ElasticSearch的基本使用
一、引言
1.1 海量数据
在海量数据中执行搜索功能时,如果使用MySQL,效率太低。
1.2 全文检索
在海量数据中执行搜索功能时,如果使用MySQL,效率太低。
1.3 高亮显示
将搜索关键字,以红色的字体展示。
二、ES概述
2.1 ES的介绍
ES是一个使用Java语言并且基于Lucene( https://lucene.apache.org/ )编写的搜索引擎框架,他提供了分布式的全文搜索功能,提供了一个统一的基于RESTful风格的WEB接口,官方客户端也对多种语言都提供了相应的API。
Lucene:Lucene本身就是一个搜索引擎的底层。
分布式:ES主要是为了突出他的横向扩展能力。
全文检索:将一段词语进行分词,并且将分出的单个词语统一的放到一个分词库中,在搜索时,根据关键字去分词库中检索,找到匹配的内容。(倒排索引)
RESTful风格的WEB接口:操作ES很简单,只需要发送一个HTTP请求,并且根据请求方式的不同,携带参数的同,执行相应的功能。
应用广泛:Github.com,WIKI,Gold Man用ES每天维护将近10TB的数据。
2.2 ES的由来
| ES回忆时光 |
|---|
 |
2.3 ES和Solr
- Solr在查询死数据时,速度相对ES更快一些。但是数据如果是实时改变的,Solr的查询速度会降低很多,ES的查询的效率基本没有变化。
- Solr搭建基于需要依赖Zookeeper来帮助管理。ES本身就支持集群的搭建,不需要第三方的介入。
- 最开始Solr的社区可以说是非常火爆,针对国内的文档并不是很多。在ES出现之后,ES的社区火爆程度直线上升,ES的文档非常健全。
- ES对现在云计算和大数据支持的特别好。
2.4 倒排索引
假设有两篇文章1和2:
文章1的内容为:老超在卡子门工作,我也是。
文章2的内容为:小超在鼓楼工作。
首先要取得这两篇文章的关键词。如果我们把文章看成一个字符串,我们需要取得字符串中的所有单词,即分词。分词时,忽略”在“、”的“之类的没有意义的介词,以及标点符号可以过滤。。
| 文章1 |
|---|
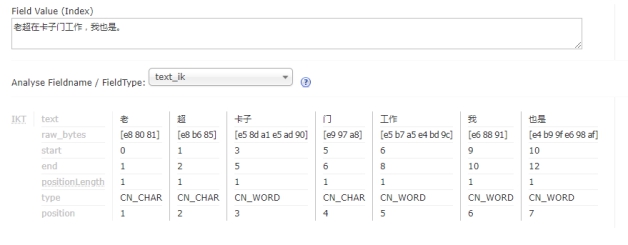 |
| 文章2 |
|---|
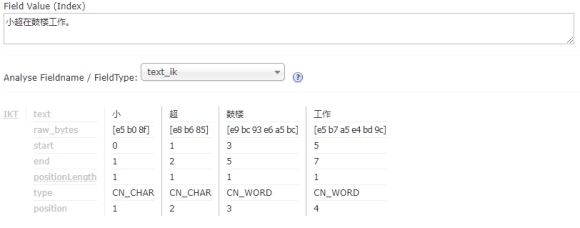 |
接下来,有了关键词后,我们就可以建立倒排索引了。上面的对应关系是:“文章号”对“文章中所有关键词”。倒排索引把这个关系倒过来,变成: “关键词”对“拥有该关键词的所有文章号”。
| 文章1、文章2经过倒排后变成 |
|---|
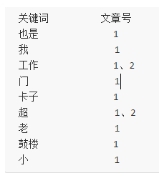 |
通常仅知道关键词在哪些文章中出现还不够,我们还需要知道关键词在文章中出现次数和出现的位置,通常有两种位置:
a.字符位置,即记录该词是文章中第几个字符(优点是关键词亮显时定位快);
b.关键词位置,即记录该词是文章中第几个关键词(优点是节约索引空间、词组(phase)查询快.
| 加上出现频率和出现位置信息后,我们的索引结构变为: |
|---|
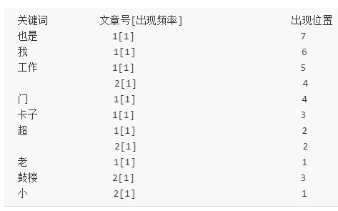 |
三、 ElasticSearch安装
3.1 安装ES&Kibana
修改这里的配置需要切换成root用户,这里需要修改/etc/sysctl.conf才能完成设置,在这个个文件中修改最大进程数为es要求的值。
root用户修改配置sysctl.conf
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
添加下面配置
vm.max_map_count=655360
执行命令
sysctl -p
重新启动docker
yml文件
version: "3.1"
services:
elasticsearch:
image: daocloud.io/library/elasticsearch:6.5.4
restart: always
container_name: elasticsearch
ports:
- 9200:9200
kibana:
image: daocloud.io/library/kibana:6.5.4
restart: always
container_name: kibana
ports:
- 5601:5601
environment:
- elasticsearch_url=http://192.168.40.100:9200
depends_on: ## 指定依赖于哪个服务
- elasticsearch
3.2 安装IK分词器
由于网络问题,采用国内的路径去下载:http://tomcat01.qfjava.cn:81/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip
进去到ES容器内部,跳转到bin目录下,执行bin目录下的脚本文件:
./elasticsearch-plugin install http://tomcat01.qfjava.cn:81/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip
重启ES的容器,让IK分词器生效。
| 校验IK分词器 |
|---|
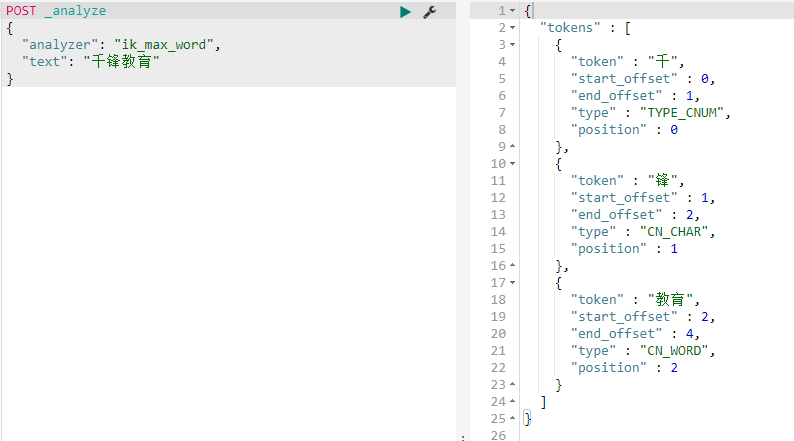 |
默认使用 "analyzer": "standard"分词器
四、 ElasticSearch基本操作
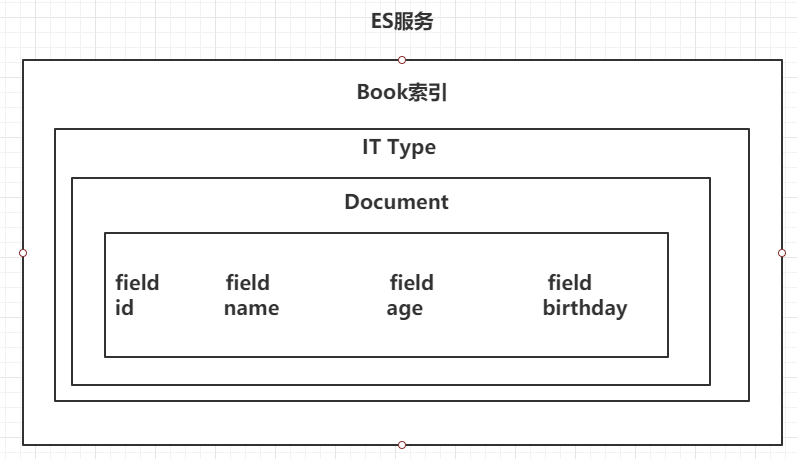
4.1 ES的结构
4.1.1 索引Index,分片和备份
索引是ElasticSearch存放数据的地方,可以理解为关系型数据库中的一个数据库。事实上,我们的数据被存储和索引在分片(shards)中,索引只是一个把一个或多个分片分组在一起的逻辑空间。然而,这只是一些内部细节——我们的程序完全不用关心分片。对于我们的程序而言,文档存储在索引(index)中。剩下的细节由Elasticsearch关心既可(索引的名字必须是全部小写,不能以下划线开头,不能包含逗号)
ES的服务中,可以创建多个索引。
每一个索引默认被分成5片存储。
每一个分片都会存在至少一个备份分片。
备份分片默认不会帮助检索数据,当ES检索压力特别大的时候,备份分片才会帮助检索数据。
备份的分片必须放在不同的服务器中。
| 索引分片备份 |
|---|
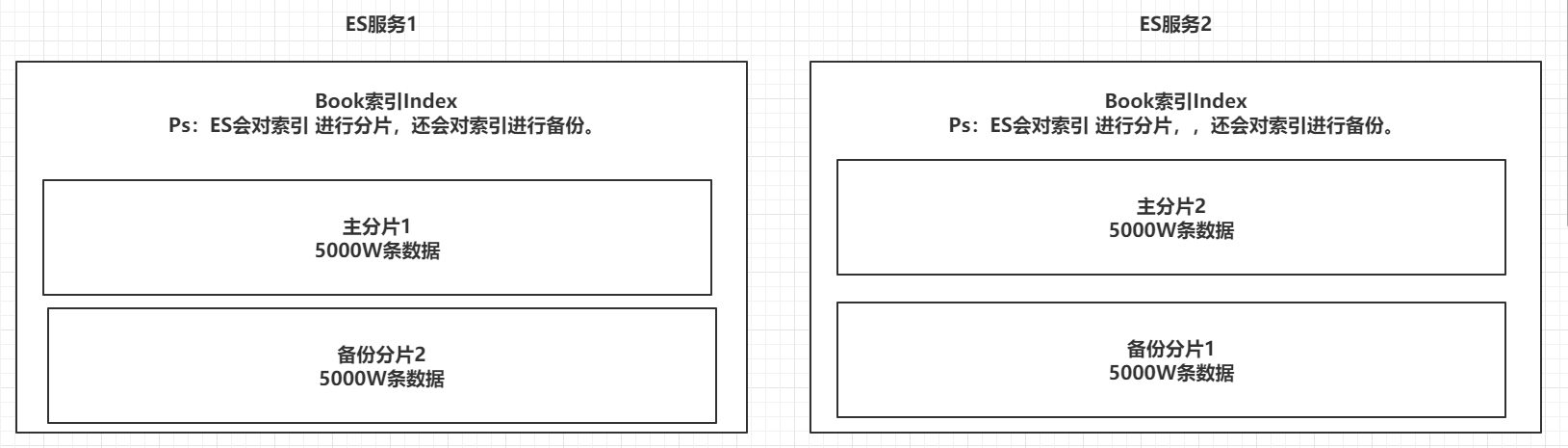 |
4.1.2 类型 Type
类型用于区分同一个索引下不同的数据类型,相当于关系型数据库中的表。在Elasticsearch中,我们使用相同类型(type)的文档表示相同的“事物”,因为他们的数据结构也是相同的。每个类型(type)都有自己的映射(mapping)或者结构定义,就像传统数据库表中的列一样。所有类型下的文档被存储在同一个索引下,但是类型的映射(mapping)会告诉Elasticsearch不同的文档如何被索引。
es 6.0 开始不推荐一个index下多个type的模式,并且会在 7.0 中完全移除。在 6.0 的index下是无法创建多个type
| 类型 |
|---|
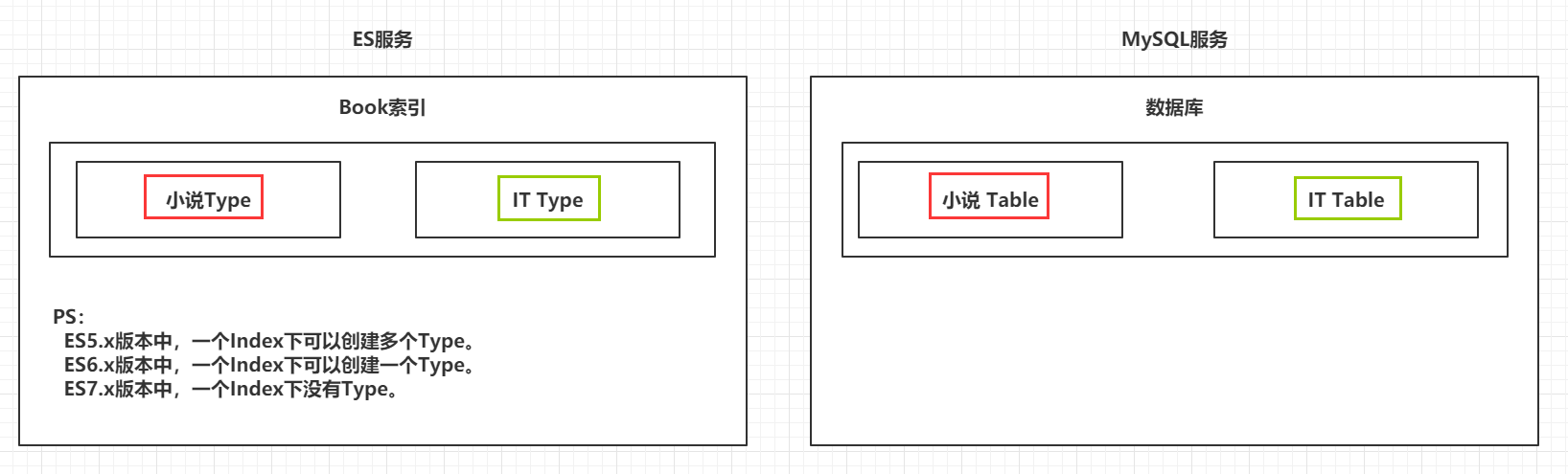 |
4.1.3 文档 Doc
文档是ElasticSearch中存储的实体,类比关系型数据库,每个文档相当于数据库表中的一行数据。 在Elasticsearch中,文档(document)这个术语有着特殊含义。它特指最顶层结构或者根对象(root object)序列化成的JSON数据(以唯一ID标识并存储于Elasticsearch中)。
一个类型下,可以有多个文档。这个文档就类似于MySQL表中的多行数据。
| 文档 |
|---|
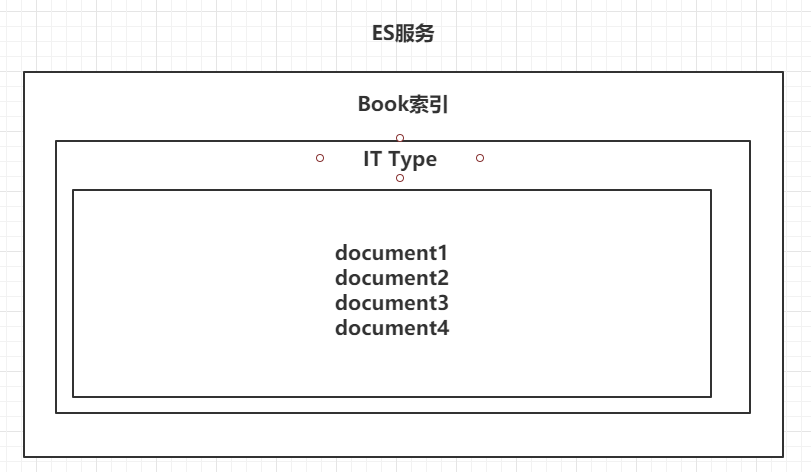 |
