JavaWeb-初识Spring
目录
内容
Spring简介
-
Spring是什么
Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java的开放源代码的设计层面框架。Spring解决的是业务逻辑层和其他各层的松耦合问题,因此它将面向接口的编程思想贯穿整个系统应用。
-
Spring核心是什么
Spring的核心是控制反转(IOC)和面向切面(AOP)。
-
IOC:控制反转,将创建对象的过程交给spring进行管理。
-
AOP:面向切面,在不修改源代码的情况之下进行代码功能的增强。
-
-
Spring优势是什么
Spring是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。Spring框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许使用者选择使用哪一个组件,同时为 JavaEE 应用程序开发提供集成的框架。总结下来分以下几点:
-
方便解耦,简化开发,Spring就是一个大工厂,可以将所有对象创建和依赖关系维护,交给Spring管理,这也是IOC的作用。
-
AOP编程的支持,Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能。
-
声明式事务的支持,只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程。
-
方便程序的测试,Spring对Junit4支持,可以通过注解方便的测试Spring程序。
-
方便集成各种优秀框架,Spring不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如:Struts2、Hibernate、MyBatis等)的直接支持。
-
降低JavaEE API的使用难度,Spring 对JavaEE开发中非常难用的一些API(JDBC、JavaMail等),都提供了封装,使这些API应用难度大大降低。
-
-
Bean是什么
Bean是Spring容器管理的对象。
-
Spring容器是什么
Spring容器是创建以及管理Bean对象的。
Spring项目
-
IDEA创建项目
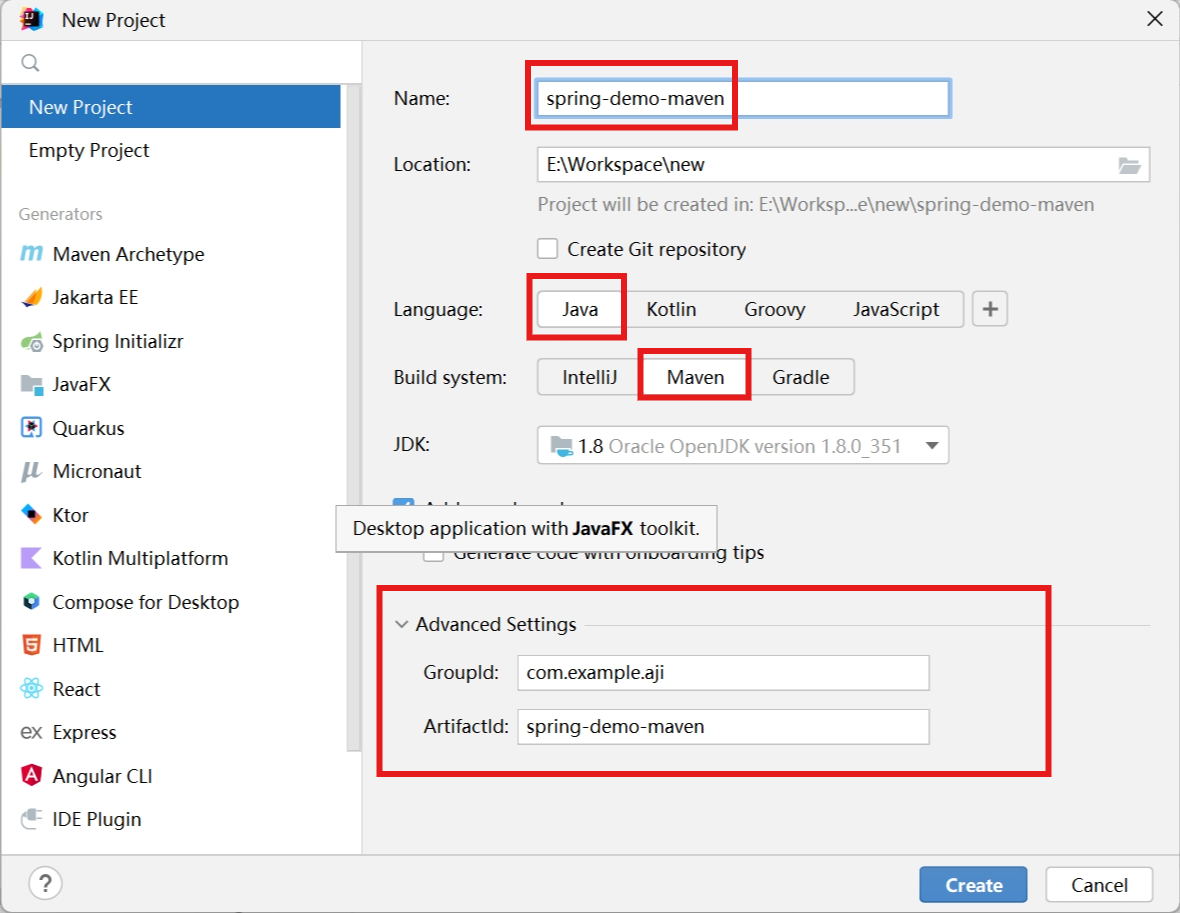
-
配置Maven,使用默认版本也可以
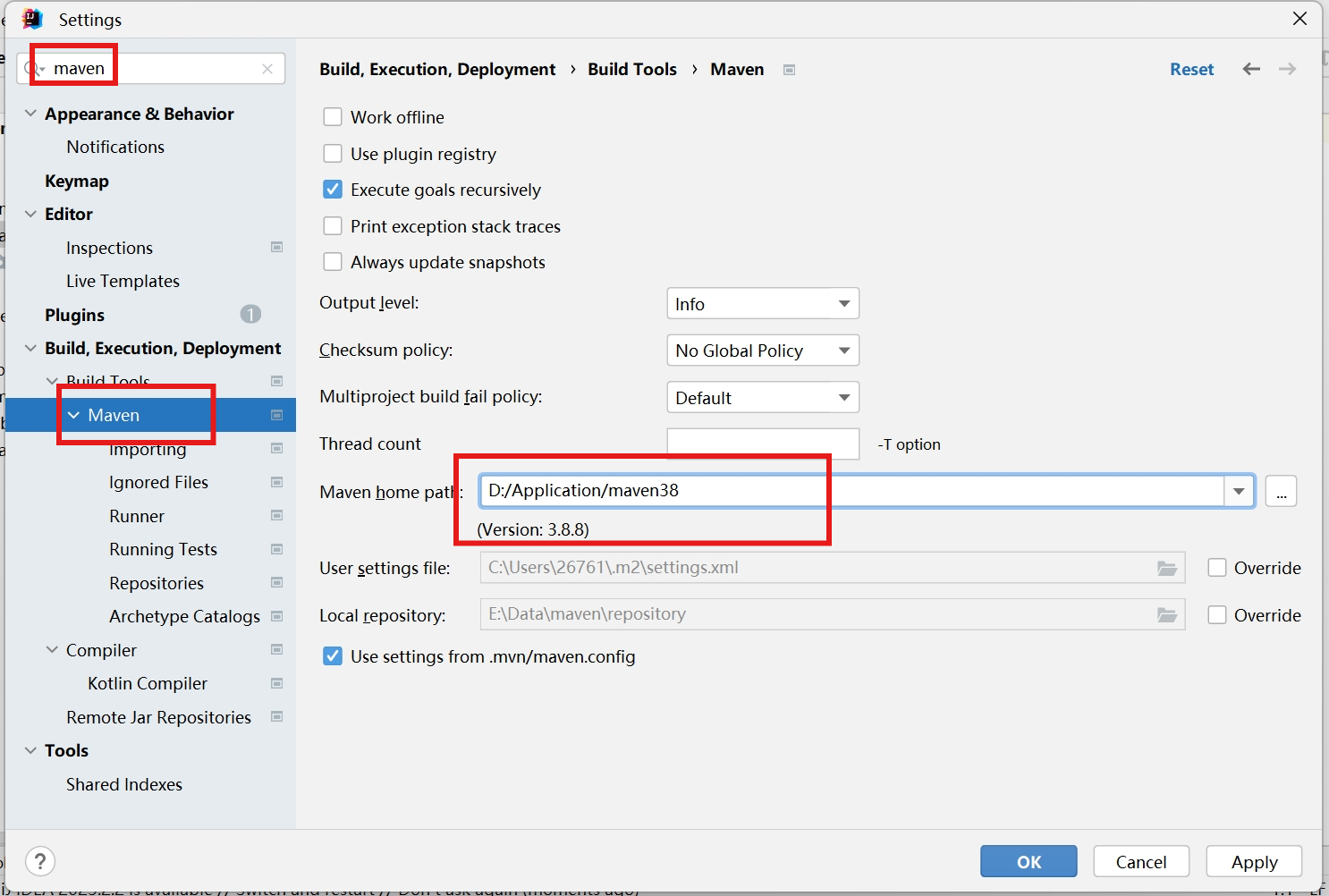
-
导入spring和单元测试junit依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>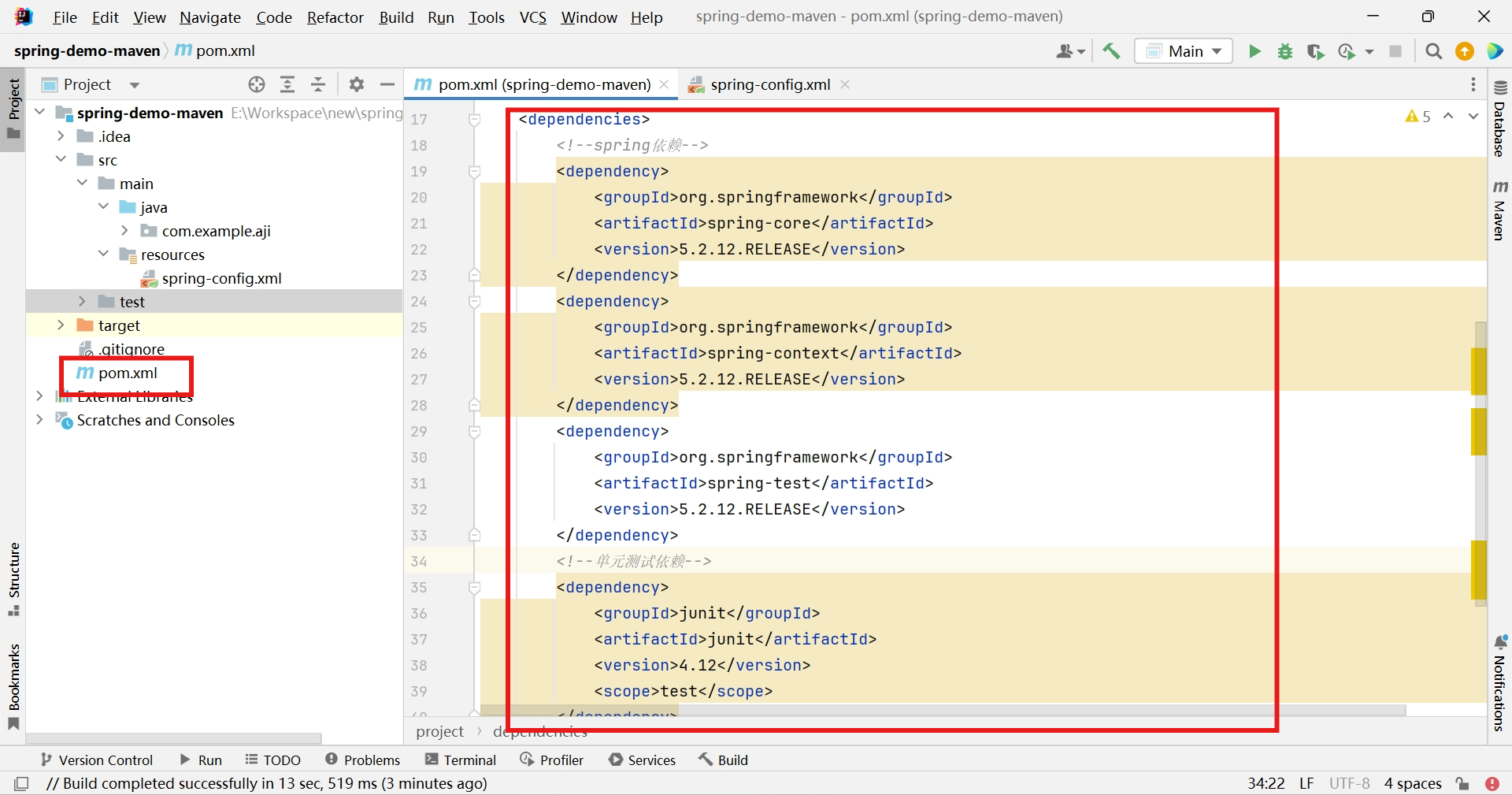
-
创建spring-config.xml(文件名随便取)
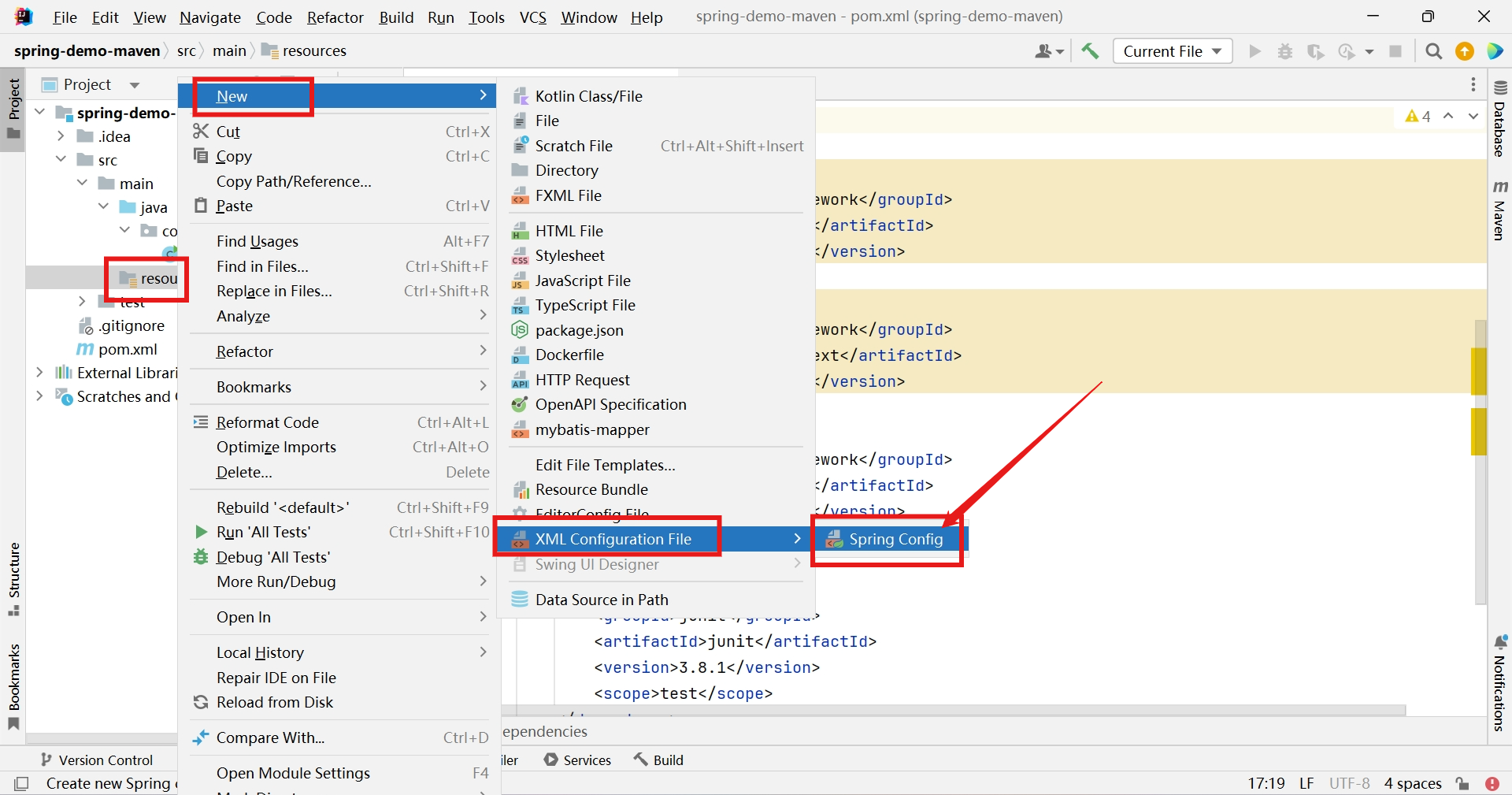
Bean管理
-
创建Demo类
