智能指针
智能指针
在C++中管理动态内存可以使用new和delete,但通过这种方式得到的指针(裸指针)是容易忘记释放的进而导致内存泄漏。因此C++标准中提供了智能指针shared_ptr,weak_ptr和unique_ptr来进行动态内存的管理。智能指针的设计满足了RAII(Resource Acquisition Is Initialization)的特性,即资源获取即初始化,这使得程序猿能够节省更多找内存泄漏的时间去实现需要的功能。
在这些智能指针中shared_ptr和weak_ptr是一起用于管理shared_ptr智能指针对象的,而unique_ptr智能指针是单独管理动态内存的。
智能指针头文件
这几个智能指针模板类的头文件都是memory
shared_ptr
shared_ptr是共享型智能指针,其内部有引用计数器,这使得多个shared_ptr对象能指向同一个对象并且仅当引用计数为0时释放对象的内存。
shared_ptr初始化
- 使用new初始化
shared_ptr<int> test1(new int(100))
- 使用更安全的函数模板make_shared
(params) 来初始化
shared_ptr<int> test2 = make_shared<int>(100);
shared_ptr常用操作
成员函数
[shared_ptr<T> object]------------[use_count()]查看引用计数
| |-----[unique()]查看智能指针是否独占某个指向的对象
| |-----[reset()/reset(param)]置空或指向其他对象
| |-----[*]*运算符重载,用于模拟指针相关的操作
| -----[get()]获取裸指针
| 删除器
-----------shared<T>(new T, deleter)初始化shared_ptr指定删除器,当引用计数为0后调用删除器函数
use_count()成员函数
查看引用计数,使用use_count()成员函数,这个函数主要用于调试目的,效率可能不高。当使用shared_ptr进行拷贝构造,拷贝赋值运算符处理后,引用计数都会+1。
举例:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<int> test1 = make_shared<int>(100);
cout << "初始化shared_ptr,引用计数为:" << test1.use_count() << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<int> test2 = test1;
cout << "使用拷贝构造,引用计数为:" << test1.use_count() << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<int> test3;
test3 = test1;
cout << "使用拷贝赋值运算符,引用计数为:" << test1.use_count() << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
-------------------------
初始化shared_ptr,引用计数为:1
-------------------------
使用拷贝构造,引用计数为:2
-------------------------
使用拷贝赋值运算符,引用计数为:3
-------------------------
unique()成员函数
这个函数是查看shared_ptr对象是否独占某个对象,如果是则返回true,否则返回false。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<int> test1 = make_shared<int>(100);
if (test1.unique() == true)
{
cout << "test1 is unique" << endl;
}
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
-------------------------
test1 is unique
-------------------------
reset()与reset(param)成员函数
reset成员函数有两个重载,分别是带参重载和不带参数重载。带参重载的reset使智能指针指向新的对象,并使得原先对象的引用计数-1;不带参数的reset使原先指向对象的引用计数-1,并将智能指针对象置空。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<int> test1 = make_shared<int>(100);
test1.reset();
if (test1 == nullptr)
{
cout << "智能指针test1置空" << endl;
}
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
test1.reset(new int(200));
if (test1 != nullptr)
{
cout << "智能指针test1通过reset(param)成员函数指向新的对象" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
智能指针test1置空
-------------------------
智能指针test1通过reset(param)成员函数指向新的对象
*解引用
*是被重载的运算符,通过使用它可以对指针解引用。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<int> test1 = make_shared<int>(100);
cout << "*解引用: " << *test1 << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
*解引用: 100
-------------------------
get()成员函数
get()成员函数返回保护的裸指针,在获取到这个裸指针后不要用它去初始化新的shared_ptr对象,因为初始化新的智能指针后,引用计数器变为多个,当多个引用计数器=0时会释放多次内存导致程序出错。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <typeinfo>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<int> test1 = make_shared<int>(100);
