spring-data-jdbc的基础使用(一)
前言
很多人知道Mybatis,知道Jpa,但是对spring-data-jdbc可能了解的少之又少。注意我们这里说的是data-jdbc,而不是普通的jdbc。它拥有了类似jpa的一些特性,比如能够根据方法名推导出sql,基本的CRUD等,也拥有了写原生sql的能力。最为关键的是,它非常的清爽,不需要依赖hibernte或者jpa。
一、使用https://start.spring.io/ ,建立一个demo
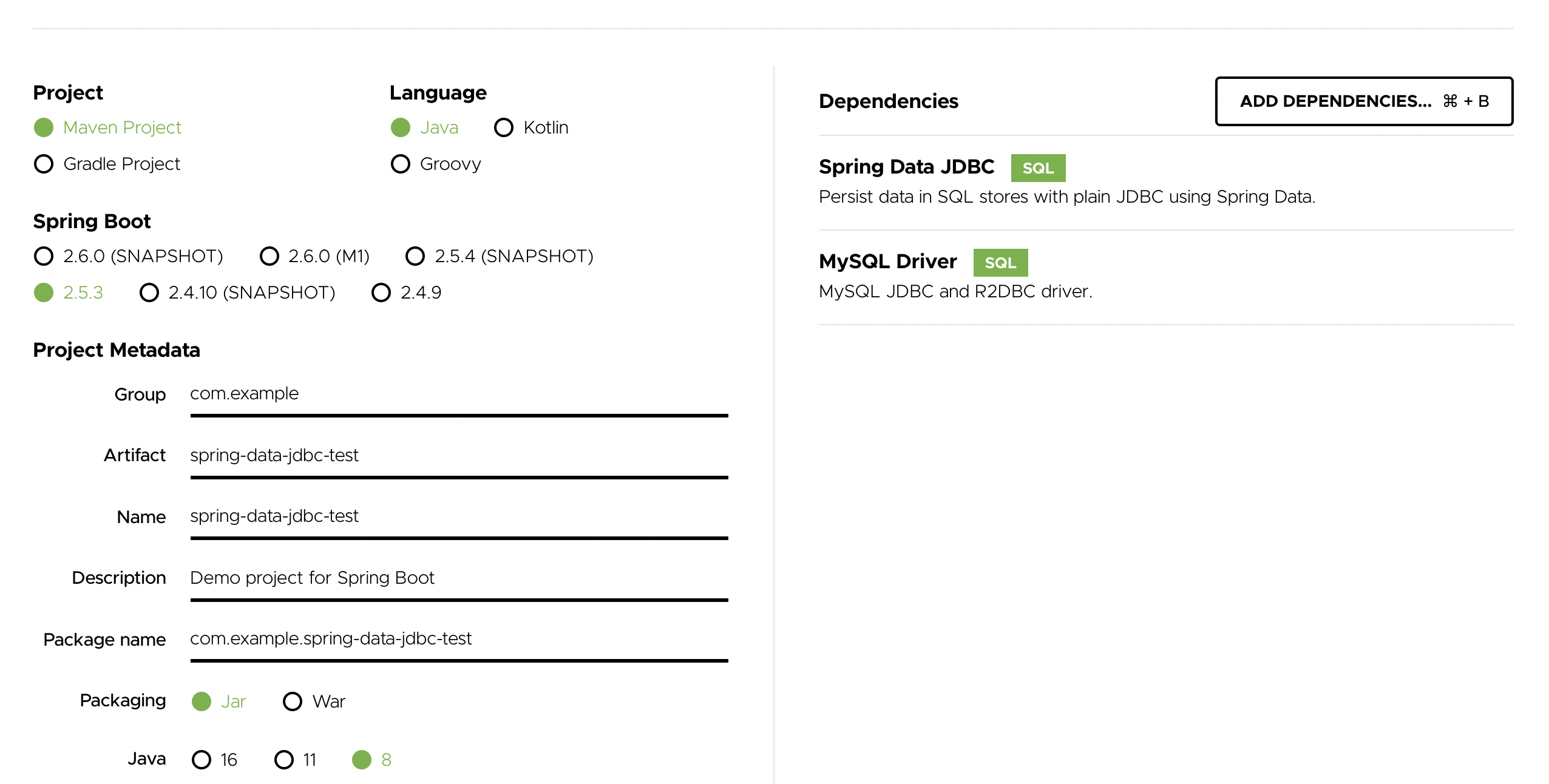
二、使用 Java 配置的 Spring Data JDBC
// @EnableJdbcRepositories 为接口Repository 创建实现
//AbstractJdbcConfiguration 提供 Spring Data JDBC 所需的各种默认 bean
@Configuration
@EnableJdbcRepositories(basePackages = "com.example.springdatajdbctest")
public class ApplicationConfiguration extends AbstractJdbcConfiguration {
/**
* 创建DataSource,使用springboot的默认的连接池,当然你也可以使用druid
* ConfigurationProperties注解,去配置项中找spring.datasource开头的配置项,来创建DataSource
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="spring.datasource" )
public DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 官方使用内置的数据库类型
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder builder = new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder();
return builder.setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.H2).build();
}
*/
/**
* NamedParameterJdbcOperations是Spring Data JDBC 用来访问数据库的
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean
NamedParameterJdbcOperations namedParameterJdbcOperations(DataSource dataSource) {
return new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
/**
* 提供的事务管理
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean
TransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
对应的application.properties内容如下:
spring.datasource.jdbc-url = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/sss?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&characterEncoding=UTF-8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&allowMultiQueries=true&useAffectedRows=true
spring.datasource.driver-class-name = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = ****
三、数据库建表、建实体类
create table user_info
(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null,
age int not null,
sex tinyint default 1 not null,
create_time datetime not null,
update_time datetime not null
)
comment '用户表';
@Data
public class UserInfo extends BaseEntity{
/**
* ID注解需要加上,标记为主键,否则无法识别主键
* 其他字段不需要加对应的列明,表名也可以不加注解,前提是类名、字段名符合标准的驼峰命名规范,否则无法对应上
*/
@Id
private Integer id ;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer sex;
}
@Data
public class BaseEntity {
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
四、建立仓储接口UserInfoRepository
/**
* 这里CrudRepository接口已经提供了常见的一些接口,因此这里继承CrudRepository
*/
public interface UserInfoRepository extends CrudRepository<UserInfo, Integer> {
}
/**
* 也可以继承PagingAndSortingRepository,它继承了CrudRepository,多了排序和分页默认方法
*/
public interface UserInfoRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<UserInfo, Integer> {
}
五、运行一下:
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
class SpringDataJdbcTestApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserInfoRepository userInfoRepository;
@Test
public void testGet() {
Optional<UserInfo> userInfo = userInfoRepository.findById(1);
System.out.println(userInfo.get());
}
@Test
public void testCount() {
long count = userInfoRepository.count();
System.out.println(count);
}
}
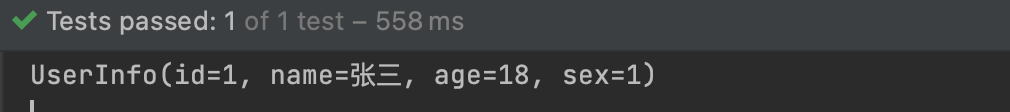
六、关键字查询方法
如果默认方法中没有我们需要的方法,我们还可以按规则来编写关键字查询方法。可以通过带有关键字的方法名来解析出SQL,比如
public interface UserInfoRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<UserInfo, Integer> {
List<UserInfo> findByName(String ame);
}
这样无需写SQL语句,就能查询出我们想要的结果。这里使用的是关键字findBy后面的既是需要的查询条件,当然还支持复合查询。比如
List<UserInfo> findByNameAndAge(String name,Integer age);
当然还支持其他的关键字查询。见下表
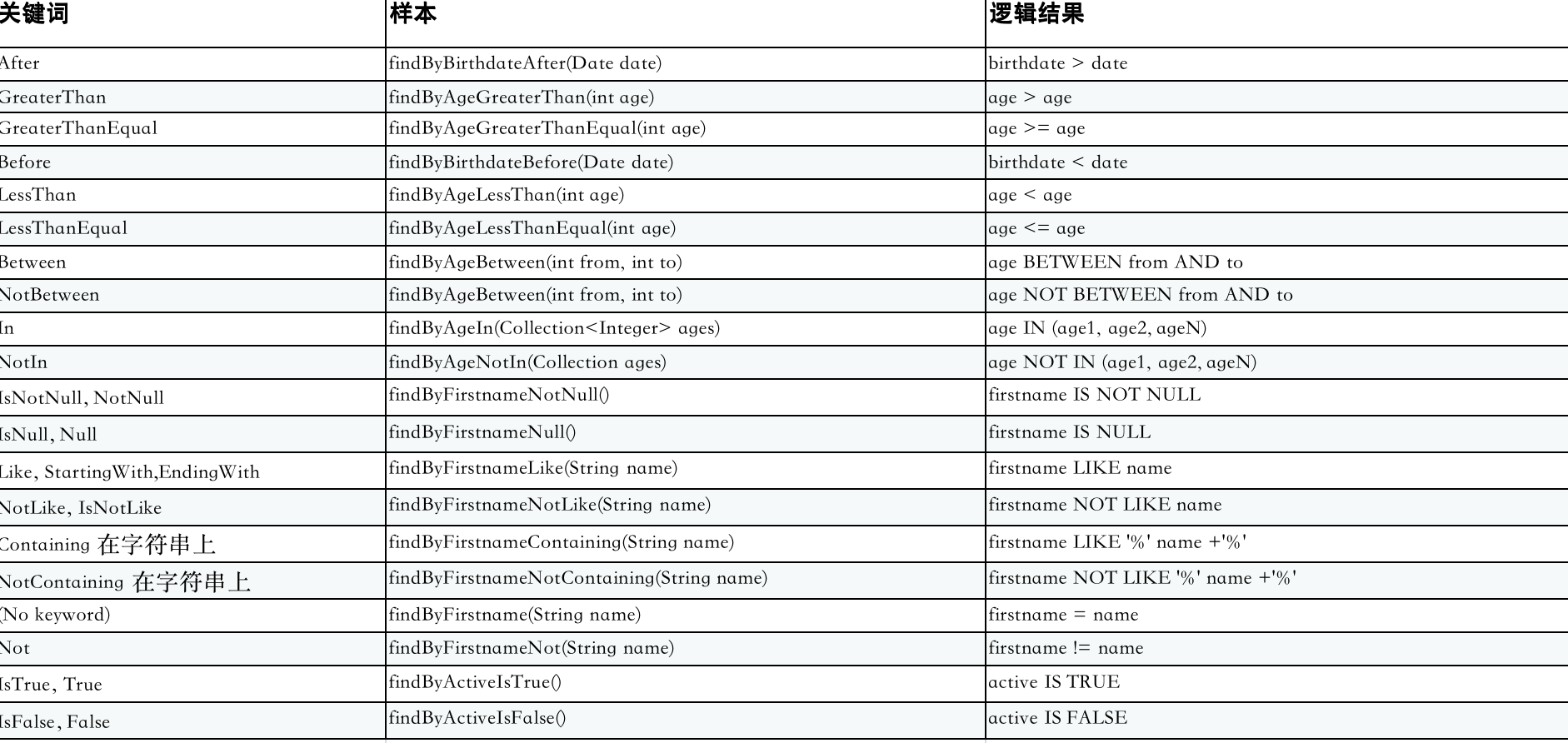
关键字方式,仅限于可以在WHERE不使用连接的情况下在子句中使用的属性
再如果你不喜欢这种关键字方式,可以自定义方法名字,你还可以使用@Query方式进行定义查询方法
@Query("select name, age from user_info u where u.name = :name")
List<UserInfo> getUserInfoByName(String name);
如果你要修改或者删除,只需要增加注解@Modifying,语句如下:
@Modifying
@Query("update user_info set age=:age where name = :name")
Boolean updateAgeById(String name,Integer age);
@Modifying
@Query("delete from user_info where id = :id")
Boolean deleteRecord(Integer id);
是不是感觉很方便,不再用去写SQL了
七、生命周期的事件机制
Spring Data JDBC 的操作可以作为事件和ApplicationListener的事件相结合
比如,监听所有插入前的操作,这里我们只演示打印日志:
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class CommonEventConfiguration {
