我带着小程序和Springboot终于战胜了WebSocket!!!胜利( •̀ ω •́ )y
WebSocket项目笔记
1. What is WebSocket?
(以下内容来源于百度百科)
- WebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通信的协议
- WebSocket使得客户端和服务器之间的数据交换变得更加简单,允许服务端主动向客户端推送数据。
- 在WebSocket API中,浏览器和服务器只需要完成一次握手,两者之间就直接可以创建持久性的连接,并进行双向数据传输。
- 背景:
- 推送技术的演进发展:轮询 ---> Comet ---> WebSocket
-
握手协议:
2. Let's try!
因为项目要求,我的小程序需要与后端服务器进行长连接,以传送数据。所以我需要在我配置好的Springboot框架中添加WebSocket。十分庆幸的是,Springboot已经集成好了WebSocket了。所以过程并不复杂。看了很多博客,内容都大同小异。
我有点懵,因为我发现大家都在说的是,客户端与服务器建立连接的过程的实现。所以有几个问题:
- 既然是服务器主动发送消息,那么服务器到底 “到底什么时候发送消息呢?怎么发送?”
- 如何传参数,传的参数如何接收与使用。
- 我只需要针对某个客户端发消息,在同时有多个socket连接的时候我怎么标识该客户端?
大概就有这些。下面我们在配置过程中将问题逐个击破!
- 开发环境:Springboot 1.5.19 Java1.8
- 配置pom文件
<!-- 引入 websocket 依赖类-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 配置Springboot开启WebSocket支持
package com.cuc.happyseat.config.websocket; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter; /** * 开启WebSocket支持 */ @Configuration public class WebSocketConfig { @Bean public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() { return new ServerEndpointExporter(); } }
- WebSocket服务类编写
这里对照下面的代码看:
- 第20行,@ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{userID}"),括号中的内容就是客户端请求Socket连接时的访问路径,userID是我要求客户端传来的参数,我这里算是为了标识该客户端吧。
- 第28行,在该类中添加属性 userID,并添加对应的getUserID()方法。
- 第46行,在onOpen()方法即建立连接的时候就接收参数userID,需要标识@PathParam("userID") 。接收参数后直接赋值给属性userID。
- 第140-157行,是针对特定客户端发送消息。服务器和客户端在建立连接成功后就生成了一个WebSocket对象,并存在集合中,对象里特有的属性是我们设置的userID。所以通过唯一的userID就能标识服务器与该客户端建立的那个连接啦!这样要求发送消息时,传入userID与消息,服务器在自己的WebSocket连接集合中遍历找到对应客户端的连接,就可以直接发消息过去啦~~
1 package com.cuc.happyseat.websocket; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet; 5 6 import javax.websocket.EncodeException; 7 import javax.websocket.OnClose; 8 import javax.websocket.OnError; 9 import javax.websocket.OnMessage; 10 import javax.websocket.OnOpen; 11 import javax.websocket.Session; 12 import javax.websocket.server.PathParam; 13 import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint; 14 15 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 16 17 /*@ServerEndpoint注解是一个类层次的注解,它的功能主要是将目前的类定义成一个websocket服务器端, 18 * 注解的值将被用于监听用户连接的终端访问URL地址,客户端可以通过这个URL来连接到WebSocket服务器端 19 */ 20 @ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{userID}") 21 @Component 22 public class WebSocketServer { 23 24 //每个客户端都会有相应的session,服务端可以发送相关消息 25 private Session session; 26 27 //接收userID 28 private Integer userID; 29 30 //J.U.C包下线程安全的类,主要用来存放每个客户端对应的webSocket连接 31 private static CopyOnWriteArraySet<WebSocketServer> copyOnWriteArraySet = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<WebSocketServer>(); 32 33 public Integer getUserID() { 34 return userID; 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * @Name:onOpen 39 * @Description:打开连接。进入页面后会自动发请求到此进行连接 40 * @Author:mYunYu 41 * @Create Date:14:46 2018/11/15 42 * @Parameters:@PathParam("userID") Integer userID 43 * @Return: 44 */ 45 @OnOpen 46 public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam("userID") Integer userID) { 47 this.session = session; 48 this.userID = userID; 49 System.out.println(this.session.getId()); 50 //System.out.println("userID:" + userID); 51 copyOnWriteArraySet.add(this); 52 System.out.println("websocket有新的连接, 总数:"+ copyOnWriteArraySet.size()); 53 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * @Name:onClose 58 * @Description:用户关闭页面,即关闭连接 59 * @Author:mYunYu 60 * @Create Date:14:46 2018/11/15 61 * @Parameters: 62 * @Return: 63 */ 64 @OnClose 65 public void onClose() { 66 copyOnWriteArraySet.remove(this); 67 System.out.println("websocket连接断开, 总数:"+ copyOnWriteArraySet.size()); 68 } 69 70 /** 71 * @Name:onMessage 72 * @Description:测试客户端发送消息,测试是否联通 73 * @Author:mYunYu 74 * @Create Date:14:46 2018/11/15 75 * @Parameters: 76 * @Return: 77 */ 78 @OnMessage 79 public void onMessage(String message) { 80 System.out.println("websocket收到客户端发来的消息:"+message); 81 } 82 83 /** 84 * @Name:onError 85 * @Description:出现错误 86 * @Author:mYunYu 87 * @Create Date:14:46 2018/11/15 88 * @Parameters: 89 * @Return: 90 */ 91 @OnError 92 public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) { 93 System.out.println("发生错误:" + error.getMessage() + "; sessionId:" + session.getId()); 94 error.printStackTrace(); 95 } 96 97 public void sendMessage(Object object){ 98 //遍历客户端 99 for (WebSocketServer webSocket : copyOnWriteArraySet) { 100 System.out.println("websocket广播消息:" + object.toString()); 101 try { 102 //服务器主动推送 103 webSocket.session.getBasicRemote().sendObject(object) ; 104 } catch (Exception e) { 105 e.printStackTrace(); 106 } 107 } 108 } 109 110 /** 111 * @Name:sendMessage 112 * @Description:用于发送给客户端消息(群发) 113 * @Author:mYunYu 114 * @Create Date:14:46 2018/11/15 115 * @Parameters: 116 * @Return: 117 */ 118 public void sendMessage(String message) { 119 //遍历客户端 120 for (WebSocketServer webSocket : copyOnWriteArraySet) { 121 System.out.println("websocket广播消息:" + message); 122 try { 123 //服务器主动推送 124 webSocket.session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message); 125 } catch (Exception e) { 126 e.printStackTrace(); 127 } 128 } 129 } 130 131 /** 132 * @throws Exception 133 * @Name:sendMessage 134 * @Description:用于发送给指定客户端消息 135 * @Author:mYunYu 136 * @Create Date:14:47 2018/11/15 137 * @Parameters: 138 * @Return: 139 */ 140 public void sendMessage(Integer userID, String message) throws Exception { 141 Session session = null; 142 WebSocketServer tempWebSocket = null; 143 for (WebSocketServer webSocket : copyOnWriteArraySet) { 144 if (webSocket.getUserID() == userID) { 145 tempWebSocket = webSocket; 146 session = webSocket.session; 147 break; 148 } 149 } 150 if (session != null) { 151 //服务器主动推送 152 tempWebSocket.session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message); 153 154 } else { 155 System.out.println("没有找到你指定ID的会话:{}"+ "; userId:" + userID); 156 } 157 } 158 159 160 161 }
- Controller类的编写。
- 我在看博客的时候,发现有的博主写了Controller类,有的没写,我就有点疑惑了。后来,咳咳,发现特地写了一个Controller类只是为了测试。。
- 一般在实际项目中,在确保建立连接过程没有问题的情况下,我们就直接在一些写好的接口中写 WebSocketServer.sendMessage(param, message)语句就行了。
- 也因此,你写的位置就决定了你什么时候给你的客户端发消息,这样也就实现了主动推送消息的功能咯~
- 前提是:在你的Controller类里,以@Resource的方式注入WebSocket,而不是@Autowired方式哦(⊙o⊙)。
@Resource
WebSocketServer webSocket;
@Autowired
UserService userService;
调用示例:
if(userID>0) { boolean location = userService.getLocation(userID); if(location==false) {//验证用户当前不在馆内 boolean i = userService.modifyLocation(userID, true); if(i==true) { modelMap.put("successEnter", true); //发消息给客户端 webSocket.sendMessage(userID, "success"); } }else { modelMap.put("successEnter", false); //发消息给客户端 webSocket.sendMessage(userID, "fail"); } }else { modelMap.put("successEnter", false); //发消息给客户端 webSocket.sendMessage(userID, "fail"); }
- 前端测试
因为我只写后端,前端部分小姐姐说看微信的官方文档就可以啦~ 链接:在此!微信封装好了吧,好像不难。
3. Problems
- 前期我看很多博客,的确产生很多问题,想不通,主要就是上面几个问题。然后我写了让前端先连WebSocket试了一下,想自己了解一下连接过程(也就是在控制台输出的文件中查),后来就慢慢通了。可以说是一帆风顺了??