4.1.4 属性 Field
一个文档中,可以包含多个属性。类似于MySQL表中的一行数据存在多个列。
| 属性 |
|---|
 |
4.2 操作ES的RESTful语法
- GET请求:
- POST请求:
- PUT请求:
- DELETE请求:
4.3 索引的操作
4.3.1 创建一个索引
语法如下
# 创建一个索引
PUT /person
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 5,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}
4.3.2 查看索引信息
语法如下
# 查看索引信息
GET /person
| 查看信息 |
|---|
 |
health:健康的情况,正常的情况下es的健康状态是绿色。
status:状态
Primaries:分片数量
Replicas:备份数量
Docs count:文档数量
这里新建的索引健康状态是黄色是因为es默认会把备份的分片放到其他服务器上面,但是目前我们是单机版找不到其他的es服务器所以是黄色。
4.3.3 删除索引
语法如下
# 删除索引
DELETE /person
4.4 ES中Field可以指定的类型
字符串类型:
- text:一把被用于全文检索。 将当前Field进行分词。
- keyword:当前Field不会被分词。
数值类型:
- long:取值范围为-9223372036854774808~922337203685477480(-2的63次方到2的63次方-1),占用8个字节
- integer:取值范围为-2147483648~2147483647(-2的31次方到2的31次方-1),占用4个字节
- short:取值范围为-32768~32767(-2的15次方到2的15次方-1),占用2个字节
- byte:取值范围为-128~127(-2的7次方到2的7次方-1),占用1个字节
- double:1.797693e+308~ 4.9000000e-324 (e+308表示是乘以10的308次方,e-324表示乘以10的负324次方)占用8个字节
- float:3.402823e+38 ~ 1.401298e-45(e+38表示是乘以10的38次方,e-45表示乘以10的负45次方),占用4个字节
- half_float:精度比float小一半。
- scaled_float:根据一个long和scaled来表达一个浮点型,long-345,scaled-100 -> 3.45
时间类型:
- date类型,针对时间类型指定具体的格式
布尔类型:
- boolean类型,表达true和false
二进制类型:
- binary类型暂时支持Base64 encode string
范围类型:
- long_range:赋值时,无需指定具体的内容,只需要存储一个范围即可,指定gt,lt,gte,lte
- integer_range:同上
- double_range:同上
- float_range:同上
- date_range:同上
- ip_range:同上
经纬度类型:
- geo_point:用来存储经纬度的
ip类型:
- ip:可以存储IPV4或者IPV6
其他的数据类型参考官网:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.5/mapping-types.html
4.5 创建索引并指定数据结构
语法如下
# 创建索引,指定数据结构
PUT /book
{
"settings": {
# 分片数
"number_of_shards": 5,
# 备份数
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
# 指定数据结构
"mappings": {
# 类型 Type
"novel": {
# 文档存储的Field
"properties": {
# Field属性名
"name": {
# 类型
"type": "text",
# 指定分词器
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
# 指定当前Field可以被作为查询的条件
"index": true ,
# 是否需要额外存储
"store": false
},
"author": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"count": {
"type": "long"
},
"on-sale": {
"type": "date",
# 时间类型的格式化方式
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
},
"descr": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}
4.6 文档的操作
文档在ES服务中的唯一标识,
_index,_type,_id三个内容为组合,锁定一个文档,如果不存在就添加,否则就是修改。
4.6.1 新建文档
自动生成_id
# 添加文档,自动生成id
POST /book/novel
{
"name": "盘龙",
"author": "我吃西红柿",
"count": 100000,
"on-sale": "2000-01-01",
"descr": "山重水复疑无路,柳暗花明又一村"
}
手动指定_id
# 添加文档,手动指定id
PUT /book/novel/1
{
"name": "红楼梦",
"author": "曹雪芹",
"count": 10000000,
"on-sale": "1985-01-01",
"descr": "一个是阆苑仙葩,一个是美玉无瑕"
}
4.6.2 修改文档
覆盖式修改
# 添加文档,手动指定id
PUT /book/novel/1
{
"name": "红楼梦",
"author": "曹雪芹",
"count": 4353453,
"on-sale": "1985-01-01",
"descr": "一个是阆苑仙葩,一个是美玉无瑕"
}
doc修改方式
# 修改文档,基于doc方式
POST /book/novel/1/_update
{
"doc": {
# 指定上需要修改的field和对应的值
"count": "1234565"
}
}
4.6.3 删除文档
根据id删除
# 根据id删除文档
DELETE /book/novel/_id
五、Java操作ElasticSearch【重点】
5.1 Java连接ES
创建Maven工程
导入依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 1. elasticsearch-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>6.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 2. elasticsearch的高级API-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>6.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 3. junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 4. lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.22</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建测试类,连接ES
public class ESClient {
public static RestHighLevelClient getClient(){
