Mybatis动态SQL
<if>:判断语句,用于单条件分支判断
<choose>(<when>、<otherwise>):相当于 Java 中的 switch...case...default语句,应用于多条件分支判断
<where>、<trim>、<set>:辅助元素,用于处理一些 SQL 拼装、特殊字符问题
<foreach>:循环语句,常用语 in 语句等列举条件中
<bind>:从 OGNL 表达式中创建一个变量,并将其绑定到上下文,常用于模糊查询 的sql中
if标签
<if>标签,如果test中的条件成立,则执行<if>标签中的语句,用于单条件分支判断
<select id="findUserByIf" parameterType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User" resultType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
select * from user
where 1 = 1
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
and username like concat('%',#{username},'%')
</if>
<if test="job!=null and job!=''">
and job = #{job}
</if>
</select>
测试传入user对象
@Test
public void test1(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("chenyu");
user.setJob("程序猿1");
List<User> users = userMapper.findUserByIf(user);
System.out.println(users);
}
sql语句拼接及结果如下
Preparing: select * from user where 1 = 1 and username like concat('%',?,'%') and job = ?
Parameters: chenyu(String), 程序猿1(String)
[User{id=1, username='chenyu', job='程序猿1'}]
只传入user对象的username
sql语句拼接及结果如下
Preparing: select * from user where 1 = 1 and username like concat('%',?,'%')
Parameters: chenyu(String)
[User{id=1, username='chenyu', job='程序猿1'}]
不传入user对象
sql语句拼接及结果如下
Preparing: select * from user where 1 = 1
Parameters:
[User{id=1, username='chenyu', job='程序猿1'}, User{id=2, username='cy', job='程序猿2'}]
choose标签
<choose>标签,按顺序判断<when>中test的条件是否成立,如果有一个成立,则结束判断,如果 所有<when>中test的条件都不成立,则执行<otherwise>中的语句,用于多条件分支判断
<select id="findUserByChoose" parameterType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User" resultType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
select * from user
where 1 = 1
<choose>
<when test="username!=null and username!=''">
and username like concat('%',#{username},'%')
</when>
<when test="job!=null and job!=''">
and job = #{job}
</when>
<otherwise>
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
测试传入user对象
@Test
public void test2(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("chenyu");
user.setJob("程序猿1");
List<User> users = userMapper.findUserByChoose(user);
System.out.println(users);
}
sql语句拼接及结果如下
Preparing: select * from user where 1 = 1 and username like concat('%',?,'%')
Parameters: chenyu(String)
[User{id=1, username='chenyu', job='程序猿1'}]
where标签
<where>标签,上面使用<if>或者<choose>标签时,都需要加上where 1=1用来防止后面判断的条件不成立时sql语句报错,使用<where>标签,如果条件成立则加上where,如果条件不成立则去掉where
<select id="findUserByWhere" parameterType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User" resultType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
and username like concat('%',#{username},'%')
</if>
<if test="job!=null and job!=''">
and job = #{job}
</if>
</where>
</select>
测试传入user对象
@Test
public void test3(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("chenyu");
user.setJob("程序猿1");
List<User> users = userMapper.findUserByWhere(user);
System.out.println(users);
}
sql语句拼接及结果如下
Preparing: select * from user WHERE username like concat('%',?,'%') and job = ?