public class Demo { private String name; private Integer age; public Demo(){} public Demo(String name, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;} public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;} @Override public String toString() { return "Demo{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
-
创建测试类
import org.junit.Test; public class Main { @Test public void test(){ } }
基于xml的Bean管理
创建对象
-
spring配置文件(spring-config.xml)添加配置,注册Demo类为Bean对象
<bean class="com.example.aji.bean.Demo" id="demo"> </bean>
-
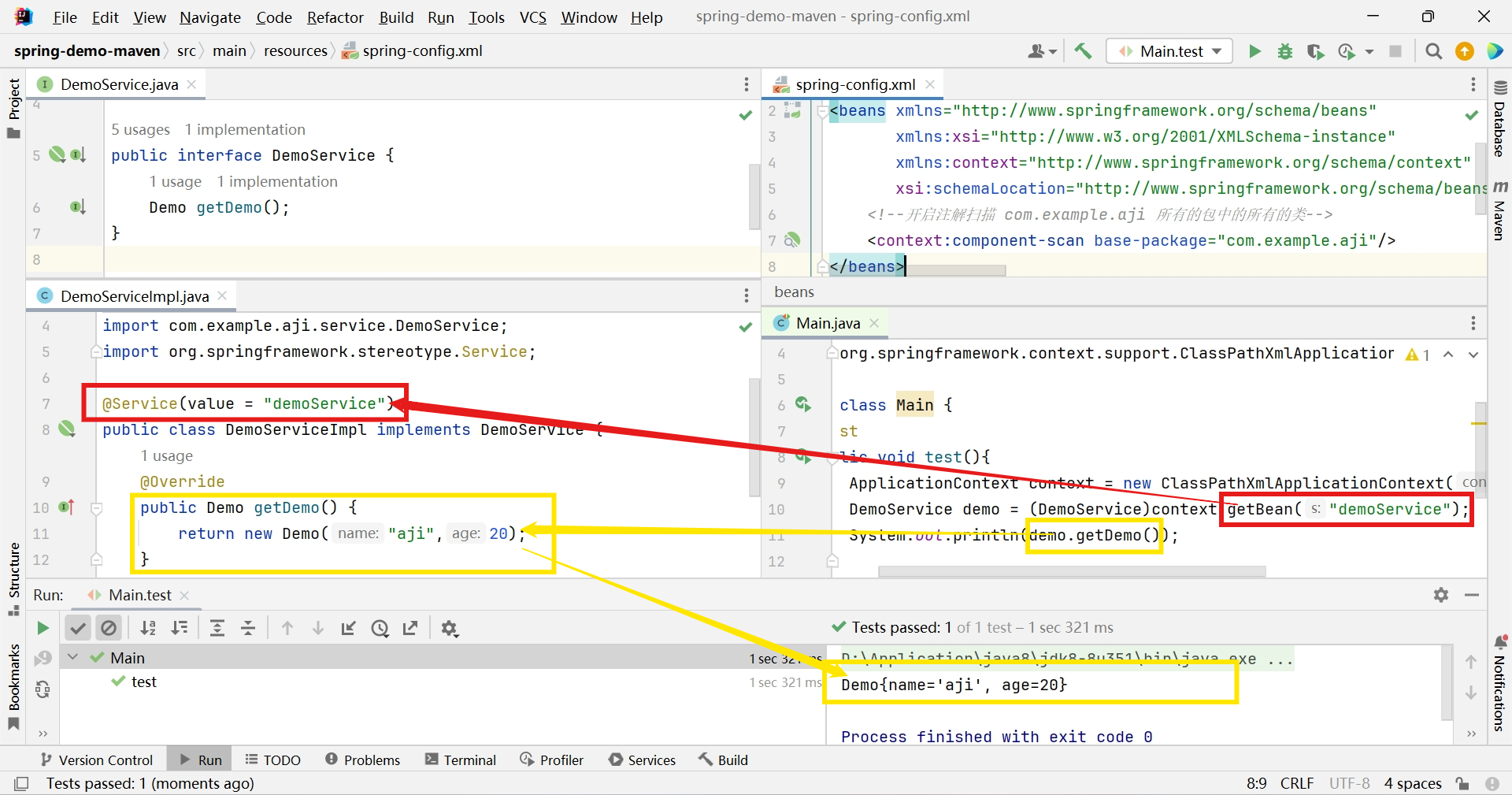
从容器中取出Demo对象
-
ApplicationContext spring上下文
-
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 以xml配置文件方式创建上下文
-
.getBean(beanName) 跟据beanName从上下文中获取Bean对象
-
.getBean(class) 跟据class从上下文中获取Bean对象
@Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); Demo demo = (Demo)context.getBean("demo"); System.out.println(demo); }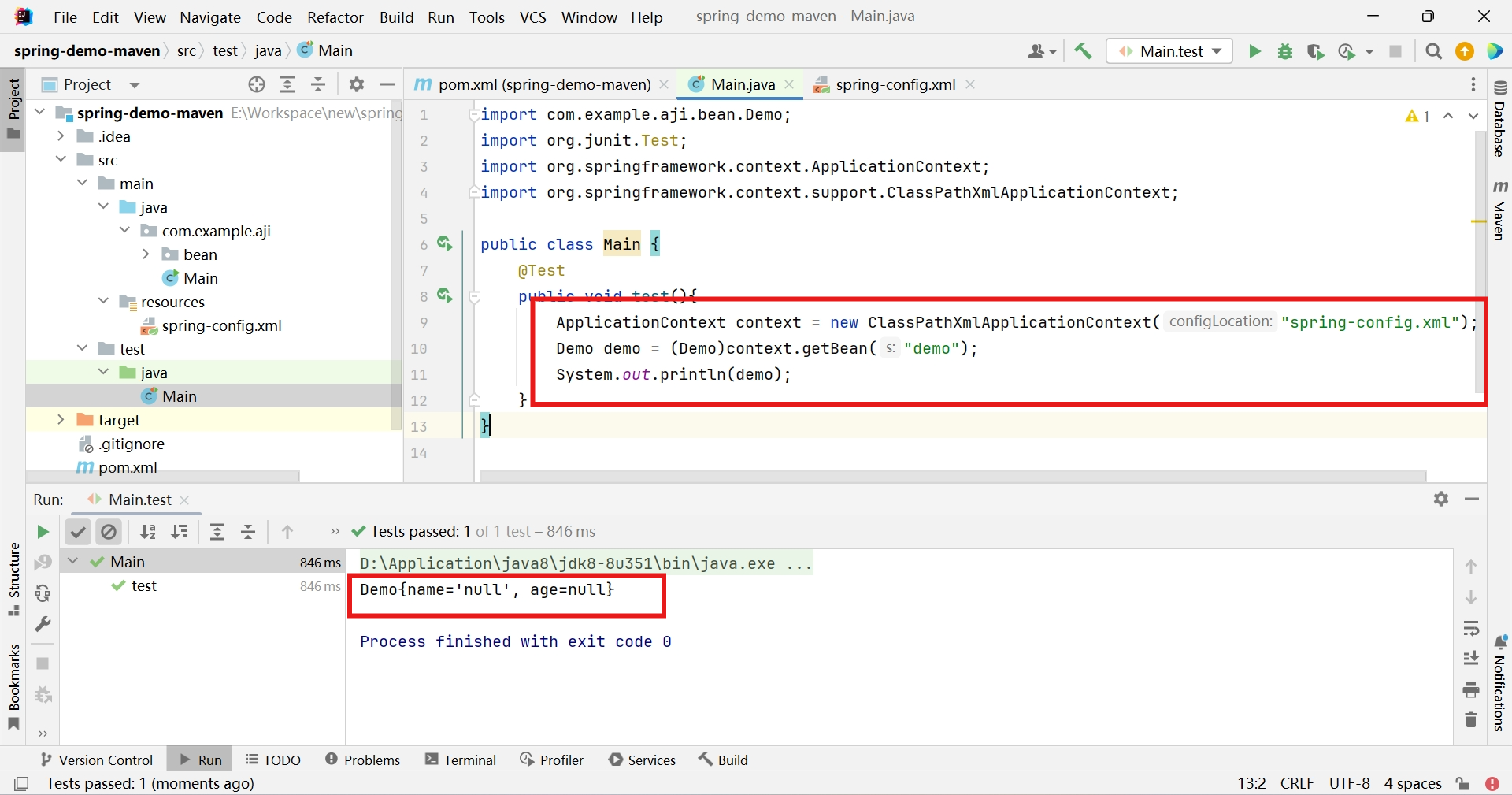
-
属性注入
-
构造器注入
- constructor-arg 通过构造器注入属性
<bean class="com.example.aji.bean.Demo" id="demo"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="aji"/> <constructor-arg name="age" value="20"/> </bean>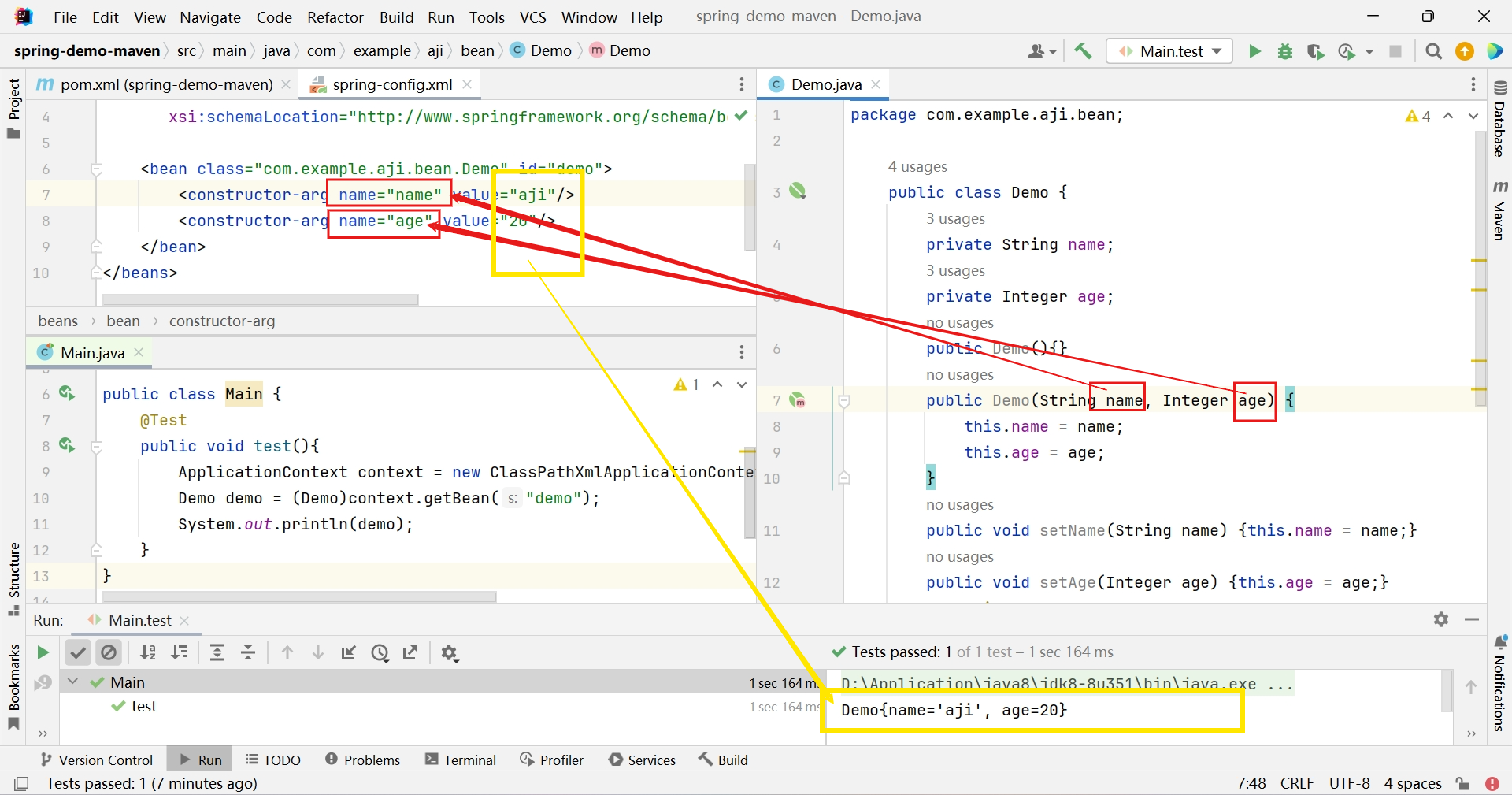
-
set方法注入
- property 通过set方法注入属性
<bean class="com.example.aji.bean.Demo" id="demo"> <property name="name" value="aji"/> <property name="age" value="21"/> </bean>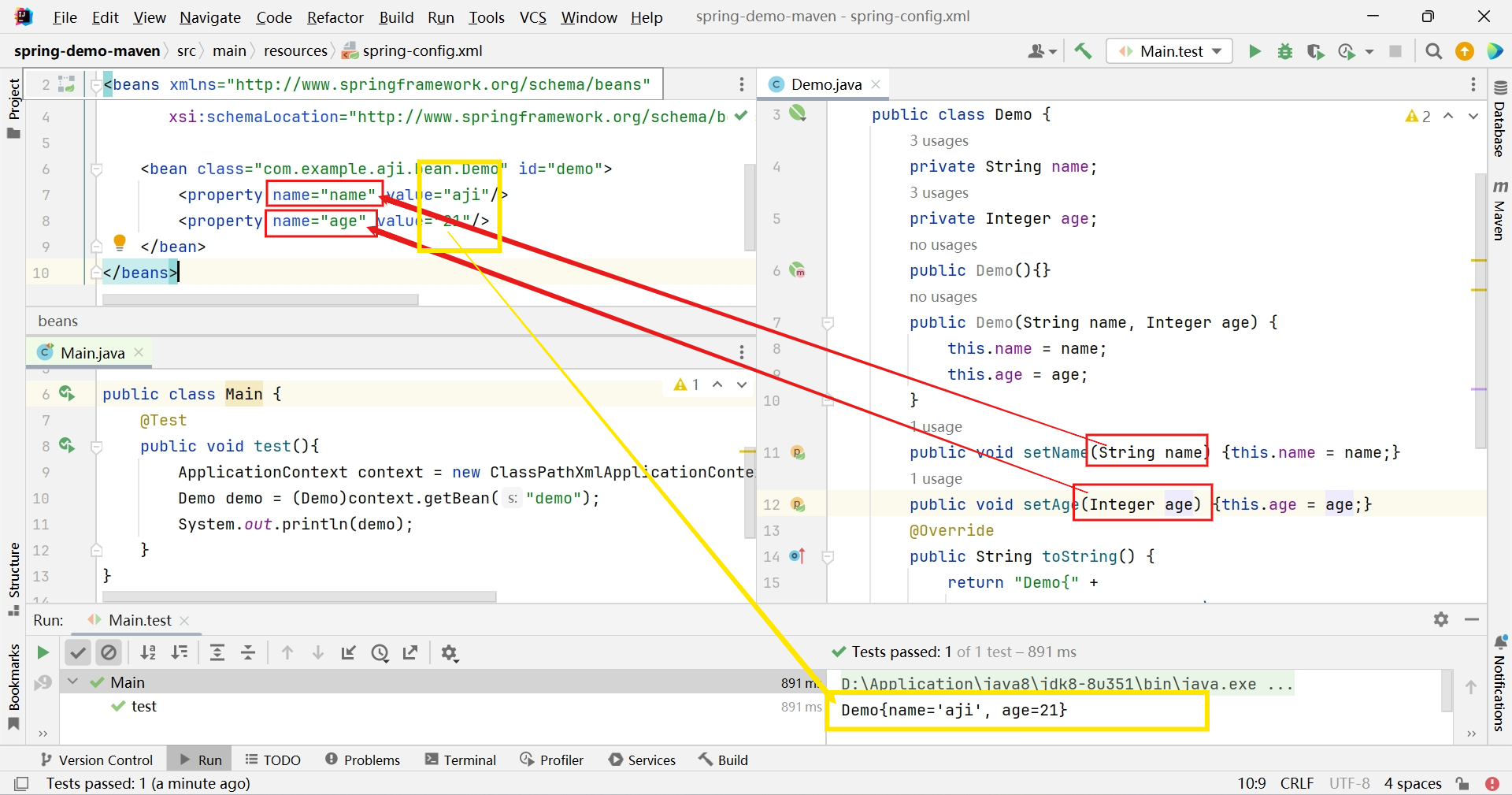
基于xml+注解的Bean管理
-
注解
-
注解是代码特殊标记,格式:@注解名称(属性名称=属性值,属性名称=属性值...)