// 创建HttpHost对象
HttpHost httpHost = new HttpHost("192.168.199.109",9200);
// 创建RestClientBuilder
RestClientBuilder clientBuilder = RestClient.builder(httpHost);
// 创建RestHighLevelClient
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(clientBuilder);
// 返回
return client;
}
}
5.2 Java操作索引
5.2.1 创建索引
| API | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Settings.Builder | 封装了settings中的信息 |
| XContentBuilder | 封装了mapping是中的信息 |
| CreateIndexRequest | 封装mapping和settins,index,type |
| RestHighLevelClient | java访问es客户端 |
| IndicesClient | 索引客户端 |
| CreateIndexResponse | 创建完索引后相应的对象 |
代码如下
public class Demo2 {
RestHighLevelClient client = ESClient.getClient();
String index = "person";
String type = "man";
@Test
public void createIndex() throws IOException {
//1. 准备关于索引的settings
Settings.Builder settings = Settings.builder()
.put("number_of_shards", 3)
.put("number_of_replicas", 1);
//2. 准备关于索引的结构mappings
XContentBuilder mappings = JsonXContent.contentBuilder()
.startObject()
.startObject("properties")
.startObject("name")
.field("type","text")
.endObject()
.startObject("age")
.field("type","integer")
.endObject()
.startObject("birthday")
.field("type","date")
.field("format","yyyy-MM-dd")
.endObject()
.endObject()
.endObject();
//3. 将settings和mappings封装到一个Request对象
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest(index)
.settings(settings)
.mapping(type,mappings);
//4. 通过client对象去连接ES并执行创建索引
CreateIndexResponse resp = client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//5. 输出
System.out.println("resp:" + resp.toString());
}
}
5.2.2 检查索引是否存在
代码如下
@Test
public void exists() throws IOException {
//1. 准备request对象
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest();
request.indices(index);
//2. 通过client去操作
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3. 输出
System.out.println(exists);
}
5.2.3 删除索引
代码如下
@Test
public void delete() throws IOException {
//1. 准备request对象
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest();
request.indices(index);
//2. 通过client对象执行
AcknowledgedResponse delete = client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3. 获取返回结果
System.out.println(delete.isAcknowledged());
}
5.3 Java操作文档
5.3.1 添加文档操作
代码如下
public class Demo3 {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
RestHighLevelClient client = ESClient.getClient();
String index = "person";
String type = "man";
@Test
public void createDoc() throws IOException {
//1. 准备一个json数据
Person person = new Person(1,"张三",23,new Date());
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(person);
//2. 准备一个request对象(手动指定id)
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest(index,type,person.getId().toString());
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
//3. 通过client对象执行添加
IndexResponse resp = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出返回结果
System.out.println(resp.getResult().toString());
}
}
5.3.2 修改文档
代码如下
@Test
public void updateDoc() throws IOException {
//1. 创建一个Map,指定需要修改的内容
Map<String,Object> doc = new HashMap<>();
doc.put("name","张大三"); // 如果id放在map中会把id属性设置到_source里面
String docId = "1";
//2. 创建request对象,封装数据
UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest(index,type,docId);
request.doc(doc);
//3. 通过client对象执行
UpdateResponse update = client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出返回结果
System.out.println(update.getResult().toString());
}
5.3.3 删除文档
代码如下
@Test
public void deleteDoc() throws IOException {
