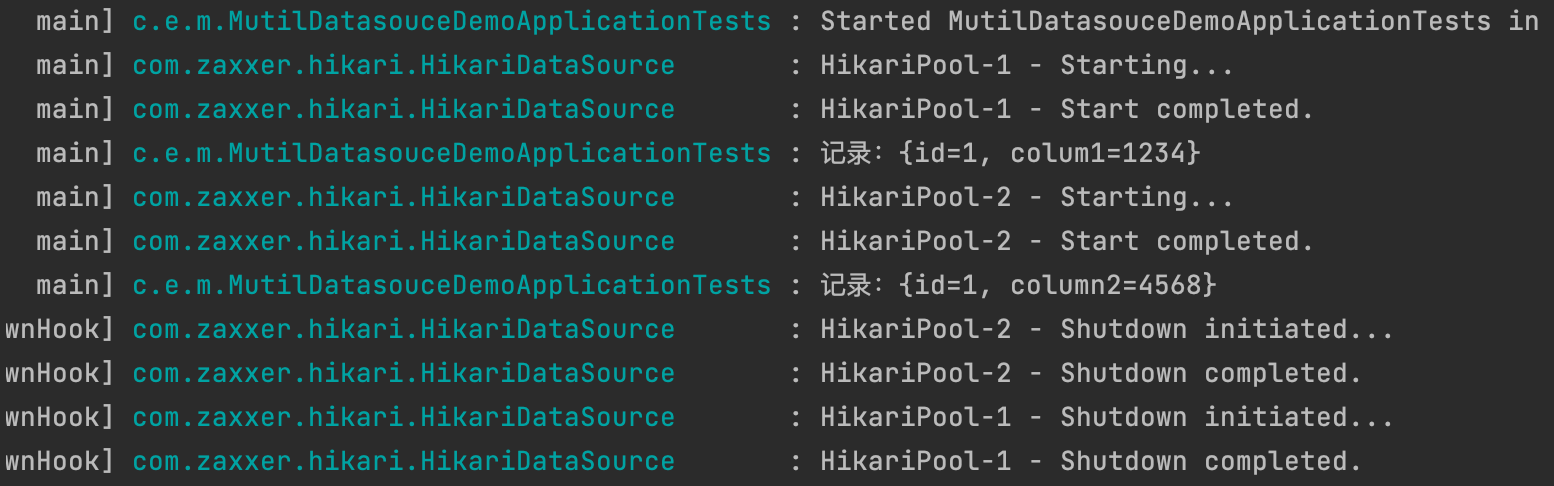
我们可以看到,两个数据源都初始化成功了,并且各自数据源执行的结果准确。
上面的方式没有集成Mybatis,使用的是jdbcTemplate,网络上还有很多配置方式,比如动态选择数据源,大同小异,不过笔者还是建议不同的业务单独指定数据源,容易维护。
我们已经演示了简单的单数据源和多数据源的配置方式,我们下一篇文章将讲一下,SpringBoot默认的连接池HikariCP。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号