js中的类数组对象,它具有数组的下标和length,但是没有数组相关的方法(push、slice、map、、、),现将数组的方法强行给它,会发生什么呢?
var obj = { '2': 3, '3': 4, 'length': 2, 'splice': Array.prototype.splice 'push': Array.prototype.push } console.log(obj) //=> ?
上面代码,强行给这个类数组对象增加一个数组的push方法,先打印一下这个类数组对象:

接下来在类数组对象中使用push方法:
var obj = { '2': 3, '3': 4, 'length': 2, 'splice': Array.prototype.splice, 'push': Array.prototype.push } obj.push(1); obj.push(2); console.log(obj) //=> ?
最后会输出什么呢?
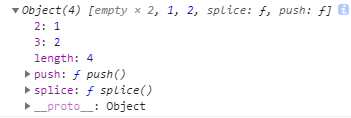
打印obj中的‘2’、‘3’对应的3,4,分别变成1,2了,其主要原因还是push。
在mdn中对push的描述:push() 方法将一个或多个元素添加到数组的末尾,并返回该数组的新长度。
push 是特意设计为通用的,既适用于数组,也适用于对象。正如下面的例子所示,Array.prototype.push 可以在一个对象上工作。 注意,我们没有创建一个数组来存储对象的集合。 相反,我们将该集合存储在对象本身上,并使用在 Array.prototype.push 上使用的 call 来调用该方法,使其认为我们正在处理数组,而它只是像平常一样运作。
var obj = { length: 0, addElem: function addElem (elem) { [].push.call(this, elem); } }; obj.addElem({}); obj.addElem({}); console.log(obj.length); //=> 2
因此可以总结push的原理如下:
Array.prototype.push = function(elem){ this[this.length] = elem; this.length ++; }
回到题目中,obj.push(1)=>obj[2] = 1; //此时obj的length为2
obj.push(2)=>obj[3] = 2; //此时obj的length为3
因此,得到上面的打印结果,由于类数组对象中没有属性为‘0’、‘1’,所以前面会有俩个值为empty。
脚踏实地行,海阔天空飞



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号