//1. 封装Request对象
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest(index,type,"1");
//2. client执行
DeleteResponse resp = client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3. 输出结果
System.out.println(resp.getResult().toString());
}
5.4 Java批量操作文档
5.4.1 批量添加
代码如下
@Test
public void bulkCreateDoc() throws IOException {
//1. 准备多个json数据
Person p1 = new Person(1,"张三",23,new Date());
Person p2 = new Person(2,"李四",24,new Date());
Person p3 = new Person(3,"王五",25,new Date());
String json1 = mapper.writeValueAsString(p1);
String json2 = mapper.writeValueAsString(p2);
String json3 = mapper.writeValueAsString(p3);
//2. 创建Request,将准备好的数据封装进去
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
request.add(new IndexRequest(index,type,p1.getId().toString()).source(json1,XContentType.JSON));
request.add(new IndexRequest(index,type,p2.getId().toString()).source(json2,XContentType.JSON));
request.add(new IndexRequest(index,type,p3.getId().toString()).source(json3,XContentType.JSON));
//3. 用client执行
BulkResponse resp = client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
System.out.println(resp.toString());
}
5.4.2 批量删除
代码如下
@Test
public void bulkDeleteDoc() throws IOException {
//1. 封装Request对象
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
request.add(new DeleteRequest(index,type,"1"));
request.add(new DeleteRequest(index,type,"2"));
request.add(new DeleteRequest(index,type,"3"));
//2. client执行
BulkResponse resp = client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3. 输出
System.out.println(resp);
}
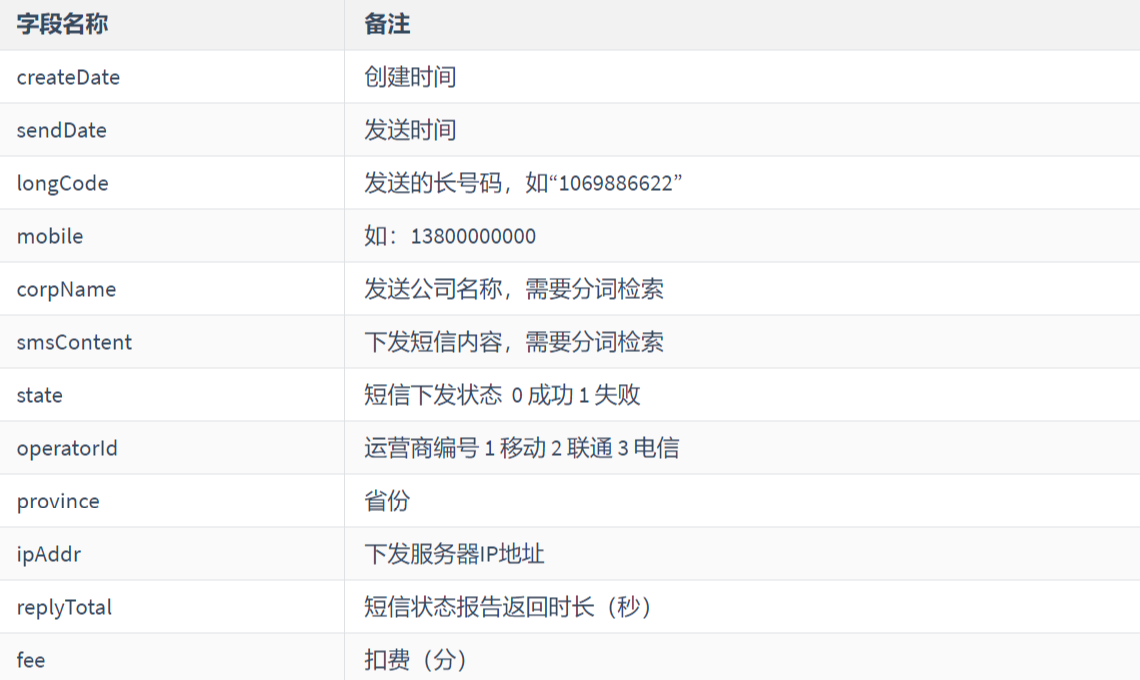
5.5 ElasticSearch练习
创建索引,指定数据结构
索引名:sms-logs-index
类型名:sms-logs-type
结构如下:
| 索引结构图 |
|---|
 |
5.6 测试数据
SmsLogs
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class SmsLogs {
private String id;// 唯一ID 1
private Date createDate;// 创建时间
private Date sendDate; // 发送时间
private String longCode;// 发送的长号码
private String mobile;// 下发手机号
private String corpName;// 发送公司名称
private String smsContent; // 下发短信内容
private Integer state; // 短信下发状态 0 成功 1 失败
private Integer operatorId; // '运营商编号 1 移动 2 联通 3 电信
private String province;// 省份
private String ipAddr; //下发服务器IP地址
private Integer replyTotal; //短信状态报告返回时长(秒)
private Integer fee; // 费用
}
TestData
RestHighLevelClient client = ESClinet.getClient();
String index = "sms-logs-index";
String type = "sms-logs-type";
@Test
public void createSmsLogsIndex() throws IOException {
//1. settings
Settings.Builder settings = Settings.builder()
.put("number_of_shards", 3)
.put("number_of_replicas", 1);
//2. mapping.
XContentBuilder mapping = JsonXContent.contentBuilder()
.startObject()
.startObject("properties")
.startObject("createDate")
.field("type", "date")
.endObject()
.startObject("sendDate")
.field("type", "date")
.endObject()
.startObject("longCode")
.field("type", "keyword")
.endObject()
.startObject("mobile")
.field("type", "keyword")
.endObject()
.startObject("corpName")
.field("type", "keyword")
.endObject()
.startObject("smsContent")
.field("type", "text")
.field("analyzer", "ik_max_word")
.endObject()
.startObject("state")
.field("type", "integer")
.endObject()
.startObject("operatorId")
.field("type", "integer")
.endObject()
.startObject("province")
.field("type", "keyword")
.endObject()
.startObject("ipAddr")
.field("type", "ip")
.endObject()
.startObject("replyTotal")
.field("type", "integer")
.endObject()
.startObject("fee")
.field("type", "long")
.endObject()
.endObject()
.endObject();
//3. 添加索引.