cout << "test1的类型: " << typeid(test1).name() << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
auto ptr = test1.get();
cout << "ptr1的类型: " << typeid(ptr).name() << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
test1的类型: class std::shared_ptr<int>
-------------------------
ptr1的类型: int *
swap()成员函数
swap()用于交换两个智能指针指向的对象。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<string> ptr1 = make_shared<string>("shared_ptr1");
shared_ptr<string> ptr2 = make_shared<string>("shared_ptr2");
ptr1.swap(ptr2);
cout << "*ptr1: " << *ptr1 << endl;
cout << "*ptr2: " << *ptr2 << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
*ptr1: shared_ptr2
*ptr2: shared_ptr1
-------------------------
删除器
shared_ptr删除器就是使用程序猿自己写的删除器函数或者lambda表达式在智能指针对象引用计数为0时调用。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
/*
* @brief 删除器函数
*/
void deleter(int* p)
{
cout << "调用删除器函数" << endl;
delete p;
}
int main()
{
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<int> ptr(new int(100), deleter);
//引用计数=0,调用删除器
ptr.reset();
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
ptr = shared_ptr<int>(new int(200), [](int* p)
{
cout << "lambda表达式删除器" << endl;
delete p;
});
//引用计数=0,调用删除器
ptr.reset();
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
调用删除器函数
-------------------------
lambda表达式删除器
-------------------------
注意事项
当使用shared_ptr来管理数组对象时要写删除器,因为shared_ptr默认的删除器不会释放数组对象。当遇到这种情况时有三种方式能正常释放内存
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
//方法1.用lambda表达式或者删除器函数来处理
shared_ptr<int> ptr1(new int[10], [](int* p)
{
cout << "释放int数组的内存" << endl;
delete[]p;
});
//引用计数=0
ptr1.reset();
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
//方法2.调用标准库的default_delete
shared_ptr<int> ptr2(new int[10], default_delete<int[]>());
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
//方法3.在尖括号中也加上[],这样使用默认删除器也能正常释放内存
shared_ptr<int[]> ptr3(new int[10]);
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
释放int数组的内存
-------------------------
-------------------------
weak_ptr
weak_ptr是用来辅助shared_ptr工作的,weak_ptr通常用于绑定shared_ptr指向的对象并获取强引用计数及初始化新的shared_ptr对象。
weak_ptr初始化
初始化weak_ptr对象有两种方式,一种是用shared_ptr对象初始化,另一种是用另一个weak_ptr对象初始化 。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
shared_ptr<int> s_ptr = make_shared<int>(100);
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
weak_ptr<int> w_ptr1(s_ptr);
cout << "使用shared_ptr对象初始化的weak_ptr: " << *(w_ptr1.lock()) << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
weak_ptr<int> w_ptr2(w_ptr1);
cout << "使用weak_ptr初始化的weak_ptr: " << *(w_ptr2.lock()) << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
使用shared_ptr对象初始化的weak_ptr: 100
-------------------------
使用weak_ptr初始化的weak_ptr: 100
weak_ptr常用操作
常用函数
[weak_ptr]------------------[use_count()] 强引用计数
