LeetCode高频算法面试题 - 002 - 两数相加
大家好,我是漫步coding, 最近在整理2022年LeetCode高频算法面试题 ,感觉好的, 可以点赞、收藏哈。同时有补充的也欢迎大家给出反馈。本文首发于公众号: 漫步coding
题目来源于 LeetCode 上第 2 号问题:两数相加。题目难度为 Medium,目前通过率为 33.9% 。
题目描述
给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
题目难度: ★★
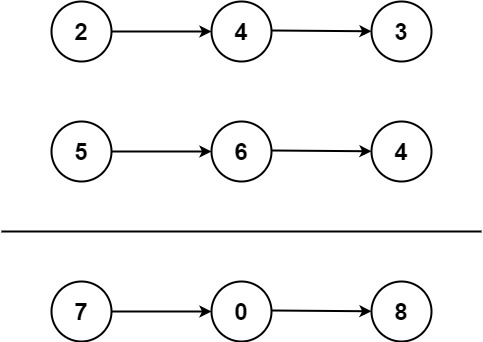
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
每个链表中的节点数在范围 [1, 100] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 9
题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
题目解析
设立一个表示进位的变量carried,建立一个新链表,把输入的两个链表从头往后同时处理,每两个相加,将结果加上carried后的值作为一个新节点到新链表后面。
代码实现
tips: 以下代码是使用Go代码实现的不同解法, 文章最后可以看C++、C、Java、Python实现
1、循环遍历, 进行求和
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
var carry int
resultList := &ListNode{}
current := resultList
for{
if l1 == nil && l2 == nil && carry == 0{
break
}
if l1 != nil{
carry += (*l1).Val
l1 = l1.Next
}
if l2 != nil{
carry += (*l2).Val
l2 = l2.Next
}
node := ListNode{}
if carry <= 9{
node = ListNode{
Val: carry,
}
carry = 0
}else{
node = ListNode{
Val: carry - 10,
}
carry = 1
}
current.Next = &node
current = &node
}
return resultList.Next
}
执行结果

2、改进方法, 如果l1、l2长度差别很大, 就可以直接利用偏长链表后面的部分, 避免重复new Node节点。
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
var carry int
resultList := &ListNode{}
current := resultList
for{
node := ListNode{}
if l1 == nil && l2 == nil && carry == 0{
break
}
if l1 != nil{
if l2 == nil && carry == 0{
current.Next = l1
break
}else{
carry += (*l1).Val
l1 = l1.Next
}
}
if l2 != nil{
if l1 == nil && carry == 0{
current.Next = l2
break
}else{
carry += (*l2).Val
l2 = l2.Next
}
}
if carry <= 9{
node = ListNode{
Val: carry,
}
carry = 0
}else{
node = ListNode{
Val: carry - 10,
}
carry = 1
}
current.Next = &node
current = &node
}
return resultList.Next
}
执行结果

3、方法三利用递归方法对两个array进行求和, 这里就不展开细讲了
其他语言版本
C++
/// 时间复杂度: O(n)
/// 空间复杂度: O(n)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *p1 = l1, *p2 = l2;
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
int carried = 0;
while(p1 || p2 ){
int a = p1 ? p1->val : 0;
int b = p2 ? p2->val : 0;
cur->next = new ListNode((a + b + carried) % 10);
carried = (a + b + carried) / 10;
cur = cur->next;
p1 = p1 ? p1->next : NULL;
p2 = p2 ? p2->next : NULL;
}
cur->next = carried ? new ListNode(1) : NULL;
ListNode* ret = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return ret;
}
};
执行结果

Java
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
int carry = 0;
while(l1 != null || l2 != null)
{
int sum = carry;
if(l1 != null)
{
sum += l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if(l2 != null)
{
sum += l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
}
// 创建新节点
carry = sum / 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
cur = cur.next;
}
if (carry > 0) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
执行结果

Python
class Solution(object):
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
res=ListNode(0)
head=res
carry=0
while l1 or l2 or carry!=0:
sum=carry
if l1:
sum+=l1.val
l1=l1.next
if l2:
sum+=l2.val
l2=l2.next
# set value
if sum<=9:
res.val=sum
carry=0
else:
res.val=sum%10
carry=sum//10
# creat new node
if l1 or l2 or carry!=0:
res.next=ListNode(0)
res=res.next
return head
执行结果

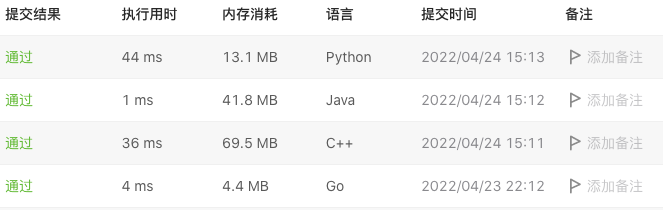
几种语言运行效果对比
也欢迎关注我的公众号: 漫步coding。 一起交流, 在coding的世界里漫步。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号