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest(index);
request.settings(settings);
request.mapping(type,mapping);
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("OK!!");
}
@Test
public void addTestData() throws IOException {
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
SmsLogs smsLogs = new SmsLogs();
smsLogs.setMobile("13800000000");
smsLogs.setCorpName("途虎养车");
smsLogs.setCreateDate(new Date());
smsLogs.setSendDate(new Date());
smsLogs.setIpAddr("10.126.2.9");
smsLogs.setLongCode("10690000988");
smsLogs.setReplyTotal(10);
smsLogs.setState(0);
smsLogs.setSmsContent("【途虎养车】亲爱的张三先生/女士,您在途虎购买的货品(单号TH123456)已 到指定安装店多日," + "现需与您确认订单的安装情况,请点击链接按实际情况选择(此链接有效期为72H)。您也可以登录途 虎APP进入" + "“我的-待安装订单”进行预约安装。若您在服务过程中有任何疑问,请致电400-111-8868向途虎咨 询。");
smsLogs.setProvince("北京");
smsLogs.setOperatorId(1);
smsLogs.setFee(3);
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "21").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs), XContentType.JSON));
smsLogs.setMobile("13700000001");
smsLogs.setProvince("上海");
smsLogs.setSmsContent("【途虎养车】亲爱的刘红先生/女士,您在途虎购买的货品(单号TH1234526)已 到指定安装店多日," + "现需与您确认订单的安装情况,请点击链接按实际情况选择(此链接有效期为72H)。您也可以登录途 虎APP进入" + "“我的-待安装订单”进行预约安装。若您在服务过程中有任何疑问,请致电400-111-8868向途虎咨 询。");
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "22").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs), XContentType.JSON));
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SmsLogs smsLogs1 = new SmsLogs();
smsLogs1.setMobile("13100000000");
smsLogs1.setCorpName("盒马鲜生");
smsLogs1.setCreateDate(new Date());
smsLogs1.setSendDate(new Date());
smsLogs1.setIpAddr("10.126.2.9");
smsLogs1.setLongCode("10660000988");
smsLogs1.setReplyTotal(15);
smsLogs1.setState(0);
smsLogs1.setSmsContent("【盒马】您尾号12345678的订单已开始配送,请在您指定的时间收货不要走开 哦~配送员:" + "刘三,电话:13800000000");
smsLogs1.setProvince("北京");
smsLogs1.setOperatorId(2);
smsLogs1.setFee(5);
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "23").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs1), XContentType.JSON));
smsLogs1.setMobile("18600000001");
smsLogs1.setProvince("上海");
smsLogs1.setSmsContent("【盒马】您尾号7775678的订单已开始配送,请在您指定的时间收货不要走开 哦~配送员:" + "王五,电话:13800000001");
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "24").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs1), XContentType.JSON));
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SmsLogs smsLogs2 = new SmsLogs();
smsLogs2.setMobile("15300000000");
smsLogs2.setCorpName("滴滴打车");
smsLogs2.setCreateDate(new Date());
smsLogs2.setSendDate(new Date());
smsLogs2.setIpAddr("10.126.2.8");
smsLogs2.setLongCode("10660000988");
smsLogs2.setReplyTotal(50);
smsLogs2.setState(1);
smsLogs2.setSmsContent("【滴滴单车平台】专属限时福利!青桔/小蓝月卡立享5折,特惠畅骑30天。" + "戳 https://xxxxxx退订TD");
smsLogs2.setProvince("上海");
smsLogs2.setOperatorId(3);
smsLogs2.setFee(7);
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "25").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs2), XContentType.JSON));
smsLogs2.setMobile("18000000001");
smsLogs2.setProvince("武汉");
smsLogs2.setSmsContent("【滴滴单车平台】专属限时福利!青桔/小蓝月卡立享5折,特惠畅骑30天。" + "戳 https://xxxxxx退订TD");
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "26").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs2), XContentType.JSON));
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SmsLogs smsLogs3 = new SmsLogs();
smsLogs3.setMobile("13900000000");
smsLogs3.setCorpName("招商银行");
smsLogs3.setCreateDate(new Date());
smsLogs3.setSendDate(new Date());
smsLogs3.setIpAddr("10.126.2.8");
smsLogs3.setLongCode("10690000988");
smsLogs3.setReplyTotal(50);
smsLogs3.setState(0);
smsLogs3.setSmsContent("【招商银行】尊贵的李四先生,恭喜您获得华为P30 Pro抽奖资格,还可领100 元打" + "车红包,仅限1天");
smsLogs3.setProvince("上海");
smsLogs3.setOperatorId(1);
smsLogs3.setFee(8);
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "27").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs3), XContentType.JSON));
smsLogs3.setMobile("13990000001");
smsLogs3.setProvince("武汉");
smsLogs3.setSmsContent("【招商银行】尊贵的李四先生,恭喜您获得华为P30 Pro抽奖资格,还可领100 元打" + "车红包,仅限1天");
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "28").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs3), XContentType.JSON));
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SmsLogs smsLogs4 = new SmsLogs();
smsLogs4.setMobile("13700000000");
smsLogs4.setCorpName("中国平安保险有限公司");
smsLogs4.setCreateDate(new Date());
smsLogs4.setSendDate(new Date());
smsLogs4.setIpAddr("10.126.2.8");
smsLogs4.setLongCode("10690000998");
smsLogs4.setReplyTotal(18);
smsLogs4.setState(0);
smsLogs4.setSmsContent("【中国平安】奋斗的时代,更需要健康的身体。中国平安为您提供多重健康保 障,在奋斗之路上为您保驾护航。退订请回复TD");
smsLogs4.setProvince("武汉");
smsLogs4.setOperatorId(1);
smsLogs4.setFee(5);
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "29").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs4), XContentType.JSON));
smsLogs4.setMobile("13990000002");
smsLogs4.setProvince("武汉");
smsLogs4.setSmsContent("【招商银行】尊贵的王五先生,恭喜您获得iphone 56抽奖资格,还可领5 元打" + "车红包,仅限100天");
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "30").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs4), XContentType.JSON));
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SmsLogs smsLogs5 = new SmsLogs();
smsLogs5.setMobile("13600000000");
smsLogs5.setCorpName("中国移动");
smsLogs5.setCreateDate(new Date());
smsLogs5.setSendDate(new Date());
smsLogs5.setIpAddr("10.126.2.8");
smsLogs5.setLongCode("10650000998");
smsLogs5.setReplyTotal(60);
smsLogs5.setState(0);
smsLogs5.setSmsContent("【北京移动】尊敬的客户137****0000,5月话费账单已送达您的139邮箱," + "点击查看账单详情 http://y.10086.cn/; " + " 回Q关闭通知,关注“中国移动139邮箱”微信随时查账单【中国移动 139邮箱】");
smsLogs5.setProvince("武汉");
smsLogs5.setOperatorId(1);
smsLogs5.setFee(4);
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "31").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs5), XContentType.JSON));
smsLogs5.setMobile("13990001234");
smsLogs5.setProvince("山西");
smsLogs5.setSmsContent("【北京移动】尊敬的客户137****1234,8月话费账单已送达您的126邮箱,\" + \"点击查看账单详情 http://y.10086.cn/; \" + \" 回Q关闭通知,关注“中国移动126邮箱”微信随时查账单【中国移动 126邮箱】");
request.add(new IndexRequest(index, type, "32").source(JSON.toJSONString(smsLogs5), XContentType.JSON));
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("OK!");
}
六、 ElasticSearch的各种查询
6.1 term&terms查询【重点】
6.1.1 term查询(分页)
term的查询是代表完全匹配,搜索之前不会对你搜索的关键字进行分词,对你的关键字去文档分词库中去匹配内容。
# term查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"from": 0, # limit ?
"size": 5, # limit x,?