-
使用注解,注解作用在类上面,方法上面,属性上边
-
使用注解的目的:简化XML配置
-
-
编辑Spring配置文件添加注解扫描功能
<!--开启注解扫描 com.example.aji 所有的包中的所有的类--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.example.aji"/>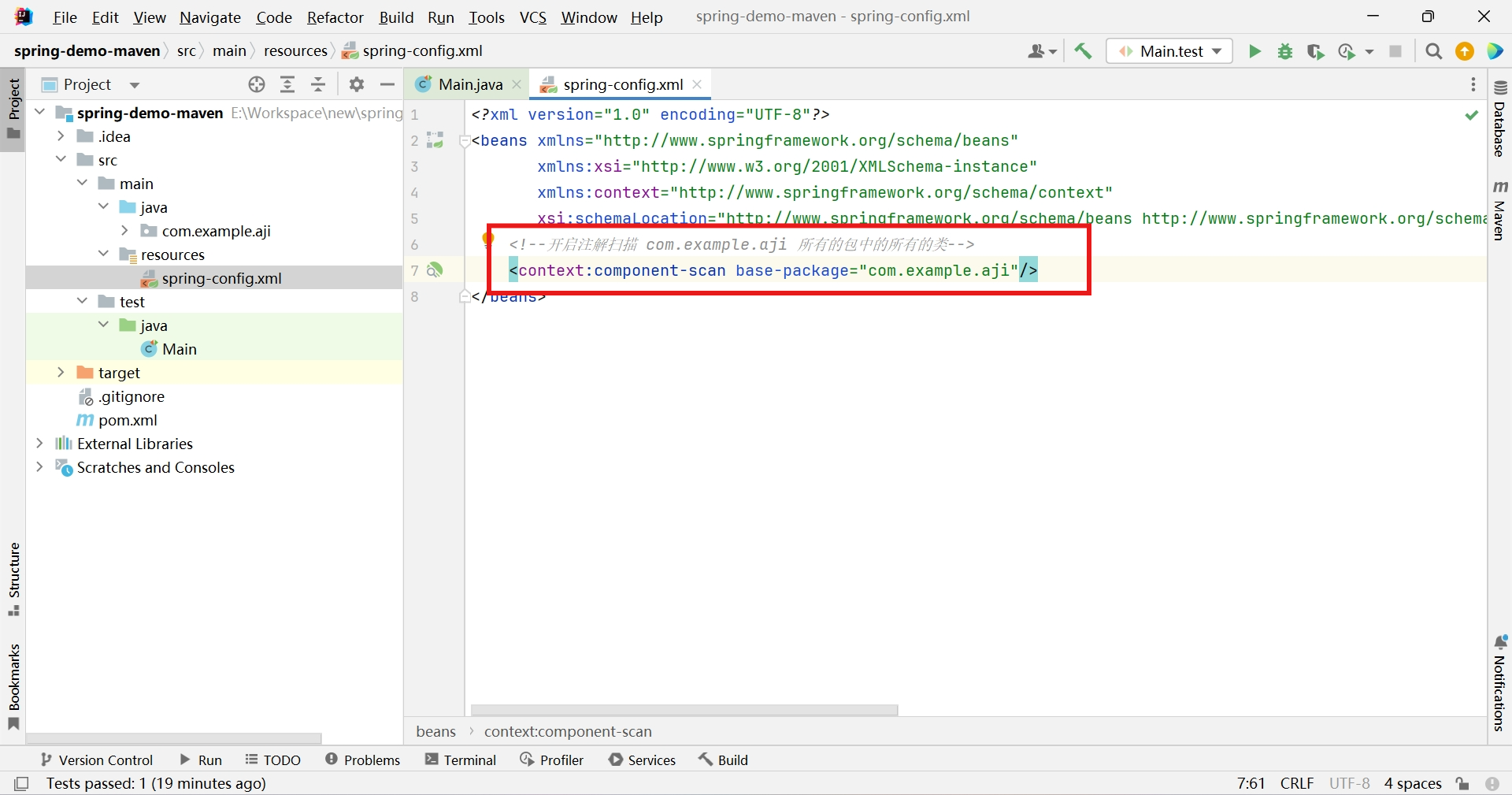
创建对象
-
Spring针对Bean管理中创建对象提供的注解
-
@Component 普通的类
-
@Controller 表现层
-
@Service 业务层
-
@Repository 持久层
-
-
创建普通对象
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Demo { private String name; private Integer age; public Demo(){} public Demo(String name, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Demo{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }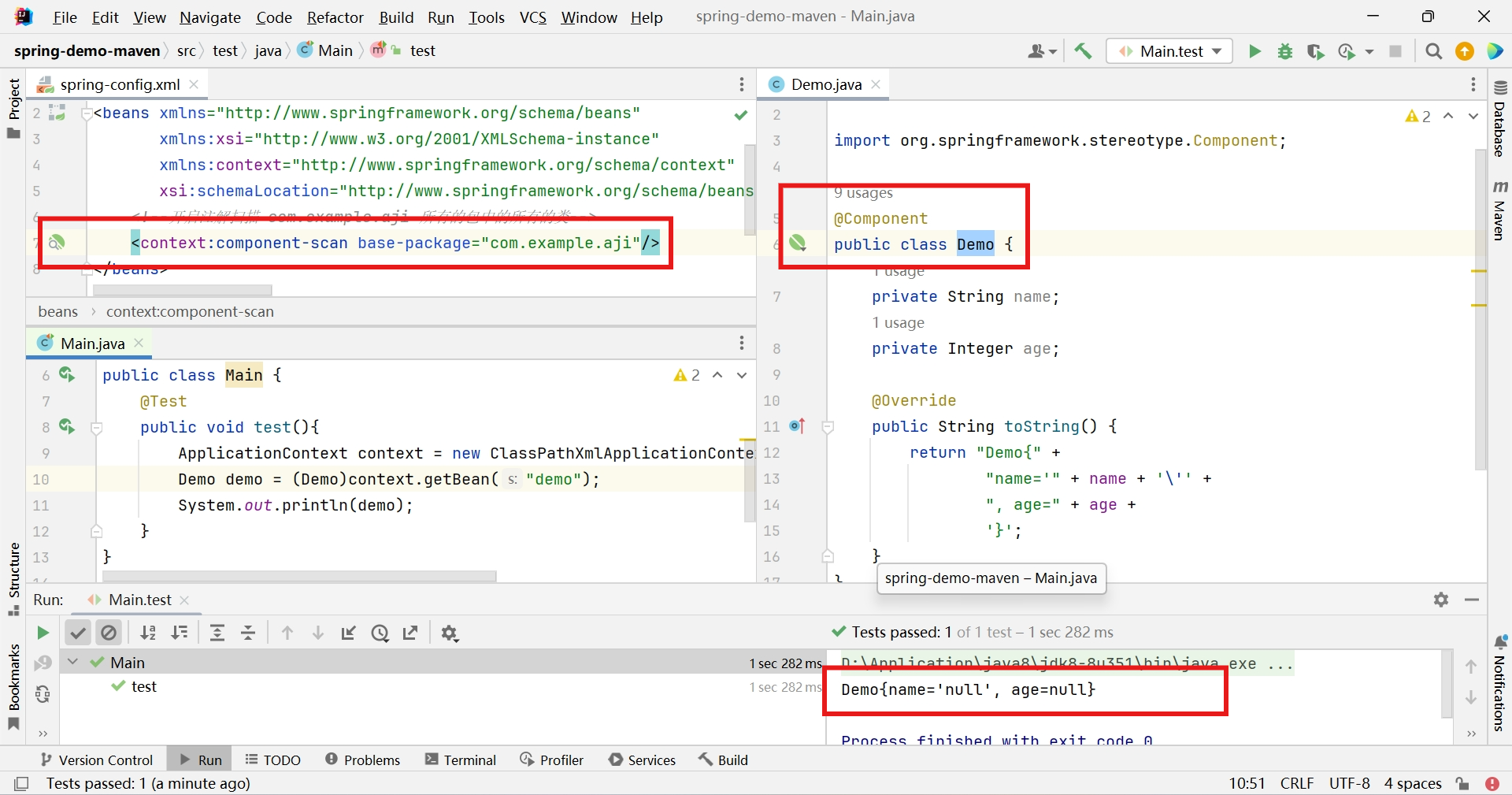
-
创建业务层对象
