CodeForces 232C Doe Graphs(分治+搜索)
题意
题意翻译
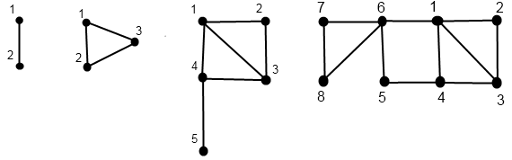
\(Doe\)以她自己的名字来命名下面的无向图
\(D(0)\)是只有一个编号为\(1\)的结点的图.
\(D(1)\)是只有两个编号分别为\(1\)和\(2\)的点与一条连接这两个点的边的图.
\(D(n)\)以如下方法构造
将\(D(n-2)\)中所有点的编号加上\(|D(n-1)|\)
在点\(|D(n-1)|\)与点\(|D(n-1)|+1\)之间连边。
在点\(|D(n-1)|+1\)与点1之间连边
现在\(Doe\)已经构造出了\(D(n)(n\leq 100)\),她会多次询问你在这张图中\(a\ b\)两点间的最短路
输入输出格式
输入格式:
The first line contains two integers \(t\) and \(n\) ( \(1\leq t\leq 10^{5}; 1\leq n\leq 10^{3}\) ) — the number of queries and the order of the given graph. The \(i\)-th of the next \(t\) lines contains two integers \(a_{i}\) and \(b_{i}\) ( \(1\leq a_{i},b_{i}\leq 10^{16}, a_{i}\neq b_{i}\) ) — numbers of two vertices in the \(i\)-th query. It is guaranteed that \(a_{i},b_{i}\leq |D(n)|\).
Please, do not use the %lld specifier to read or write 64-bit integers in С++. It is preferred to use cin, cout streams or the %I64d specifier.
输出格式:
For each query print a single integer on a single line — the length of the shortest path between vertices \(a_{i}\) and \(b_{i}\). Print the answers to the queries in the order, in which the queries are given in the input.
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
10 5
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
2 3
2 4
2 5
3 4
3 5
4 5
输出样例#1:
1
1
1
2
1
2
3
1
2
1
思路
首先想到,每张图的点的数量是有规律的:
这不就是斐波那契数列吗?我们不妨直接记\(F(n)\)为\(D(n)\)的顶点数。
然后考虑查询两点\(a\ b\)在\(D(n)\)中的最短路,一开始我的想法是这样的:如果有\(1\leq a,b\leq F(n-1)\),那么\(a\ b\)在\(D(n)\)中的最短路也就是在\(D(n-1)\)中的最短路;如果有\(F(n-1)< a,b\leq F(n)\),那么\(a\ b\)在\(D(n)\)中的最短路也就是在\(D(n-2)\)中的最短路。其余的情况再分治下去。但是这是有问题的,因为有的时候两点可以绕到下一张图上去,然后再绕回一张图中,这样的距离可能会更短。
具体来说,一共有这几种情况:
- \(a\ b\)都在\(D(n-1)\)的范围内:
- \(a\)直接走图\(D(n-1)\)到达\(b\);
- \(a\)通过点\(1\)走到图\(D(n-2)\),再绕回到图\(D(n-1)\),到达\(b\);
- \(a\)通过点\(F(n-1)\)走到图\(D(n-2)\),再绕回到图\(D(n-1)\),到达\(b\)。
- \(a\ b\)都在\(D(n-2)\)的范围内:
- \(a\)直接走图\(D(n-2)\)到达\(b\)。
- \(a\)在\(D(n-1)\)范围内,而\(b\)在\(D(n-2)\)范围内:
- \(a\)通过点\(1\)走到图\(D(n-2)\),再走到\(b\);
- \(a\)通过点\(F(n-1)\)走到图\(D(n-2)\),再走到\(b\)。
那么我们就可以在搜索的过程中分类讨论来优化了。
但是这样还是会\(TLE\)。接下来,我们发现有多次重复询问是关于\(a\)点如何最快到达\(1\)点或者\(F(n-1)\)点,我们就可以先把它预处理出来,再搜索。具体实现见代码。
AC代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL n,m,f[1005],d[1005],d1[1005],d2[1005],d3[1005],d4[1005];
LL read()
{
LL re=0;char ch=getchar();
while(!isdigit(ch)) ch=getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) re=(re<<3)+(re<<1)+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return re;
}
void prework(LL x,LL g,LL *a1,LL *a2)
{
if(!g){a1[g]=a2[g]=0;return ;}
if(g==1){a1[g]=(x==2),a2[g]=(x==1);return ;}
if(x<=f[g-1])
{
prework(x,g-1,a1,a2);
a1[g]=min(a1[g-1],a2[g-1]+2);
a2[g]=min(a1[g-1],a2[g-1])+1+d[g-2];
}
else
{
prework(x-f[g-1],g-2,a1,a2);
a1[g]=a1[g-2]+1;
a2[g]=a2[g-2];
}
}
LL ask(LL g,LL x,LL y)
{
if(g<=1) return x!=y;
if(x<=f[g-1]&&y<=f[g-1]) return min(ask(g-1,x,y),min(d1[g-1]+d4[g-1],d2[g-1]+d3[g-1])+2);
if(x<=f[g-1]&&y>f[g-1]) return min(d1[g-1],d2[g-1])+1+d3[g-2];
else return ask(g-2,x-f[g-1],y-f[g-1]);
}
int main()
{
f[0]=1,f[1]=2,d[0]=0,d[1]=1;
for(LL i=2;i<80;i++) f[i]=f[i-1]+f[i-2],d[i]=d[i-2]+1;
m=read(),n=min(read(),LL(80));
while(m--)
{
LL x=read(),y=read();if(x>y) swap(x,y);
prework(x,n,d1,d2);prework(y,n,d3,d4);
printf("%lld\n",ask(n,x,y));
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号