"query": {
"term": {
"province": {
"value": "北京"
}
}
}
}
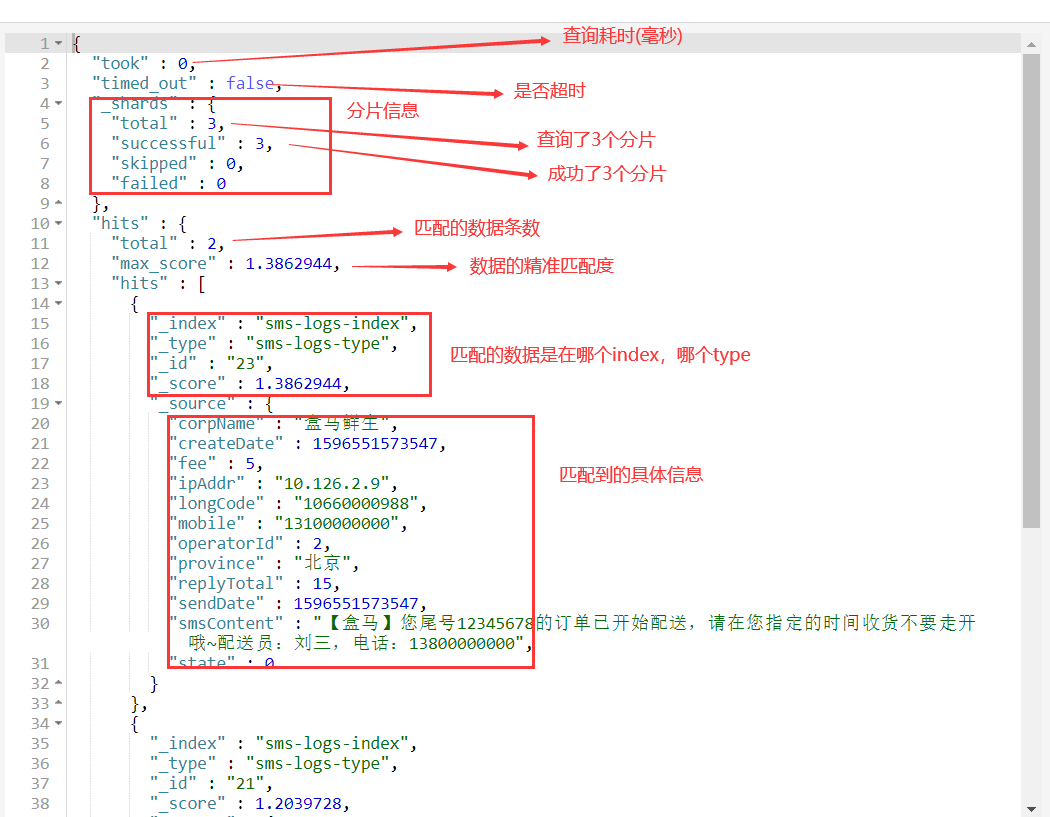
max_score匹配度越高,数据的排名就越靠前。
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现方式
@Test
public void termQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建Request对象
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
builder.from(0);
builder.size(5);
builder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("province","北京"));
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 获取到_source中的数据,并展示
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
Map<String, Object> result = hit.getSourceAsMap();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
6.1.2 terms查询
terms和term的查询机制是一样,都不会将指定的查询关键字进行分词,直接去分词库中匹配,找到相应文档内容。
terms是在针对一个字段包含多个值的时候使用。
term:where province = 北京;
terms:where province = 北京 or province = ?or province = ?
# terms查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"province": [
"北京",
"山西",
"武汉"
]
}
}
}
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"_source": ["province","fee"], ## 返回指定的列
"query": {
"terms": {
"province": [
"北京",
"山西",
"武汉"
]
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java实现
@Test
public void termsQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 封装查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
builder.query(QueryBuilders.termsQuery("province","北京","山西"));
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出_source
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.2 match查询【重点】
match查询属于高层查询,他会根据你查询的字段类型不一样,采用不同的查询方式。
- 查询的是日期或者是数值的话,他会将你基于的字符串查询内容转换为日期或者数值对待。
- 如果查询的内容是一个不能被分词的内容(keyword),match查询不会对你指定的查询关键字进行分词。
- 如果查询的内容时一个可以被分词的内容(text),match会将你指定的查询内容根据一定的方式去分词,去分词库中匹配指定的内容。
match查询,实际底层就是多个term查询,将多个term查询的结果给你封装到了一起。
6.2.1 match_all查询
查询全部内容,不指定任何查询条件。
# match_all查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
代码实现方式
// java代码实现
@Test
public void matchAllQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
builder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
builder.size(20); // ES默认只查询10条数据,如果想查询更多,添加size
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
System.out.println(resp.getHits().getHits().length);
}
6.2.2 match查询
指定一个Field作为筛选的条件 会先对查询的字段进行拆词,再进行匹配
# match查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"smsContent": "收货安装"
}
}
}
代码实现方式
@Test
public void matchQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//-----------------------------------------------
builder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("smsContent","收货安装"));
//-----------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.2.3 布尔match查询
基于一个Field匹配的内容,采用and或者or的方式连接
# 布尔match查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"smsContent": {
"query": "中国 健康",
"operator": "and" # 内容既包含中国也包含健康
}
}
}
}
# 布尔match查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"smsContent": {
"query": "中国 健康",
"operator": "or" # 内容包括健康或者包括中国
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现
@Test
public void booleanMatchQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//----------------------------------------------- 选择AND或者OR
builder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("smsContent","中国 健康").operator(Operator.OR));
//-----------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.2.4 multi_match查询
match针对一个field做检索,multi_match针对多个field进行检索,多个field对应一个text。
# multi_match 查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "北京", # 指定text
"fields": ["province","smsContent"] # 指定field们
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// java代码实现
@Test
public void multiMatchQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//-----------------------------------------------
builder.query(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("北京","province","smsContent"));
//-----------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.3 其他查询
6.3.1 id查询
根据id查询 where id = ?
# id查询
GET /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/1
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现
@Test
public void findById() throws IOException {
//1. 创建GetRequest
GetRequest request = new GetRequest(index,type,"1");
//2. 执行查询
GetResponse resp = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3. 输出结果
System.out.println(resp.getSourceAsMap());
}
6.3.2 ids查询
根据多个id查询,类似MySQL中的where id in(id1,id2,id2...)
# ids查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": ["1","2","3"]
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现
@Test
public void findByIds() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//----------------------------------------------------------
builder.query(QueryBuilders.idsQuery().addIds("1","2","3"));
//----------------------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.3.3 prefix查询
前缀查询,可以通过一个关键字去指定一个Field的前缀,从而查询到指定的文档。
#prefix 查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"corpName": {
"value": "途虎"
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java实现前缀查询
@Test
public void findByPrefix() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//----------------------------------------------------------
builder.query(QueryBuilders.prefixQuery("corpName","盒马"));
//----------------------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.3.4 fuzzy查询
模糊查询,我们输入字符的大概,ES就可以去根据输入的内容大概去匹配一下结果。
# fuzzy查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"corpName": {
"value": "盒马先生",
"prefix_length": 2 # 指定前面几个字符是不允许出现错误的
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现Fuzzy查询
@Test
public void findByFuzzy() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//----------------------------------------------------------
builder.query(QueryBuilders.fuzzyQuery("corpName","盒马先生").prefixLength(2));
//----------------------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.3.5 wildcard查询
通配查询,和MySQL中的like是一个套路,可以在查询时,在字符串中指定通配符*和占位符?
