LeetCode 199. Binary Tree Right Side View
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
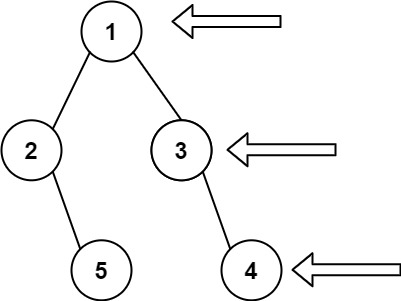
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,3]
Output: [1,3]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
实现思路:
谁知道20年的pat就考到这题了呢?姥姥竟然上leetcode抄题目,常规操作了。
采用两种方法实现,bfs+dfs,其中bfs多补充一种重要思路。
AC代码:
bfs方法一
利用计算层数的办法保留每一层的右边第一个
class Solution {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
bool vist[110]= {false}; //记录每一层最右边的第一个结点是否访问
vector<int> ans;
unordered_map<TreeNode*,TreeNode*> father;
unordered_map<TreeNode*,int> high;
public:
void bfs(TreeNode *root) {
if(root==nullptr) return;
q.push(root);
high[root]=1;
while(!q.empty()) {
TreeNode *now=q.front();
if(!vist[high[now]]) {
ans.push_back(now->val);
vist[high[now]]=1;
}
q.pop();
if(now->right) {
father[now->right]=now;
high[now->right]=high[now]+1;
q.push(now->right);
}
if(now->left) {
father[now->left]=now;
high[now->left]=high[now]+1;
q.push(now->left);
}
}
}
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
bfs(root);
return ans;
}
};
bfs方法二
这里应用到了一个重点的方法,就是size--,层序遍历把一层结点全部出队的做法,在很多题目中都有应用,要掌握。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if (!root) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (q.size()) {
int size = q.size();
while (size--) {//先判断进入后马上-1
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (!t) continue; //判断空节点
if (size==0) res.push_back(t->val); //存入该层最右边一个节点
if (t->left) q.push(t->left);
if (t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
dfs方法三
class Solution {
bool vist[110]= {0};
vector<int> ans;
public:
void dfs(TreeNode *root,int depth) {
if(!root) return;
if(!vist[depth]) {
ans.push_back(root->val);
vist[depth]=1;
}
dfs(root->right,depth+1);
dfs(root->left,depth+1);
}
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root,1);
return ans;
}
};



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号