Parameters: chenyu(String), 程序猿1(String)
[User{id=1, username='chenyu', job='程序猿1'}]
此时加上了where
不传入user对象
sql语句拼接及结果如下
Preparing: select * from user
Parameters:
[User{id=1, username='chenyu', job='程序猿1'}, User{id=2, username='cy', job='程序猿2'}]
此时去掉了where
trim标签
<trim>标签同样可以实现<where>标签的功能,但是更加灵活,可以设置前缀和后缀以及覆盖
<select id="findUserByTrim" parameterType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User" resultType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
select * from user
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and"><!--prefixOverrides="and"覆盖username前的and-->
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
and username like concat('%',#{username},'%')
</if>
<if test="job!=null and job!=''">
and job = #{job}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
prefixOverrides还可以设置多个,如
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and|or">
set标签
<set>标签一般用于update,防止当传入对象的某个值为空时,对应表的值也被修改为空
根据id更新user
<update id="updateUserBySet" parameterType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
update user set username=#{username},job=#{job} where id=#{id}
</update>
如果不传入user的job
@Test
public void test5(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("chenyu11");
user.setId(1);
int count = userMapper.updateUserBySet(user);
System.out.println(count);
}
运行后查看表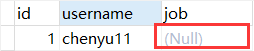 ,job变为null
,job变为null
使用<set>标签
<update id="updateUserBySet" parameterType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
update user
<set>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
username=#{username},
</if>
<if test="job!=null and job!=''">
job=#{job},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
重新运行后查看表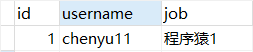 ,job没有变为null
,job没有变为null
也可以使用<trim>标签来实现<set>标签的功能
<update id="updateUserByTrim" parameterType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
update user
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","><!--后缀覆盖-->
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
username=#{username},
</if>
<if test="job!=null and job!=''">
job=#{job},
</if>
</trim>
where id=#{id}
</update>
foreach标签
<foreach>标签有遍历的功能,可以用来进行批量操作
<select id="findUserByIdsForeach" parameterType="list"
resultType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
select * from user
where id in
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
其中属性:
- collection:传入的集合,可以填collection或者list
- item:每一项的名称
- open:以什么开始
- close:以什么结束
- separator:分隔符
测试传入一个id集合
@Test
public void test7(){
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
List<User> users = userMapper.findUserByIdsForeach(ids);
System.out.println(users);
}
sql语句拼接及结果如下
Preparing: select * from user where id in ( ? , ? )
Parameters: 1(Integer), 2(Integer)
[User{id=1, username='chenyu111', job='程序猿111'}, User{id=2, username='cy', job='程序猿2'}]
如果传入的id集合为空,则需要配合<where>和<if>标签使用
<select id="findUserByIdsForeach" parameterType="list"
resultType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="list!=null and list.size()>0">
id in
<foreach collection="collection" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
批量插入
<insert id="insertUserByUserListForeach" parameterType="list">
insert into user(username,job) values
<foreach collection="list" item="user" separator=",">
(#{user.username},#{user.job})
</foreach>
</insert>
测试运行
@Test
public void test8(){
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new User("cheny","程序猿2"));
userList.add(new User("cyu","程序猿3"));
int count = userMapper.insertUserByUserListForeach(userList);
System.out.println(count);
}
查看表 ,多了两条数据
,多了两条数据
批量删除
<delete id="deleteUserByIdsForeach" parameterType="list">
delete from user where id in
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>
测试运行
@Test
public void test9(){
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
ids.add(3);
int count = userMapper.deleteUserByIdsForeach(ids);
System.out.println(count);
}
bind标签
使用 bind 拼接字符串不仅可以避免因更换数据库而修改 SQL,也能预防 SQL 注入
例如查询时进行模糊查询,Mysql使用concat拼接,而Oracle使用||拼接,如果更换数据库,则sql要重写,而bind是通用的
<select id="findUserByBind" parameterType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User"
resultType="com.chenpeng.mybatismt.bean.User">
<bind name="usernamePattern" value="'%',#{username},'%'"/>
select * from user
where 1 = 1
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
and username like #{usernamePattern}
</if>
<if test="job!=null and job!=''">
and job = #{job}
</if>
</select>
测试运行
@Test
public void test10(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("cyu");
user.setJob("程序猿3");
List<User> users = userMapper.findUserByBind(user);
System.out.println(users);
}
sql语句拼接及结果如下
Preparing: select * from user where 1 = 1 and username like ? and job = ?
Parameters: %(String), 程序猿3(String)
[User{id=4, username='cyu', job='程序猿3'}]


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号