|-------[expired()] 判断强引用计数是否为0
|-------[reset()] 重置weak_ptr对象,原对象弱引用计数-1
-------[lock()] 获取监视的shared_ptr,用于初始化shared_ptr对象
use_count()成员函数
weak_ptr中的use_count()成员函数的功能和shared_ptr中的同名函数一样,都是用于获取shared_ptr的引用计数。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
shared_ptr<int> s_ptr = make_shared<int>(100);
shared_ptr<int> s_ptr2 = s_ptr;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
weak_ptr<int> w_ptr(s_ptr);
cout << "当前shared_ptr中的引用计数为: " << s_ptr.use_count() << endl;
cout << "当前weak_ptr中的引用计数为: " << w_ptr.use_count() << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
当前shared_ptr中的引用计数为: 2
当前weak_ptr中的引用计数为: 2
-------------------------
expired()成员函数
weak_ptr对象是用于监视shared_ptr对象的,weak_ptr中的expired用于判断监视的shared_ptr对象中的引用计数是否为0,如果计数=0则返回true,反之返回false。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
shared_ptr<int> s_ptr = make_shared<int>(100);
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
weak_ptr<int> w_ptr(s_ptr);
if (!w_ptr.expired())
{
cout << "此时shared_ptr引用计数不等于0" << endl;
}
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
s_ptr.reset();
if (w_ptr.expired())
{
cout << "此时shared_ptr引用计数为0" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
此时shared_ptr引用计数不等于0
-------------------------
此时shared_ptr引用计数为0
reset()成员函数
reset()成员函数用于将weak_ptr对象置空,不影响指向之前对象的强引用数量,但弱引用数量会减1。
lock()成员函数
lock()成员函数用于获取监视的shared_ptr智能指针,可以用lock()函数来初始化新的shared_ptr对象。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
shared_ptr<int> s_ptr = make_shared<int>(100);
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
weak_ptr<int> w_ptr(s_ptr);
shared_ptr<int> s_ptr2 = w_ptr.lock();
cout << "通过weak_ptr获取的shared_ptr对象解引用的结果为: " << *s_ptr << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
通过weak_ptr获取的shared_ptr对象解引用的结果为: 100
-------------------------
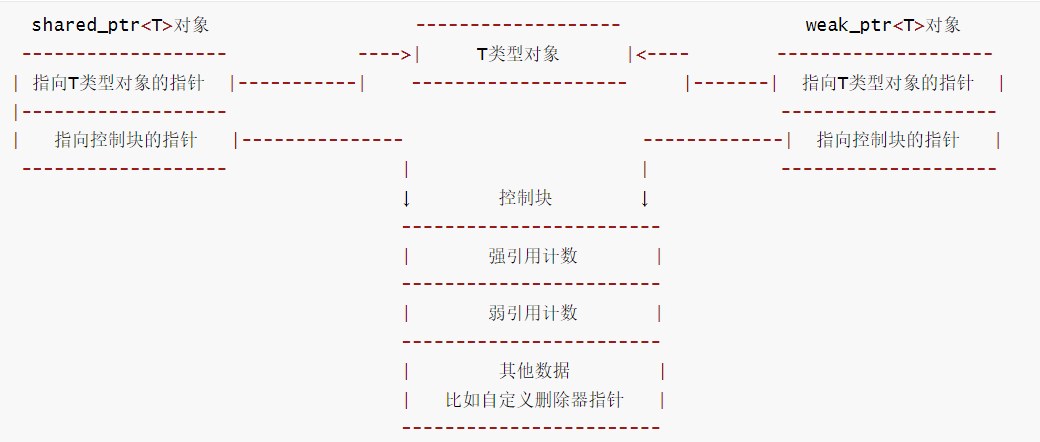
shared_ptr和weak_ptr的内部细节
当使用创建了shared_ptr
使用shared_ptr和weak_ptr的注意事项
在成员函数中要用shared_from_this()函数来返回this指针
这一部分我建议大家先看错误案例分析及如何解决后再去记使用方法。
enable_shared_from_this及shared_from_this()用法
//头文件memory
#include <memory>
class object: public std::enable_shared_from_this<object>
{
shared_ptr<object> getself()
{
return shared_from_this();
}
};
错误案例及分析
//成员函数返回this的错误做法
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class test
{
public:
shared_ptr<test> getThis()
{
return shared_ptr<test>(this);
}
};
int main()
{
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<test> s_ptr = make_shared<test>();
shared_ptr<test> s_ptr2 = s_ptr->getThis();
cout << "s_ptr的引用计数为:" << s_ptr.use_count() << endl;
cout << "s_ptr2的引用计数为:" << s_ptr2.use_count() << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
s_ptr的引用计数为:1
s_ptr2的引用计数为:1
-------------------------
17行创建了智能指针对象s_ptr,而在18行创建s_ptr2时问题出现了。this指针是裸指针,这就导致在使用getThis()时创建了另一个新的引用计数的shared_ptr对象,这就使s_ptr和s_ptr2对象的引用计数不是同一个,最终导致在销毁s_ptr和s_ptr2时会导致释放两次内存报错。
如何解决这个错误?