-
创建DemoService接口
public interface DemoService { Demo getDemo(); } -
创建DemoServiceImpl实现DemoService接口变更添加
import com.example.aji.bean.Demo; import com.example.aji.service.DemoService; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service(value = "demoService") public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService { @Override public Demo getDemo() { return new Demo("aji",20); } }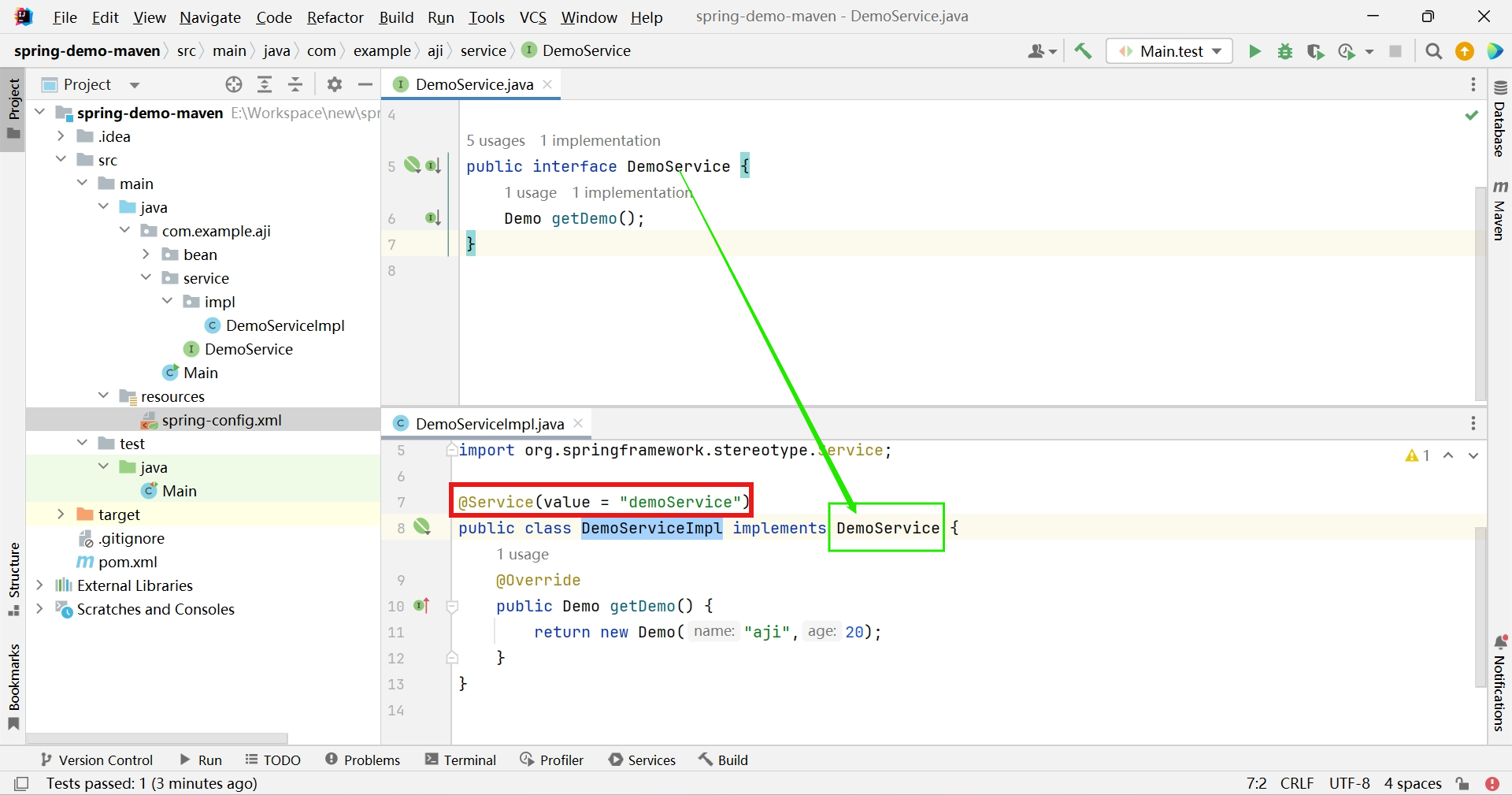
-
-
其他对象也类似,添加相应注解即可
属性注入
-
属性注入注解
-
@Value 用于注入普通类型(String,int,double等类型)
-
@Autowired 默认按类型进行自动装配(引用类型)
-
@Qualifier 不能单独使用必须和@Autowired一起使用,强制使用名称注入
-
@Resource Java提供的注解,也被支持。使用name属性,按名称注入