# wildcard 查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"corpName": {
"value": "中国*" # 可以使用*和?指定通配符和占位符(指定长度)
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现Wildcard查询
@Test
public void findByWildCard() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//----------------------------------------------------------
builder.query(QueryBuilders.wildcardQuery("corpName","中国*"));
//----------------------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.3.6 range查询
范围查询,只针对数值类型,对某一个Field进行大于或者小于的范围指定
# range 查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"fee": {
"gt": 5,
"lte": 10
# 可以使用 gt:> gte:>= lt:< lte:<=
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java实现range范围查询
@Test
public void findByRange() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//----------------------------------------------------------
builder.query(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("fee").lte(10).gte(5));
//----------------------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.3.7 regexp查询
正则查询,通过你编写的正则表达式去匹配内容。
# regexp 查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"mobile": "180[0-9]{8}" # 编写正则
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现正则查询
@Test
public void findByRegexp() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//----------------------------------------------------------
builder.query(QueryBuilders.regexpQuery("mobile","139[0-9]{8}"));
//----------------------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.4 深分页Scroll
ES对from + size是有限制的,from和size二者之和不能超过1W
原理:
from+size在ES查询数据的方式:
- 第一步现将用户指定的关键进行分词。
- 第二步将词汇去分词库中进行检索,得到多个文档的id。
- 第三步去各个分片中去拉取指定的数据。耗时较长。
- 第四步将数据根据score进行排序。耗时较长。
- 第五步根据from的值,将查询到的数据舍弃一部分。
- 第六步返回结果。
scroll+size在ES查询数据的方式:
- 第一步现将用户指定的关键进行分词。
- 第二步将词汇去分词库中进行检索,得到多个文档的id。
- 第三步将文档的id存放在一个ES的上下文中。
- 第四步根据你指定的size的个数去ES中检索指定个数的数据,拿完数据的文档id,会从上下文中移除。
- 第五步如果需要下一页数据,直接去ES的上下文中,找后续内容。
- 第六步循环第四步和第五步
# 执行scroll查询,返回第一页数据,并且将文档id信息存放在ES上下文中,指定生存时间1m
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search?scroll=1m
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 2,
"sort": [ # 排序
{
"fee": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
# 根据scroll查询下一页数据
POST /_search/scroll
{
"scroll_id": "<根据第一步得到的scorll_id去指定>",
"scroll": "<scorll信息的生存时间>"
}
# 删除scroll在ES上下文中的数据
DELETE /_search/scroll/scroll_id
代码实现方式
// Java实现scroll分页
@Test
public void scrollQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定scroll信息
request.scroll(TimeValue.timeValueMinutes(1L));
//3. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
builder.size(4);
builder.sort("fee", SortOrder.DESC);
builder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
request.source(builder);
//4. 获取返回结果scrollId,source
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
String scrollId = resp.getScrollId();
System.out.println("----------首页---------");
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
while(true) {
//5. 循环 - 创建SearchScrollRequest
SearchScrollRequest scrollRequest = new SearchScrollRequest(scrollId);
//6. 指定scrollId的生存时间
scrollRequest.scroll(TimeValue.timeValueMinutes(1L));
//7. 执行查询获取返回结果
SearchResponse scrollResp = client.scroll(scrollRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//8. 判断是否查询到了数据,输出
SearchHit[] hits = scrollResp.getHits().getHits();
if(hits != null && hits.length > 0) {
System.out.println("----------下一页---------");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}else{
//9. 判断没有查询到数据-退出循环
System.out.println("----------结束---------");
break;
}
}
//10. 创建CLearScrollRequest
ClearScrollRequest clearScrollRequest = new ClearScrollRequest();
//11. 指定ScrollId
clearScrollRequest.addScrollId(scrollId);
//12. 删除ScrollId
ClearScrollResponse clearScrollResponse = client.clearScroll(clearScrollRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//13. 输出结果
System.out.println("删除scroll:" + clearScrollResponse.isSucceeded());
}
6.5 delete-by-query
根据term,match等查询方式去删除大量的文档
Ps:如果你需要删除的内容,是index下的大部分数据,推荐创建一个全新的index,将保留的文档内容,添加到全新的索引
# delete-by-query
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_delete_by_query
{
"query": {
"range": {
"fee": {
"lt": 4
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现
@Test
public void deleteByQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建DeleteByQueryRequest
DeleteByQueryRequest request = new DeleteByQueryRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定检索的条件 和SearchRequest指定Query的方式不一样
request.setQuery(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("fee").lt(4));
//3. 执行删除
BulkByScrollResponse resp = client.deleteByQuery(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出返回结果
System.out.println(resp.toString());
}
6.6 复合查询
6.6.1 bool查询
复合过滤器,将你的多个查询条件,以一定的逻辑组合在一起。
- must: 所有的条件,用must组合在一起,表示And的意思
- must_not:将must_not中的条件,全部都不能匹配,标识Not的意思
- should:所有的条件,用should组合在一起,表示Or的意思
# 查询省份为武汉或者北京
# 运营商不是联通
# smsContent中包含中国和平安
# bool查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"province": {
"value": "北京"
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"province": {
"value": "武汉"
}
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"term": {
"operatorId": {
"value": "2"
}
}
}
],
"must": [
{
"match": {
"smsContent": "中国"
}
},
{
"match": {
"smsContent": "平安"
}
}
]
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现Bool查询
@Test
public void BoolQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// # 查询省份为武汉或者北京
boolQuery.should(QueryBuilders.termQuery("province","武汉"));
boolQuery.should(QueryBuilders.termQuery("province","北京"));
// # 运营商不是联通
boolQuery.mustNot(QueryBuilders.termQuery("operatorId",2));
// # smsContent中包含中国和平安
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("smsContent","中国"));
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("smsContent","平安"));
builder.query(boolQuery);
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.6.2 boosting查询
boosting查询可以帮助我们去影响查询后的score。
- positive:只有匹配上positive的查询的内容,才会被放到返回的结果集中。
- negative:如果匹配上和positive并且也匹配上了negative,就可以降低这样的文档score。
- negative_boost:指定系数,必须小于1.0
关于查询时,分数是如何计算的:
- 搜索的关键字在文档中出现的频次越高,分数就越高
- 指定的文档内容越短,分数就越高
- 我们在搜索时,指定的关键字也会被分词,这个被分词的内容,被分词库匹配的个数越多,分数越高
# boosting查询 收货安装
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"boosting": {
"positive": {
"match": {
"smsContent": "收货安装"
}
},
"negative": {
"match": {
"smsContent": "王五"
}
},
"negative_boost": 0.5
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java实现Boosting查询
@Test
public void BoostingQuery() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
BoostingQueryBuilder boostingQuery = QueryBuilders.boostingQuery(
QueryBuilders.matchQuery("smsContent", "收货安装"),
QueryBuilders.matchQuery("smsContent", "王五")
).negativeBoost(0.5f);
builder.query(boostingQuery);
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.7 filter查询
query,根据你的查询条件,去计算文档的匹配度得到一个分数,并且根据分数进行排序,不会做缓存的。
filter,根据你的查询条件去查询文档,不去计算分数,而且filter会对经常被过滤的数据进行缓存。
# filter查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"term": {
"corpName": "盒马鲜生"
}
},
{
"range": {
"fee": {
"lte": 4
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java实现filter操作
@Test
public void filter() throws IOException {
//1. SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("corpName","盒马鲜生"));
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("fee").lte(5));
builder.query(boolQuery);
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
6.8 高亮查询【重点】
高亮查询就是你用户输入的关键字,以一定的特殊样式展示给用户,让用户知道为什么这个结果被检索出来。
高亮展示的数据,本身就是文档中的一个Field,单独将Field以highlight的形式返回给你。
ES提供了一个highlight属性,和query同级别的。
- fragment_size:指定高亮数据展示多少个字符回来,默认为100.