在C++标准库中提供了一种类模板enable_shared_from_this
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class test : public enable_shared_from_this<test>
{
public:
shared_ptr<test> getThis()
{
return shared_from_this();
}
};
int main()
{
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
shared_ptr<test> s_ptr = make_shared<test>();
shared_ptr<test> s_ptr2 = s_ptr->getThis();
cout << "s_ptr的引用计数为:" << s_ptr.use_count() << endl;
cout << "s_ptr2的引用计数为:" << s_ptr2.use_count() << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
s_ptr的引用计数为:2
s_ptr2的引用计数为:2
-------------------------
避免循环引用
当我们在多个类中使用shared_ptr来获取其他类的资源时可能会造成循环引用使得内存泄漏,循环引用案例如下
错误案例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class B;
class A
{
public:
shared_ptr<B> b;
~A() { cout << "A的析构函数" << endl; }
};
class B
{
public:
shared_ptr<A> a;
~B() { cout << "B的析构函数" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
{
cout << "作用域内进行a和b对象的创建,并让内部的成员变量指向其他对象" << endl;
shared_ptr<A> a = make_shared<A>();
shared_ptr<B> b = make_shared<B>();
a->b = b;
b->a = a;
cout << "a和b的析构应该在这句话之后和横杠之前完成并显示出来" << endl;
}
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
作用域内进行a和b对象的创建,并让内部的成员变量指向其他对象
a和b的析构应该在这句话之后和横杠之前完成并显示出来
-------------------------
错误案例分析
造成出作用域后a和b对象不销毁的原因是对象内的a和b成员的强引用计数永远是1,在作用域内a和b智能指针的强引用计数都为2,但一出作用域a和b的智能指针对象销毁使计数-1,但不是0的强引用计数就不会销毁对象调用析构函数进而导致内存泄漏。
解决方法
在类内使用weak_ptr可以很好的解决循环引用造成的内存泄漏,因为weak_ptr对象不会使强引用计数增加,对上述的错误案例进行改进得到解决方法。
改进案例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class B;
class A
{
public:
weak_ptr<B> b;
~A() { cout << "A的析构函数" << endl; }
};
class B
{
public:
weak_ptr<A> a;
~B() { cout << "B的析构函数" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
{
cout << "作用域内进行a和b对象的创建,并让内部的成员变量指向其他对象" << endl;
shared_ptr<A> a = make_shared<A>();
shared_ptr<B> b = make_shared<B>();
a->b = b;
b->a = a;
cout << "a和b的析构应该在这句话之后和横杠之前完成并显示出来" << endl;
}
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
作用域内进行a和b对象的创建,并让内部的成员变量指向其他对象
a和b的析构应该在这句话之后和横杠之前完成并显示出来
B的析构函数
A的析构函数
-------------------------
unique_ptr
unique_ptr是独占式指针,在同一个时刻,有且仅有一个unique_ptr
初始化
使用new
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
unique_ptr<int> ptr(new int(100));
cout << "使用new的方法初始化unique_ptr<int>" << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
使用make_unique函数(C++14后才支持这个函数)
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
unique_ptr<int> ptr = make_unique<int>(100);
cout << "使用make_unique的方法初始化unique_ptr<int>" << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
常用操作
使用移动语义操作
虽然unique_ptr是独占式指针,但如果一个unique_ptr对象不再某功能使用但另一个功能又需要这个对象的内部资源时,可以用移动语义std::move()函数来将对象进行转移。
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
unique_ptr<int> funA_obj1 = make_unique<int>(20);
cout << "功能funA中的obj1不用在此功能中使用" << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
cout << "功能funB的obj1需要funA中obj1的资源" << endl;
unique_ptr<int> funB_obj1(std::move(funA_obj1));
cout << "功能funB的obj1的资源数值为: " << *funB_obj1 << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
功能funA中的obj1不用在此功能中使用
-------------------------
功能funB的obj1需要funA中obj1的资源
功能funB的obj1的资源数值为: 20
release()成员函数
release()成员函数放弃对指针的控制权,返回裸指针,并将智能指针置空。返回的这个裸指针需要手工delete释放,或者用新的shared_ptr
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unique_ptr<int> ptr1 = make_unique<int>(100);
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
unique_ptr<int> ptr2(ptr1.release());
cout << "ptr2获取了ptr1的指针资源,*ptr2 = " << *ptr2 << endl;
cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果
-------------------------
ptr2获取了ptr1的指针资源,*ptr2 = 100
-------------------------
swap()成员函数
和shared_ptr
reset()成员函数
和shared_ptr
get()成员函数
和shared_ptr
*解引用
和shared_ptr


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号