@Bean
public ApplicationListener<BeforeSaveEvent<Object>> loggingSaves() {
return event -> {
Object entity = event.getEntity();
log.info("{} is getting saved.", entity);
};
}
}
当然你不想对所有的操作都监听处理,你可以指定具体某一个表的操作,如下:
@Slf4j
@Repository
public class UserSavedListener extends AbstractRelationalEventListener<UserInfo> {
@Override
protected void onAfterSave(AfterSaveEvent<UserInfo> userInfoAfterSaveEvent) {
log.info("用户:{},保存成功",userInfoAfterSaveEvent.getEntity());
}
}
执行测试代码:
@Test
public void testInsert() {
UserInfo userInfo =new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("王五");
userInfo.setAge(20);
userInfo.setSex(1);
UserInfo result = userInfoRepository.save(userInfo);
System.out.println(result);
}
执行结果:

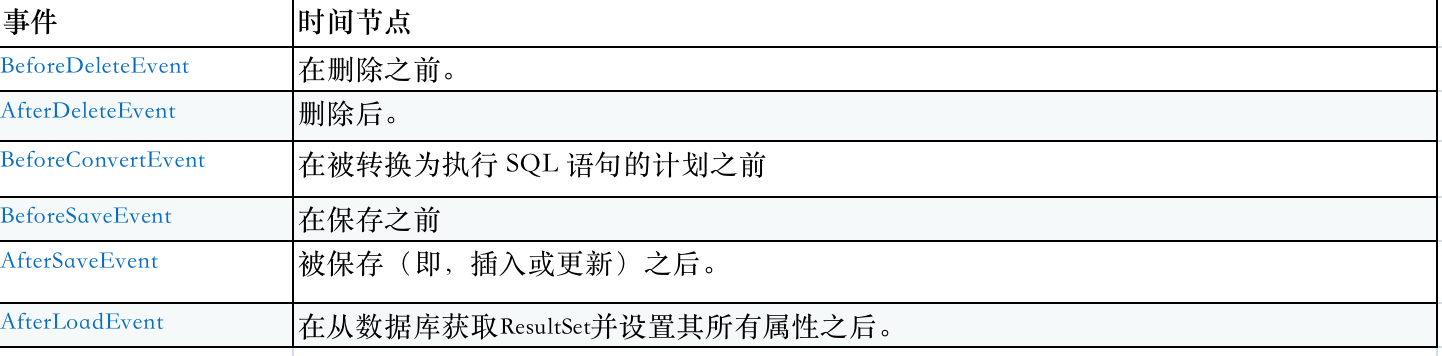
可用事件有:
八、实体回调
Spring Data 基础设施提供了在调用某些方法之前和之后修改实体的钩子。也许你已经注意到了,user_info表的创建时间和更新时间我们没有赋值,数据库里的两个时间都是有值的,这就是用实体回调来实现的。
建立一个实体回调类
@Component
public class DefaultingEntityCallback implements BeforeSaveCallback<BaseEntity> {
@Override
public BaseEntity onBeforeSave(BaseEntity baseEntity, MutableAggregateChange<BaseEntity> mutableAggregateChange) {
baseEntity.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
baseEntity.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
return baseEntity;
}
}
另外一种场景,在查询结果出来后需要将用户的敏感信息脱敏,则可以使用AfterLoadCallback实体回调
完结


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号