-
-
@Value
@Component public class Demo { @Value("aji") private String name; @Value(value = "21") private Integer age; @Override public String toString() { return "Demo{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }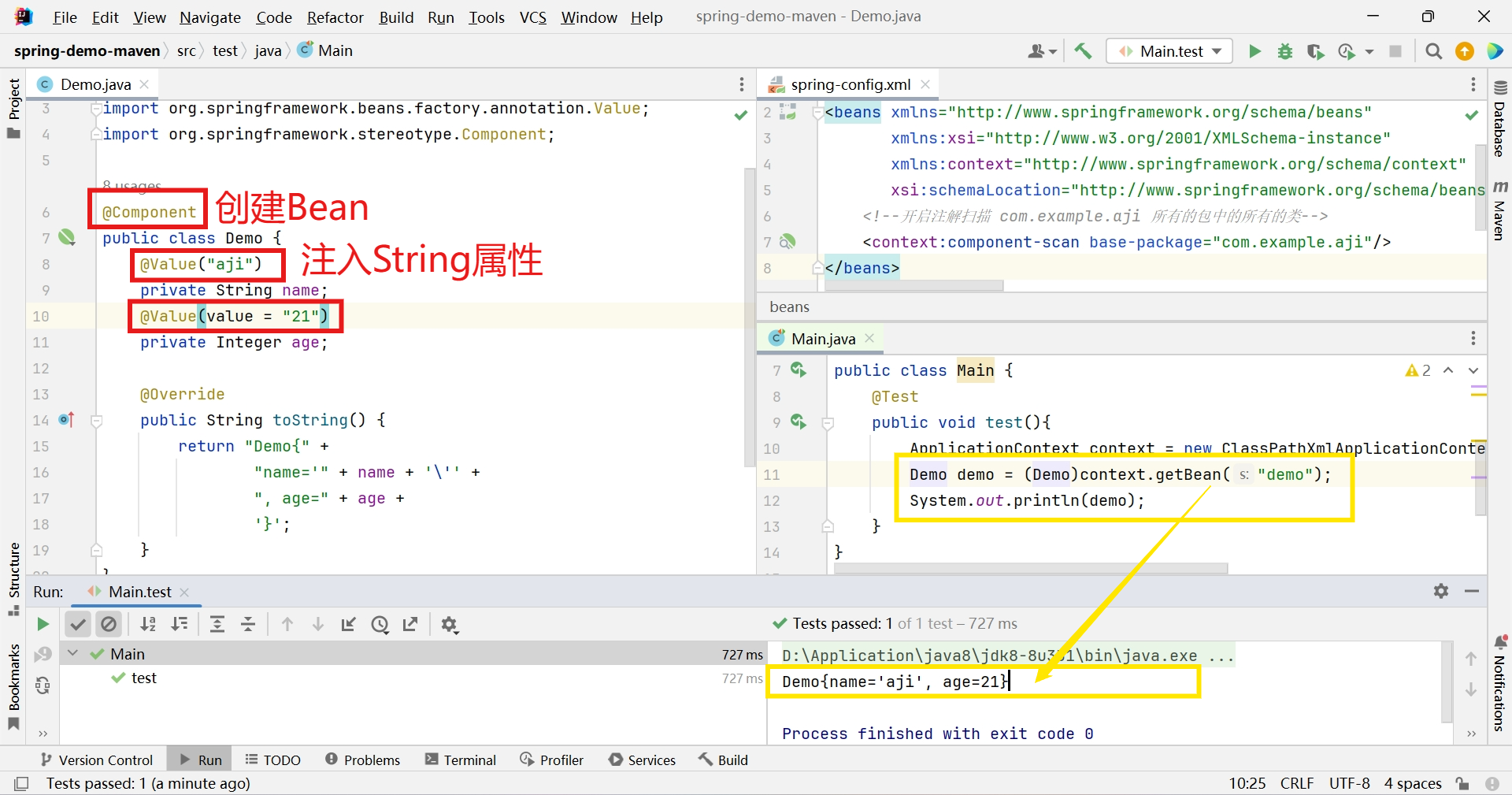
-
@Autowired
import com.example.aji.bean.Demo; import com.example.aji.service.DemoService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service(value = "demoService") public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService { @Autowired private Demo demo; @Override public Demo getDemo() { return demo; } }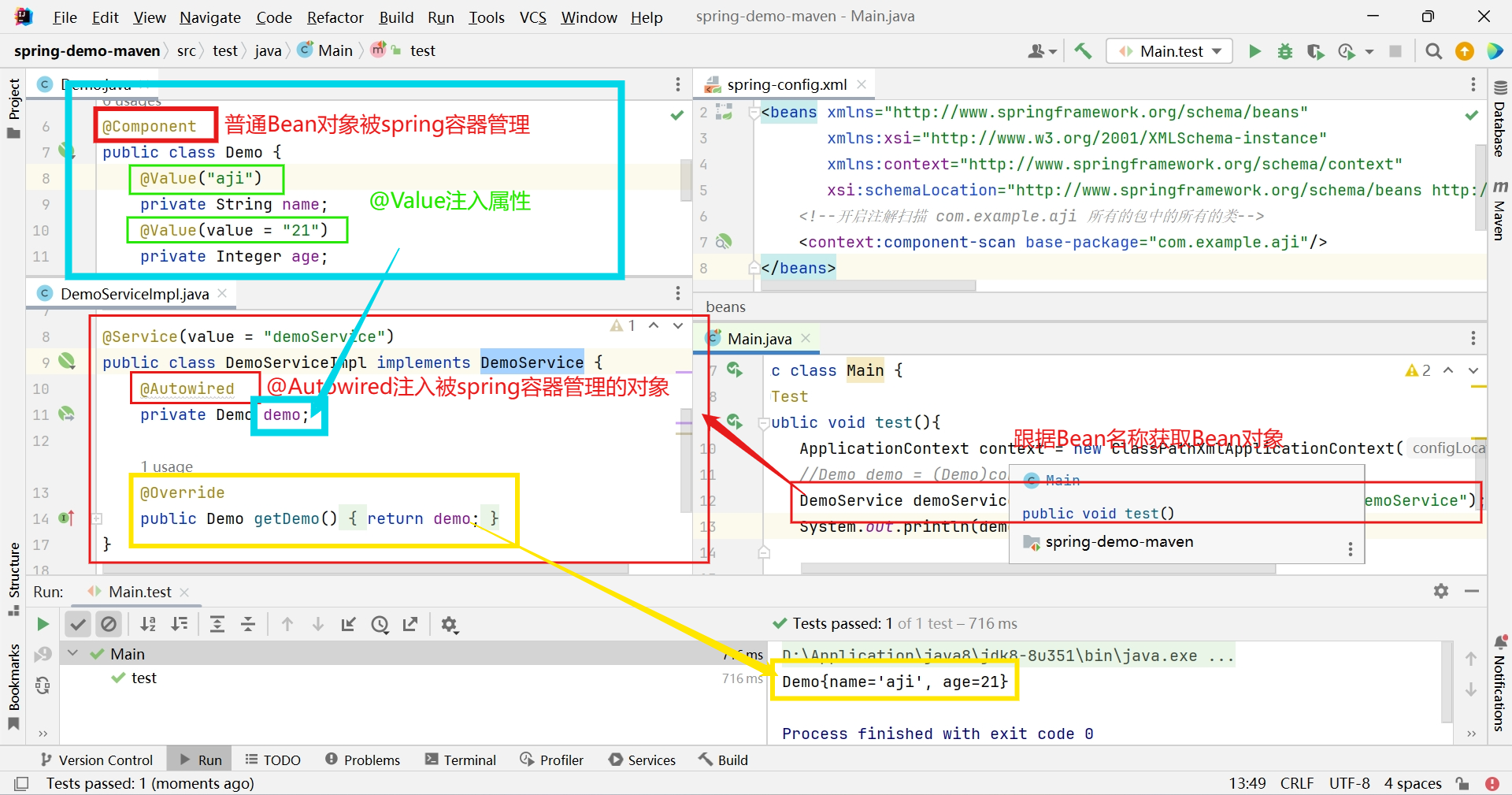
