23.哈希表
1.哈希表的故事导入
故事情节
为了提高开发团队精神,缓解工作压力,某IT公司组织开发团队的12位男同事和测试团队的12位女同事开展真人CS 4vs4 野战联谊!面对性感的女同事,男同事们个个摩拳擦掌,跃跃欲试!
野战活动那天,根据男女搭配,干活不累的原则,带队的专业教练让男同事站成一排,女同事站成一排,然后要求从女生这排开始从1 开始报数,每个报数的队员都要记住自己的编号。
报数时,教练发给每人一个白色的臂章贴在肩膀上,每个臂章上写着报数人自己报过的编号!
当所有人都报完数后,教练发出命令将24 人均分成6个组!
编号除6 能整除的为第一组: 6 12 18 24
编号除6 余数为1 的为第二组: 1 7 13 19
编号除6 余数为2 的为第三组: 2 8 14 20
编号除6 余数为3 的为第四组: 3 9 15 21
编号除6 余数为4 的为第五组: 4 10 16 22
编号除6 余数为5 的为第六组: 5 11 17 23
通过这种编号方式划分队列,无论队员归队,还是裁判确认队员身份,都非常方便,此后林子里传来隆隆的笑声和枪炮声!
这种编号的方式就是高效的散列,我们俗称“哈希”!
以上过程是通过把关键码值key(编号)映射到表中一个位置(数组的下标)来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
2.哈希表的原理精讲
哈希表- 散列表,它是基于快速存取的角度设计的,也是一种典型的“空间换时间”的做法
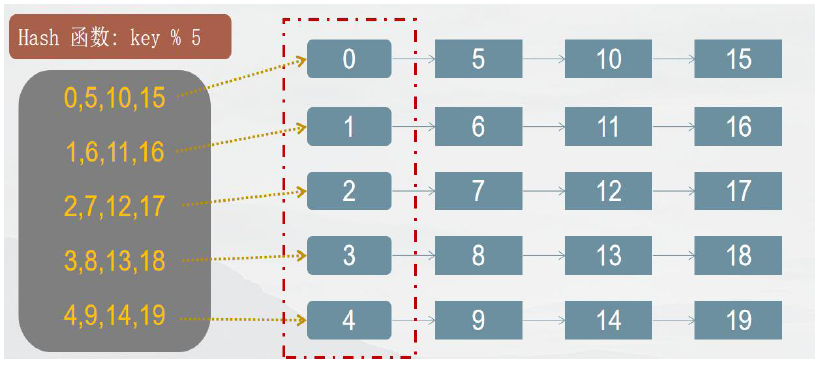
键(key): 组员的编号如, 1 、5 、19 。。。
值(value): 组员的其它信息(包含性别、年龄和战斗力等)
索引: 数组的下标(0,1,2,3,4) ,用以快速定位和检索数据
哈希桶: 保存索引的数组(链表或数组),数组成员为每一个索引值相同的多个元素
哈希函数: 将组员编号映射到索引上,采用求余法,如: 组员编号19
3.哈希链表的算法实现
3.1哈希链表数据结构的定义
//哈希链表数据结构的定义
typedef struct _ListNode
{
struct _ListNode* next;
int key;
void* data;
}ListNode;
typedef ListNode* List;//当链表使用
typedef ListNode* Element;//哈希表中的元素
typedef struct _HashTable//哈希表
{
int TableSize;//哈希桶的数量
List* Thelists;//动态分配尺寸,数据用数组存储
}HashTable;
3.2哈希函数
//哈希函数
/*根据key 计算索引,定位Hash桶的位置*/
int Hash(int key, int TableSize)
{
return (key % TableSize);
}
3.3初始化哈希表
/*初始化哈希表*/
HashTable* InitHash(int TableSize)
{
int i = 0;
HashTable* hTable = NULL;
if (TableSize <= 0) {
TableSize = DEFAULT_SIZE;
}
hTable = (HashTable*)malloc(sizeof(HashTable));
if (NULL == hTable)
{
printf("HashTable malloc error.\n");
return NULL;
}
hTable->TableSize = TableSize;
//为Hash 桶分配内存空间,其为一个指针数组
hTable->Thelists = (List*)malloc(sizeof(List) * TableSize);
if (NULL == hTable->Thelists)
{
printf("HashTable malloc error\n");
free(hTable);
return NULL;
}
//为Hash 桶对应的指针数组初始化链表节点
for (i = 0; i < TableSize; i++)
{
hTable->Thelists[i] = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (NULL == hTable->Thelists[i])
{
printf("HashTable malloc error\n");
free(hTable->Thelists);
free(hTable);
return NULL;
}
else
{
memset(hTable->Thelists[i], 0, sizeof(ListNode));
}
}
return hTable;
}
3.4哈希链表插入元素
/*哈希表插入元素,元素为键值对*/
void Insert(HashTable* HashTable, int key, void* value)
{
Element e = NULL, tmp = NULL;
List L = NULL;
e = Find(HashTable, key);
if (NULL == e)
{
tmp = (Element)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (NULL == tmp)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return;
}
L = HashTable->Thelists[Hash(key, HashTable->TableSize)];
tmp->data = value;
tmp->key = key;
tmp->next = L->next;
L->next = tmp;
}
else
printf("the key already exist\n");
}
3.5哈希链表查找元素
/*从哈希表中根据键值查找元素*/
Element Find(HashTable* HashTable, int key)
{
int i = 0;
List L = NULL;
Element e = NULL;
i = Hash(key, HashTable->TableSize);
L = HashTable->Thelists[i];
e = L->next;
while (e != NULL && e->key != key)
e = e->next;
return e;
}
3.6哈希链表删除元素
/*哈希表删除元素,元素为键值对*/
void Delete(HashTable* HashTable, int key)
{
Element e = NULL, last = NULL;
List L = NULL;
int i = Hash(key, HashTable->TableSize);
L = HashTable->Thelists[i];
last = L;
e = L->next;
while (e != NULL && e->key != key)
{
last = e;
e = e->next;
}
if (e) //如果键值对存在
{
last->next = e->next;
free(e);
}
}
3.7哈希表销毁
/*销毁哈希表*/
void Destory(HashTable* HashTable)
{
int i = 0;
List L = NULL;
Element cur = NULL, next = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < HashTable->TableSize; i++)
{
L = HashTable->Thelists[i];
cur = L->next;
while (cur != NULL)
{
next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(L);
}
free(HashTable->Thelists);
free(HashTable);
}
3.8哈希表元素中提取数据
/*哈希表元素中提取数据*/
void* Retrieve(Element e)