- pre_tags:指定前缀标签,举个栗子< font color="red" >
- post_tags:指定后缀标签,举个栗子< /font >
- fields:指定哪几个Field以高亮形式返回
| 效果图 |
|---|
 |
RESTful实现
# highlight查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"smsContent": "盒马"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"smsContent": {}
},
"pre_tags": "<font color='red'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fragment_size": 10
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java实现高亮查询
@Test
public void highLightQuery() throws IOException {
//1. SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定查询条件(高亮)
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//2.1 指定查询条件
builder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("smsContent","盒马"));
//2.2 指定高亮
HighlightBuilder highlightBuilder = new HighlightBuilder();
highlightBuilder.field("smsContent",10)
.preTags("<font color='red'>")
.postTags("</font>");
builder.highlighter(highlightBuilder);
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 获取高亮数据,输出
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getHighlightFields().get("smsContent"));
}
}
6.9 聚合查询【重点】
ES的聚合查询和MySQL的聚合查询类似,ES的聚合查询相比MySQL要强大的多,ES提供的统计数据的方式多种多样。
# ES聚合查询的RESTful语法
POST /index/type/_search
{
"aggs": {
"名字(agg)": {
"agg_type": {
"属性": "值"
}
}
}
}
6.9.1 去重计数查询
去重计数,即Cardinality,第一步先将返回的文档中的一个指定的field进行去重,统计一共有多少条
# 去重计数查询 北京 上海 武汉 山西
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"aggs": {
"agg": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "province"
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java代码实现去重计数查询
@Test
public void cardinality() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定使用的聚合查询方式
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
builder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.cardinality("agg").field("province"));
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 获取返回结果
Cardinality agg = resp.getAggregations().get("agg");
long value = agg.getValue();
System.out.println(value);
}
6.9.2 范围统计
统计一定范围内出现的文档个数,比如,针对某一个Field的值在 0100,100200,200~300之间文档出现的个数分别是多少。
范围统计可以针对普通的数值,针对时间类型,针对ip类型都可以做相应的统计。
range,date_range,ip_range
数值统计
# 数值方式范围统计
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"aggs": {
"agg": {
"range": {
"field": "fee",
"ranges": [
{
"to": 5
},
{
"from": 5, # from有包含当前值的意思
"to": 10
},
{
"from": 10
}
]
}
}
}
}
时间范围统计
# 时间方式范围统计
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"aggs": {
"agg": {
"date_range": {
"field": "createDate",
"format": "yyyy",
"ranges": [
{
"to": 2000
},
{
"from": 2000
}
]
}
}
}
}
ip统计方式
# ip方式 范围统计
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"aggs": {
"agg": {
"ip_range": {
"field": "ipAddr",
"ranges": [
{
"to": "10.126.2.9"
},
{
"from": "10.126.2.9"
}
]
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java实现数值 范围统计
@Test
public void range() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定使用的聚合查询方式
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//---------------------------------------------
builder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.range("agg").field("fee")
.addUnboundedTo(5)
.addRange(5,10)
.addUnboundedFrom(10));
//---------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 获取返回结果
Range agg = resp.getAggregations().get("agg");
for (Range.Bucket bucket : agg.getBuckets()) {
String key = bucket.getKeyAsString();
Object from = bucket.getFrom();
Object to = bucket.getTo();
long docCount = bucket.getDocCount();
System.out.println(String.format("key:%s,from:%s,to:%s,docCount:%s",key,from,to,docCount));
}
}
6.9.3 统计聚合查询
他可以帮你查询指定Field的最大值,最小值,平均值,平方和等
使用:extended_stats
# 统计聚合查询
POST /sms-logs-index/sms-logs-type/_search
{
"aggs": {
"agg": {
"extended_stats": {
"field": "fee"
}
}
}
}
代码实现方式
// Java实现统计聚合查询
@Test
public void extendedStats() throws IOException {
//1. 创建SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定使用的聚合查询方式
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//---------------------------------------------
builder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.extendedStats("agg").field("fee"));
//---------------------------------------------
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 获取返回结果
ExtendedStats agg = resp.getAggregations().get("agg");
double max = agg.getMax();
double min = agg.getMin();
System.out.println("fee的最大值为:" + max + ",最小值为:" + min);
}
其他的聚合查询方式查看官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.5/index.html
6.10 地图经纬度搜索
ES中提供了一个数据类型 geo_point,这个类型就是用来存储经纬度的。
创建一个带geo_point类型的索引,并添加测试数据
# 创建一个索引,指定一个name,locaiton
PUT /map
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 5,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"map": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
}
}
}
}
}
# 添加测试数据
PUT /map/map/1
{
"name": "天安门",
"location": {
"lon": 116.403981,
"lat": 39.914492
}
}
PUT /map/map/2
{
"name": "海淀公园",
"location": {
"lon": 116.302509,
"lat": 39.991152
}
}
PUT /map/map/3
{
"name": "北京动物园",
"location": {
"lon": 116.343184,
"lat": 39.947468
}
}
6.10.1 ES的地图检索方式
| 语法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| geo_distance | 直线距离检索方式 |
| geo_bounding_box | 以两个点确定一个矩形,获取在矩形内的全部数据 |
| geo_polygon | 以多个点,确定一个多边形,获取多边形内的全部数据 |
6.10.2 基于RESTful实现地图检索
geo_distance
# geo_distance
POST /map/map/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_distance": {
"location": { # 确定一个点
"lon": 116.433733,
"lat": 39.908404
},
"distance": 3000, # 确定半径
"distance_type": "arc" # 指定形状为圆形
}
}
}
geo_bounding_box
# geo_bounding_box
POST /map/map/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_bounding_box": {
"location": {
"top_left": { # 左上角的坐标点
"lon": 116.326943,
"lat": 39.95499
},
"bottom_right": { # 右下角的坐标点
"lon": 116.433446,
"lat": 39.908737
}
}
}
}
}
geo_polygon
# geo_polygon
POST /map/map/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_polygon": {
"location": {
"points": [ # 指定多个点确定一个多边形
{
"lon": 116.298916,
"lat": 39.99878
},
{
"lon": 116.29561,
"lat": 39.972576
},
{
"lon": 116.327661,
"lat": 39.984739
}
]
}
}
}
}
6.10.3 Java实现geo_polygon
// 基于Java实现geo_polygon查询
@Test
public void geoPolygon() throws IOException {
//1. SearchRequest
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(index);
request.types(type);
//2. 指定检索方式
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
List<GeoPoint> points = new ArrayList<>();
// geo_polygon
// points.add(new GeoPoint(39.99878,116.298916));
// points.add(new GeoPoint(39.972576,116.29561));
// points.add(new GeoPoint(39.984739,116.327661));
// builder.query(QueryBuilders.geoPolygonQuery("location",points));
// geo_bounding_box
// GeoBoundingBoxQueryBuilder location1 = QueryBuilders.geoBoundingBoxQuery("location");
// location1.topLeft().reset(22.56794,114.040744);
// location1.bottomRight().reset(22.508789,114.057273);
// builder.query(location1);
//distance
GeoDistanceQueryBuilder location = QueryBuilders.geoDistanceQuery("location");
location.point(22.573813,114.05023).distance("2000");
builder.query(location);
request.source(builder);
//3. 执行查询
SearchResponse resp = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//4. 输出结果
for (SearchHit hit : resp.getHits().getHits()) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsMap());
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号