基于纯注解的Bean管理
-
删除spring-config.xml文件,并创建SpringConfig类,添加@Component注解把该类交给spring处理,添加@ComponentScan注解指定spring扫描的包路径
@Component @ComponentScan("com.example.aji") public class SpringConfig { }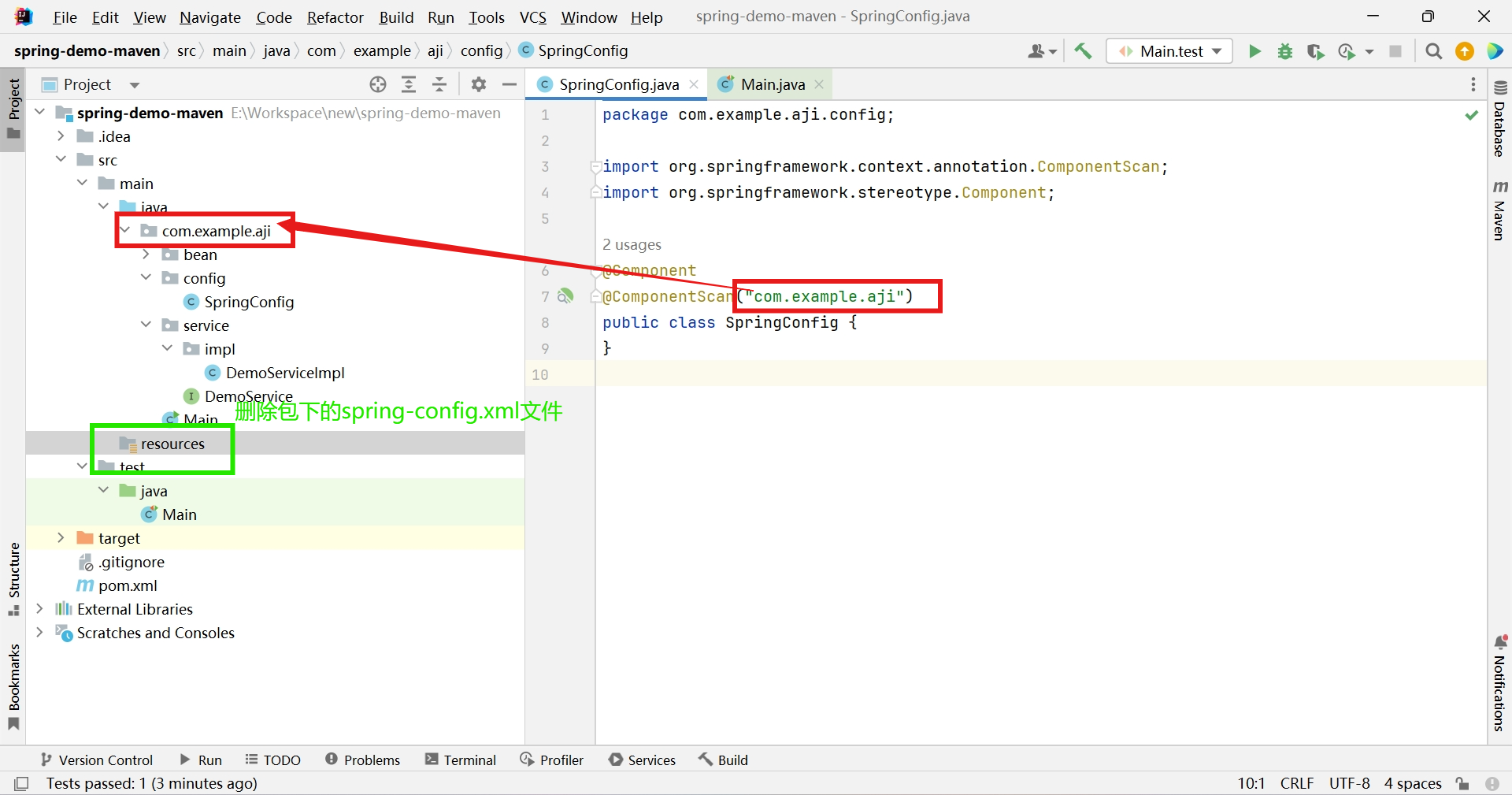
-
测试(其余部分与xml+注解方式一致)
@Test public void test(){ //ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); /*Demo demo = (Demo)context.getBean("demo"); System.out.println(demo);*/ DemoService demoService = (DemoService)context.getBean("demoService"); System.out.println(demoService.getDemo()); }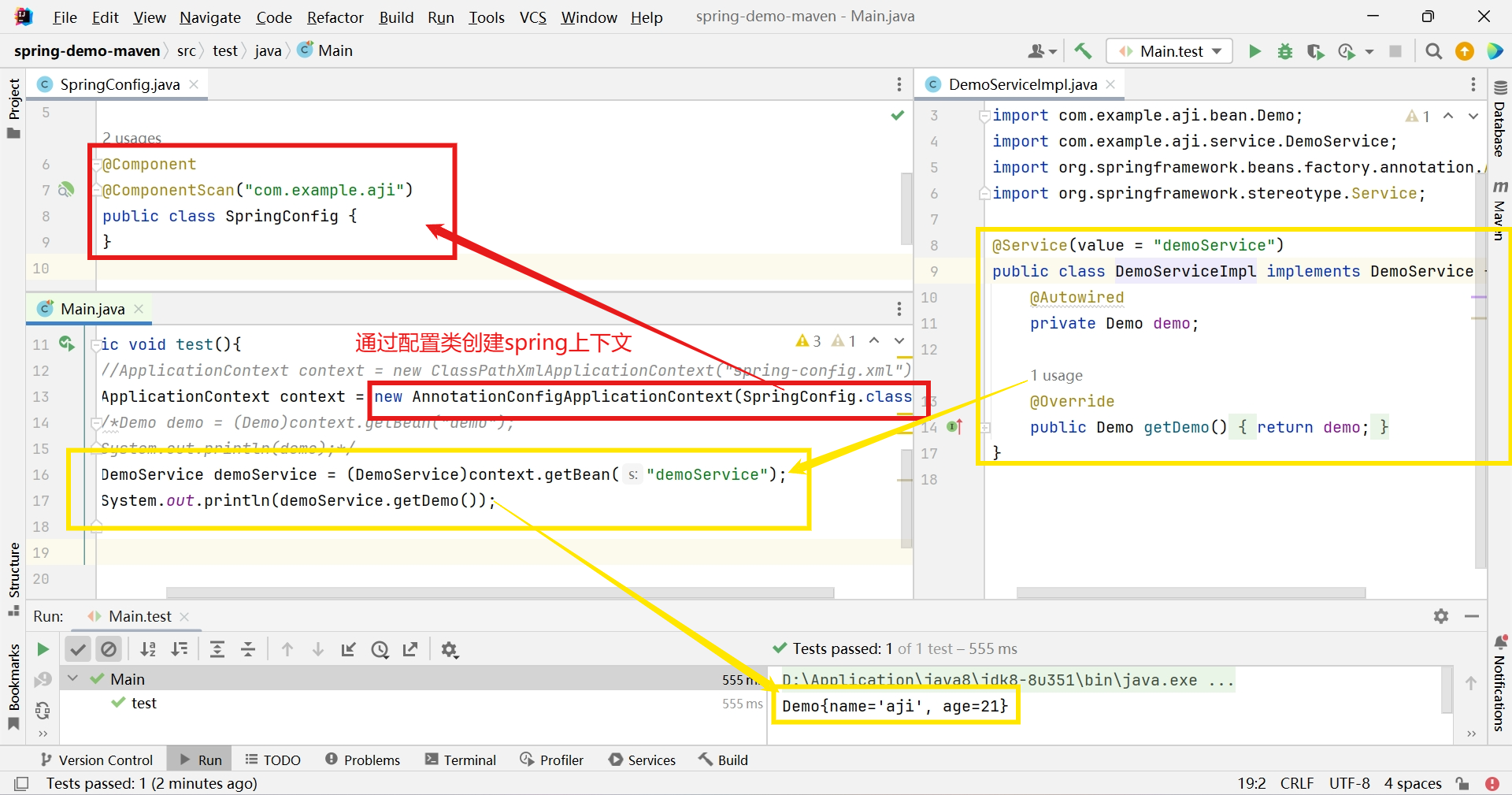



 初识spring,搭建spring项目,认识spring基础注释
初识spring,搭建spring项目,认识spring基础注释