{
return e ? e->data : NULL;
}
源码实现:
hash_table.h
#pragma once
#define DEFAULT_SIZE 16
/*哈希表元素定义*/
typedef struct _ListNode
{
struct _ListNode* next;
int key;
void* data;
}ListNode;
typedef ListNode* List;
typedef ListNode* Element;
/*哈希表结构定义*/
typedef struct _HashTable
{
int TableSize;
List* Thelists;
}HashTable;
/*哈希函数*/
int Hash(void* key, int TableSize);
/*初始化哈希表*/
HashTable* InitHash(int TableSize);
/*哈希表插入*/
void Insert(HashTable* HashTable, int key, void* value);
/*哈希表查找*/
Element Find(HashTable* HashTable, int key);
/*哈希表销毁*/
void Destory(HashTable* HashTable);
/*哈希表元素中提取数据*/
void* Retrieve(Element e);
hash_table.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "hash_table.h"
/*根据key 计算索引,定位Hash 桶的位置*/
int Hash(int key, int TableSize)
{
return (key % TableSize);
}
/*初始化哈希表*/
HashTable* InitHash(int TableSize)
{
int i = 0;
HashTable* hTable = NULL;
if (TableSize <= 0) {
TableSize = DEFAULT_SIZE;
}
hTable = (HashTable*)malloc(sizeof(HashTable));
if (NULL == hTable)
{
printf("HashTable malloc error.\n");
return NULL;
}
hTable->TableSize = TableSize;
//为Hash 桶分配内存空间,其为一个指针数组
hTable->Thelists = (List*)malloc(sizeof(List) * TableSize);
if (NULL == hTable->Thelists)
{
printf("HashTable malloc error\n");
free(hTable);
return NULL;
}
//为Hash 桶对应的指针数组初始化链表节点
for (i = 0; i < TableSize; i++)
{
hTable->Thelists[i] = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (NULL == hTable->Thelists[i])
{
printf("HashTable malloc error\n");
free(hTable->Thelists);
free(hTable);
return NULL;
}
else
{
memset(hTable->Thelists[i], 0, sizeof(ListNode));
}
}
return hTable;
}
/*从哈希表中根据键值查找元素*/
Element Find(HashTable* HashTable, int key)
{
int i = 0;
List L = NULL;
Element e = NULL;
i = Hash(key, HashTable->TableSize);
L = HashTable->Thelists[i];
e = L->next;
while (e != NULL && e->key != key)
e = e->next;
return e;
}
/*哈希表插入元素,元素为键值对*/
void Insert(HashTable* HashTable, int key, void* value)
{
Element e = NULL, tmp = NULL;
List L = NULL;
e = Find(HashTable, key);
if (NULL == e)
{
tmp = (Element)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (NULL == tmp)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return;
}
L = HashTable->Thelists[Hash(key, HashTable->TableSize)];
tmp->data = value;
tmp->key = key;
tmp->next = L->next;
L->next = tmp;
}
else
printf("the key already exist\n");
}
/*哈希表删除元素,元素为键值对*/
void Delete(HashTable* HashTable, int key)
{
Element e = NULL, last = NULL;
List L = NULL;
int i = Hash(key, HashTable->TableSize);
L = HashTable->Thelists[i];
last = L;
e = L->next;
while (e != NULL && e->key != key)
{
last = e;
e = e->next;
}
if (e) //如果键值对存在
{
last->next = e->next;
free(e);
}
}
/*哈希表元素中提取数据*/
void* Retrieve(Element e)
{
return e ? e->data : NULL;
}
/*销毁哈希表*/
void Destory(HashTable* HashTable)
{
int i = 0;
List L = NULL;
Element cur = NULL, next = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < HashTable->TableSize; i++)
{
L = HashTable->Thelists[i];
cur = L->next;
while (cur != NULL)
{
next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(L);
}
free(HashTable->Thelists);
free(HashTable);
}
void main(void)
{
char* elems[] = { "翠花","小芳","苍老师" };
int i = 0;
HashTable* HashTable;
HashTable = InitHash(31);
Insert(HashTable, 1, elems[0]);
Insert(HashTable, 2, elems[1]);
Insert(HashTable, 3, elems[2]);
Delete(HashTable, 1);
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Element e = Find(HashTable, i);
if (e)
{
printf("%s\n", (const char*)Retrieve(e));
}
else {
printf("Not found [key:%d]\n", i);
}
}
system("pause");
}
参考资料来源:
奇牛学院


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号