Java8 使用 stream().sorted()对List集合进行排序
集合对像定义
集合对象以学生类(StudentInfo)为例,有学生的基本信息,包括:姓名,性别,年龄,身高,生日几项。
使用stream().sorted()进行排序,需要该类实现 Comparable 接口,该接口只有一个方法需要实现,如下:
public int compareTo(T o);
有关compareTo方法的实现说明,请参考:Java 关于重写compareTo方法
我的学生类代码如下:

import java.time.LocalDate; import java.util.List; public class StudentInfo implements Comparable<StudentInfo> { //名称 private String name; //性别 true男 false女 private Boolean gender; //年龄 private Integer age; //身高 private Double height; //出生日期 private LocalDate birthday; public StudentInfo(String name, Boolean gender, Integer age, Double height, LocalDate birthday){ this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.age = age; this.height = height; this.birthday = birthday; } public String toString(){ String info = String.format("%s\t\t%s\t\t%s\t\t\t%s\t\t%s",this.name,this.gender.toString(),this.age.toString(),this.height.toString(),birthday.toString()); return info; } public static void printStudents(List<StudentInfo> studentInfos){ System.out.println("[姓名]\t\t[性别]\t\t[年龄]\t\t[身高]\t\t[生日]"); System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------"); studentInfos.forEach(s->System.out.println(s.toString())); System.out.println(" "); } @Override public int compareTo(StudentInfo ob) { return this.age.compareTo(ob.getAge()); //return 1; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Boolean getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Boolean gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(Double height) { this.height = height; } public LocalDate getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(LocalDate birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } }
添加测试数据
下面来添加一些测试用的数据,代码如下:
//测试数据,请不要纠结数据的严谨性 List<StudentInfo> studentList = new ArrayList<>(); studentList.add(new StudentInfo("李小明",true,18,1.76,LocalDate.of(2001,3,23))); studentList.add(new StudentInfo("张小丽",false,18,1.61,LocalDate.of(2001,6,3))); studentList.add(new StudentInfo("王大朋",true,19,1.82,LocalDate.of(2000,3,11))); studentList.add(new StudentInfo("陈小跑",false,17,1.67,LocalDate.of(2002,10,18)));
排序
使用年龄进行升序排序
//排序前输出 StudentInfo.printStudents(studentList); //按年龄排序(Integer类型) List<StudentInfo> studentsSortName = studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(StudentInfo::getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList()); //排序后输出 StudentInfo.printStudents(studentsSortName);
结果如下图:
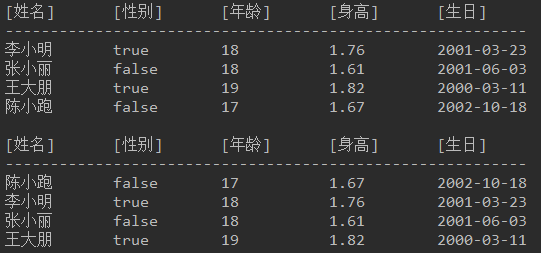
使用年龄进行降序排序(使用reversed()方法)
//排序前输出 StudentInfo.printStudents(studentList); //按年龄排序(Integer类型) List<StudentInfo> studentsSortName = studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(StudentInfo::getAge).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList()); //排序后输出 StudentInfo.printStudents(studentsSortName);
结果如下图:
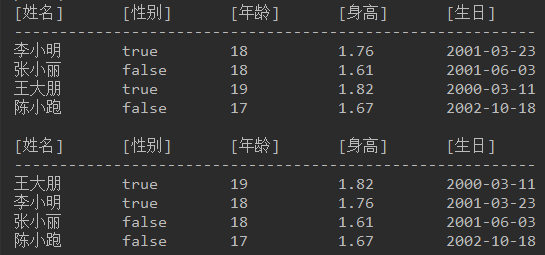
使用年龄进行降序排序,年龄相同再使用身高升序排序
//排序前输出 StudentInfo.printStudents(studentList); //按年龄排序(Integer类型) List<StudentInfo> studentsSortName = studentList.stream() .sorted(Comparator.comparing(StudentInfo::getAge).reversed().thenComparing(StudentInfo::getHeight)) .collect(Collectors.toList()); //排序后输出 StudentInfo.printStudents(studentsSortName);
结果如下图:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号