- 不过我确保我没问题不算,得前端说了算对吧。所以,,我背了锅😭。
- 第一次,她给我截图!啊喂你连WebSocket给我用https?嗯?
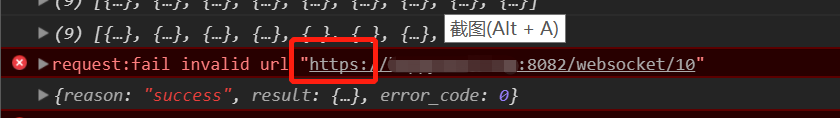
- 后来换成了ws,又说不行,我就想我哪又有问题了?然后我刚好在我打开的n篇相似的博客中找到了答案。因为小程序是只支持https访问的,所以得用wss。(感谢博主!)
- 第一次,她给我截图!啊喂你连WebSocket给我用https?嗯?

3. 然后终于传来了喜讯!开心~
前端连接成功:

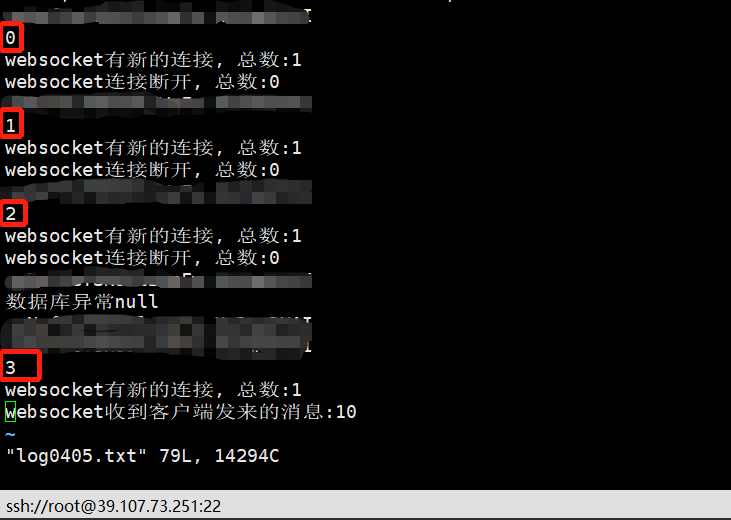
后端输出记录:
ps:红框的1,2,3,4应该是每次连接时自增长的sessionid,即上面截图中返回的socketTaskId,话说用这个来标识用户应该也可以。
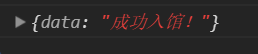
服务器主动给该客户端发消息,成功发送!
4. Summary
前期对WebSocket的知识了解估计还不够吧,导致在理解问题的过程中花费了不少时间。
不过是不是程序员都会有这种错觉呢?:当你面前有一座大山,你觉得难以跨越,但当你成功翻山越岭之后,就会觉得这座山不过尔尔?
嘿嘿嘿,下面是学习WebSocket过程中参考的几篇博文:




