MongoDB基础
MongoDB基础
传统关系型数据库在面对在面对高并发、数据量大、高扩展和高可用时有些力不从心,MongoDB则比较容易应对以上情况。
存储结构
| SQL术语/概念 | MongoDB术语/概念 | 解释/说明 |
|---|---|---|
| database | database | 数据库 |
| table | collection | 数据库表/集合 |
| row | document | 数据记录行/文档 |
| column | field | 数据字段/域 |
| index | index | 索引 |
| table joins | 表连接,MongoDB不支持 | |
| 嵌入文档 | MongoDB通过嵌入式文档来替代多表连接 | |
| primary key | primary key | 主键,MongoDB自动将_id字段设置为主键 |
数据类型
shell即在控制台与Mongodb进行交互
MongoDB中一行数据是以JSON格式进行存储的。
数据类型详表
| 数据类型 | 描述 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| 字符串 | UTF-8字符串都可表示为字符串类型的数据 | |
| 对象id | 对象id是文档的12字节的唯一 ID | |
| 布尔值 | 真或者假:true或者false | |
| 数组 | 值的集合或者列表可以表示成数组 | |
| 32位整数 | 类型不可用。JavaScript仅支持64位浮点数,所以32位整数会被自动转换。 | shell是不支持该类型的,shell中默认会转换成64位浮点数 |
| 64位整数 | 不支持这个类型。shell会使用一个特殊的内嵌文档来显示64位整数 | shell是不支持该类型的,shell中默认会转换成64位浮点数 |
| 64位浮点数 | shell中的数字就是这一种类型 | |
| null | 表示空值或者未定义的对象 | |
| undefined | 文档中也可以使用未定义类型 | |
| 符号 | shell不支持,shell会将数据库中的符号类型的数据自动转换成字符串 | |
| 正则表达式 | 文档中可以包含正则表达式,采用JavaScript的正则表达式语法 | |
| 代码 | 文档中还可以包含JavaScript代码 | {"x" : function() { /* …… */ }} |
| 二进制数据 | 二进制数据可以由任意字节的串组成,不过shell中无法使用 | |
| 最大值/最小值 | BSON包括一个特殊类型,表示可能的最大值。shell中没有这个类型。 |
安装
Windows安装
从官网下载zip包
版本命名规则:x.y.z
- y为奇数时表示当前版本为开发版,如:1.5.2、4.1.13
- y为偶数时表示当前版本为稳定版,如:1.6.3、4.0.10
- z是修正版本号,数字越大越好
解压后在目录内手动建立一个目录用于存放数据文件,如data/db;然后进入bin目录,在此处打开控制台执行:
mongod --dbpath=..\data\db
即可看到启动,默认端口为27017,也可以通过--port指定端口
配置文件方式启动
可以在data目录中创建一个config文件夹,创建一个mongod.conf文件,写入内容:
storage:
#The directory where the mongod instance stores its data.Default Value is "\data\db" on Windows.
dbPath: ../data/db
然后在bin目录控制台执行
mongod -f ../data/config/mongod.conf
#或者
mongod --config ../data/config/mongod.conf
即可启动。
Linux安装
- 先到官网下载压缩包
mongod-linux-x86_64-4.0.10.tgz。 - 上传到Linux并解压:
tar -xvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.10.tgz - 移动:
mv mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.10 /usr/local/mongodb - 创建目录:
#数据存储目录
mkdir -p /mongodb/single/data/db
#日志存储目录
mkdir -p /mongodb/single/log
- 新建并修改配置文件:
vim /mongodb/single/mongod.conf,文件内容如下
systemLog:
#MongoDB发送所有日志输出的目标指定为文件
destination: file
#mongod或mongos应向其发送所有诊断日志记录信息的日志文件的路径
path: "/mongodb/single/log/mongod.log"
#当mongos或mongod实例重新启动时,mongos或mongod会将新条目附加到现有日志文件的末尾。
logAppend: true
storage:
#mongod实例存储其数据的目录。storage.dbPath设置仅适用于mongod。
dbPath: "/mongodb/single/data/db"
journal:
#启用或禁用持久性日志以确保数据文件保持有效和可恢复。
enabled: true
processManagement:
#启用在后台运行mongos或mongod进程的守护进程模式。
fork: true
net:
#服务实例绑定的IP,默认是localhost
bindIp: localhost,192.168.40.141
#bindIp
#绑定的端口,默认是27017
port: 27017
然后启动服务:
[root@linux single]# /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod -f /mongodb/single/mongod.conf
about to fork child process, waiting until server is ready for connections.
forked process: 90384
child process started successfully, parent exiting
关闭服务
连接Shell:在bin目录执行mongo
正常关闭:
#连接到服务器(有可能需要认证)
#切换到admin库
use admin
#关闭服务
db.shutdownServer()
快捷方法(不推荐,有可能数据损坏):
Windows下在控制台Ctrl + C即可。
Linux下,使用kill命令
如果数据损坏
- 删除lock文件:
rm -f /mongodb/single/data/db/*.lock
- 修复数据:
/usr/local/mongdb/bin/mongod --repair --dbpath=/mongodb/single/data/db
可视化客户端
在官网下载官方客户端,然后安装即可。(Navicat也可以连接MongoDB)
简单使用
首先给出一个如下结构的数据库:
数据库:articledb
| 专栏文章评论 | comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 字段名称 | 字段含义 | 字段类型 | 备注 |
| _id | ID | ObjectId或String | Mongo的主键的字段 |
| articleid | 文章ID | String | |
| content | 评论内容 | String | |
| userid | 评论人ID | String | |
| nickname | 评论人昵称 | String | |
| createdatetime | 评论的日期时间 | Date | |
| likenum | 点赞数 | Int32 | |
| replynum | 回复数 | Int32 | |
| state | 状态 | String | 0:不可见;1:可见; |
| parentid | 上级ID | String | 如果为0表示文章的顶级评论 |
数据库操作
创建数据库
选择数据库,如果数据库不存在则自动创建,例如,以下语句创建spitdb数据库:
use articledb
查看所有数据库:
show dbs
#或
show databases
注意: 在 MongoDB 中,集合只有在内容插入后才会创建! 就是说,创建集合(数据表)后要再插入一个文档(记录),集合才会真正创建,因为此时use的库是在内存中,show的库是在硬盘上,所以上述命令只能看到默认的三个库。
查看当前正在使用的数据库命令:db
MongoDB 中默认的数据库为 test,如果你没有选择数据库,集合将存放在 test 数据库中。
另外:
数据库名可以是满足以下条件的任意UTF-8字符串。
- 不能是空字符串("")。
- 不得含有' '(空格)、.、$、/、\和\0 (空字符)。
- 应全部小写。
- 最多64字节。
有一些数据库名是保留的,可以直接访问这些有特殊作用的数据库。
- admin: 从权限的角度来看,这是"root"数据库。要是将一个用户添加到这个数据库,这个用户自动继承所有数据库的权限。一些特定的服务器端命令也只能从这个数据库运行,比如列出所有的数据库或者关闭服务器。
- local: 这个数据永远不会被复制,可以用来存储限于本地单台服务器的任意集合
- config: 当Mongo用于分片设置时,config数据库在内部使用,用于保存分片的相关信息。
删除数据库
db.dropDatabase()
主要用来删除已经持久化的数据库
集合操作
显式创建集合(一般不用)
db.createCollection(集合名)
查看集合:
show collections
或
show tables
集合的命名规范:
- 集合名不能是空字符串""。
- 集合名不能含有\0字符(空字符),这个字符表示集合名的结尾。
- 集合名不能以"system."开头,这是为系统集合保留的前缀。
- 用户创建的集合名字不能含有保留字符。有些驱动程序的确支持在集合名里面包含,这是因为某些系统生成的集合中包含该字符。除非你要访问这种系统创建的集合,否则千万不要在名字里出现$。
隐式创建集合:
当向一个集合中插入一个文档的时候,如果集合不存在,则会自动创建集合(通常使用这种方式)。
删除集合
db.集合名.drop()
文档的CRUD
文档的数据结构和JSON基本一致,但存储时用的是BSON,可以理解为二进制JSON。
文档插入
单个文档的插入
使用insert() 或 save() 方法向集合中插入文档:
db.collection.insert(
<document or array of documents>,
{
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
}
)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
document |
document or array | 要插入到集合中的文档或文档数组。(json格式) |
writeConcern |
document | 写入关注(即数据写入后是否确认,即确认程度),等级越高,数据越安全,但同时效率也更第 |
ordered |
boolean | 可选。如果为真,则按顺序插入数组中的文档,如果其中一个文档出现错误,MongoDB将返回而不处理数组中的其余文档。如果为假,则执行无序插入,如果其中一个文档出现错误,则继续处理数组中的主文档。在版本2.6+中默认为true |
后面两个参数一般不用写。
示例:
db.comment.insert({"articleid":"100000","content":"今天天气真好,阳光明媚","userid":"1001","nickname":"Rose","createdatetime":new Date(),"likenum":NumberInt(10),"state":null})
提示:
- comment集合如果不存在,则会隐式创建
- mongo中的数字,默认情况下是double类型,如果要存整型,必须使用函数NumberInt(整型数字),否则取出来就有问题了。
- 插入当前日期使用new Date()
- 插入的数据没有指定_id,会自动生成主键值
- 如果某字段没值,可以赋值为null,或不写该字段。
执行后,提示如下,说明插入一个数据成功了
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
注意:
- 文档中的键/值对是有序的。
- 文档中的值不仅可以是在双引号里面的字符串,还可以是其他几种数据类型(甚至可以是整个嵌入的文档)。
- MongoDB区分类型和大小写。
- MongoDB的文档不能有重复的键。
- 文档的键是字符串。除了少数例外情况,键可以使用任意UTF-8字符。
文档键命名规范:
- 键不能含有\0 (空字符)。这个字符用来表示键的结尾。
- .和$有特别的意义,只有在特定环境下才能使用。
- 以下划线"_"开头的键是保留的(不是严格要求的)。
批量插入
db.collection.insertMany(
[ <document 1> , <document 2>, ... ],
{
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
}
)
下面是一个多个插入的例子
例子
db.comment.insertMany([
{"_id":"1","articleid":"100001","content":"我们不应该把清晨浪费在手机上,健康很重要,一杯温水幸福你我他。","userid":"1002","nickname":"相忘于江湖","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-05T22:08:15.522Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(1000),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"2","articleid":"100001","content":"我夏天空腹喝凉开水,冬天喝温开水","userid":"1005","nickname":"伊人憔悴","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-05T23:58:51.485Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(888),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"3","articleid":"100001","content":"我一直喝凉开水,冬天夏天都喝。","userid":"1004","nickname":"杰克船长","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T01:05:06.321Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(666),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"4","articleid":"100001","content":"专家说不能空腹吃饭,影响健康。","userid":"1003","nickname":"凯撒","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T08:18:35.288Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(2000),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"5","articleid":"100001","content":"研究表明,刚烧开的水千万不能喝,因为烫嘴。","userid":"1003","nickname":"凯撒","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T11:01:02.521Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(3000),"state":"1"}
]);
经测试insertMany()和insert()没啥区别,只是返回值不同。
插入时指定了_id,则主键就是该值。
文档查询
db.collection.find(<query>, [projection])
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
query |
document | 可选。使用查询运算符指定选择筛选器。若要返回集合中的所有文档,请省略此参数或传递空文档({})。 |
projection |
document | 可选。指定要在与查询筛选器匹配的文档中返回的字段(投影)。若要返回匹配文档中的所有字段,请省略此参数。 |
简单来说,第一个参数是查询条件,第二个参数是查询的字段。
例如
//查询userid为1003的数据
db.comment.find({userid:'1003'})
//查询userid为1003的userid和nickname两个字段的数据
db.comment.find({userid:'1003'},{userid:1,nickname:1})
//默认_id会显示,
//查询结果只显示userid、nickname,不显示_id
db.comment.find({userid:'1003'},{userid:1,nickname:1,_id:0})
//查询所有数据,但只显示_id、userid、nickname
db.comment.find({},{userid:1,nickname:1})
文档的修改
db.collection.update(query, update, options)
//或
db.collection.update(
<query>,
<update>,
{
upsert: <boolean>,
multi: <boolean>,
writeConcern: <document>,
collation: <document>,
arrayFilters: [ <filterdocument1>, ... ],
hint: <document|string> // Available starting in MongoDB 4.2
}
)
这里主要关注前四个参数:
<query>:更新的条件,相当于SQL中WHERE后面的条件。<update>:更新的内容及规则。<upsert>:(可选)True时未找到文档将创建,默认为False<multi>:(可选)True时更新符合条件的所有文档,默认为False,只更新找到的第一条数据。
示例:
文档的覆盖修改:
db.comment.update({_id:"1"},{likenum:NumberInt(1001)})
此时,_id为1的该文档除去likenum字段外,其他字段消失,因为是覆盖修改。
局部修改
一般情况下,都是使用局部修改:
db.comment.update({_id:"2"},{$set:{likenum:NumberInt(889)}})
$set代表设置为该值(最常用)。
类似的还有:
{$inc:{field:value}}:对数字类型的field增加value{$unset:{field:1}}:删除该字段{$push:{field:value}}:把value追加到field里。field只能是数组类型,如果field不存在,会自动插入一个数组类型{$pushAll:{field:value_array}}:用法同$push一样,只是$pushAll可以一次追加多个值到一个数组字段内{$addToSet:{field:value}}:加一个值到数组内,而且只有当这个值在数组中不存在时才增加$pop:删除数组内第一个值:{$pop:{field:-1}}、删除数组内最后一个值:{$pop:{field:1}}{$pull:{field:_value}}:从数组field内删除一个等于_value的值{$pullAll:value_array}:用法同$pull一样,可以一次性删除数组内的多个值{$rename:{old_field_name:new_field_name}}:对字段进行重命名
删除文档
db.集合名称.remove(query)
查询文档
统计查询
db.collection.count(query, options)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
query |
document | 查询选择条件。 |
options |
document | 可选。用于修改计数的额外选项。 |
示例:
//统计comment集合的所有的记录数:
db.comment.count()
//统计userid为1003的记录条数
db.comment.count({userid:"1003"})
分页查询
可以使用limit()指定展示多少条,使用skip()方法来跳过指定数量的数据:
db.COLLECTION_NAME.find().limit(NUMBER).skip(NUMBER)
例如:
db.comment.find().limit(2).skip(1)
//如果find()查询到5条,则上述语句会展示第2、3条,因为第1条被跳过
排序查询
sort()方法可以通过参数指定排序的字段,并使用 1 和 -1 来指定排序的方式,其中 1 为升序排列,而 -1 是用于降序排列。
例如对userid降序排列,并对likenum进行升序排列
db.comment.find().sort({userid:-1,likenum:1})
skip(), limilt(), sort()三个放在一起执行的时候,执行的顺序是先 sort(), 然后是 skip(),最后是显示的 limit(),和命令编写顺序无关。
正则查询
MongoDB的模糊查询是通过正则表达式的方式实现的:
db.collection.find({field:/正则表达式/})
比较查询
<, <=, >, >= 这个操作符也是很常用的:
db.collection_name.find({"field":{ $gt:value}})
其中$gt代表大于,类似的还有
$gt:大于$lt:小于$gte:大于等于$lte:小于等于$ne:不等于
包含查询
包含使用$in操作符:
//查询评论的集合中userid字段包含1003或1004的文档
db.comment.find({userid:{$in:["1003","1004"]}})
条件连接查询
如果需要查询同时满足两个以上条件,需要使用$and操作符将条件进行关联。(相当于SQL的and)
$and:[{条件1},{条件2},{条件3}]
例如:
db.comment.find({$and:[{likenum:{$gte:NumberInt(700)}},{likenum:{$lt:NumberInt(2000)}}]})
同理如果是或的关系,使用$or:
$or:[{条件1},{条件2},{条件3}]
常用命令小结:
- 选择切换数据库:
use articledb - 插入数据:
db.comment.insert({bson数据}) - 查询所有数据:
db.comment.find() - 条件查询数据:
db.comment.find({条件}) - 查询符合条件的第一条记录:
db.comment.findOne({条件}) - 查询符合条件的前几条记录:
db.comment.find({条件}).limit(条数) - 查询符合条件的跳过的记录:
db.comment.find({条件}).skip(条数) - 修改数据:
db.comment.update({条件},{修改后的数据})或db.comment.update({条件},{$set:{要修改部分的字段:数据}) - 修改数据并自增某字段值:
db.comment.update({条件},{$inc:{自增的字段:步进值}}) - 删除数据:
db.comment.remove({条件}) - 统计查询:
db.comment.count({条件}) - 模糊查询:`db.comment.find({字段名:/正则表达式/})``
- 条件比较运算:`db.comment.find({字段名:{$gt:值}})
- 包含查询:
db.comment.find({字段名:{$in:[值1,值2]}})或db.comment.find({字段名:{$nin:[值1,值2]}}) - 条件连接查询:
db.comment.find({$and:[{条件1},{条件2}]})或db.comment.find({$or:[{条件1},{条件2}]})
索引
MongoDB索引使用B树数据结构(确切的说是B-Tree,MySQL是B+Tree)
单字段索引
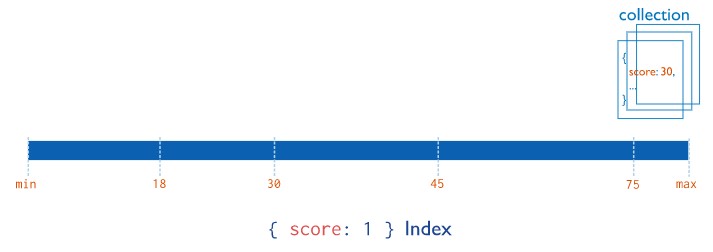
MongoDB支持在文档的单个字段上创建用户定义的升序/降序索引,称为单字段索引(Single Field Index)。
比如{score: 1} Index:
复合索引
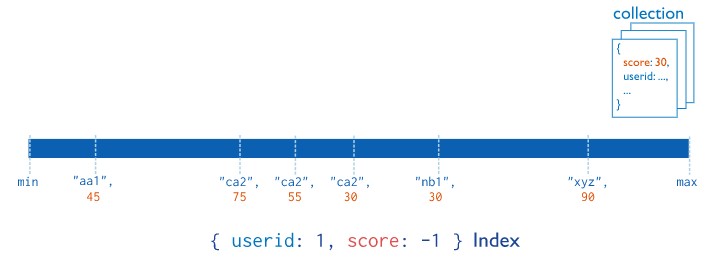
MongoDB还支持多个字段的用户定义索引,即复合索引(Compound Index)。
复合索引中列出的字段顺序具有重要意义。例如,如果复合索引由{ userid: 1, score: -1 }组成,则索引首先按userid正序排序,然后在每个userid的值内,再在按score倒序排序。
其他索引
地理空间索引(Geospatial Index)、文本索引(Text Indexes)、哈希索引(Hashed Indexes)。
地理空间索引(Geospatial Index)
为了支持对地理空间坐标数据的有效查询,MongoDB提供了两种特殊的索引:返回结果时使用平面几何的二维索引和返回结果时使用球面几何的二维球面索引。
文本索引(Text Indexes)
MongoDB提供了一种文本索引类型,支持在集合中搜索字符串内容。这些文本索引不存储特定于语言的停止词(例如“the”、“a”、“or”),而将集合中的词作为词干,只存储根词。
哈希索引(Hashed Indexes)
为了支持基于散列的分片,MongoDB提供了散列索引类型,它对字段值的散列进行索引。这些索引在其范围内的值分布更加随机,但只支持相等匹配,不支持基于范围的查询。
索引的管理操作
查看索引
返回一个集合中的所有索引的数组
db.collection.getIndexes()
运行该命令后的返回结果是:
//执行
db.comment.getIndexes()
//结果
[
{
"v": NumberInt("2"),
"key": {
"_id": NumberInt("1")
},
"name": "_id_",
"ns": "articledb.comment"
}
]
结果显示默认字段_id的索引,名称为_id_。
默认_id索引:
MongoDB在创建集合的过程中,在_id字段上创建一个唯一的索引,默认名字为_id_,该索引可防止客户端插入两个具有相同值的文档,您不能在_id字段上删除此索引。
注意:该索引是唯一索引,因此值不能重复,即_id值不能重复的。在分片集群中,通常使用_id作为片键。
创建索引
db.collection.createIndex(keys, options)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
keys |
document | 包含字段和值对的文档,其中字段是索引键,值描述该字段的索引类型。对于字段上的升序索引,请指定值1;对于降序索引,请指定值-1。比如:{字段:1或-1},其中1 为指定按升序创建索引,如果你想按降序来创建索引指定为 -1 即可。另外,MongoDB支持几种不同的索引类型,包括文本、地理空间和哈希索引。 |
options |
document | 可选。包含一组控制索引创建的选项的文档。有关详细信息,请参见选项详情列表。 |
详情列表
Options选项
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| background | Boolean | 建索引过程会阻塞其它数据库操作,background可指定以后台方式创建索引,即增加 "background" 可选参数。 "background" 默认值为false。 |
| unique | Boolean | 建立的索引是否唯一。指定为true创建唯一索引。默认值为false. |
| name | string | 索引的名称。如果未指定,MongoDB的通过连接索引的字段名和排序顺序生成一个索引名称。 |
| dropDups | Boolean | 3.0+版本已废弃。在建立唯一索引时是否删除重复记录,指定 true 创建唯一索引。默认值为 false. |
| sparse | Boolean | 对文档中不存在的字段数据不启用索引;这个参数需要特别注意,如果设置为true的话,在索引字段中不会查询出不包含对应字段的文档.。默认值为 false. |
| expireAfterSeconds | integer | 指定一个以秒为单位的数值,完成 TTL设定,设定集合的生存时间。 |
| v | index version | 索引的版本号。默认的索引版本取决于mongod创建索引时运行的版本。 |
| weights | document | 索引权重值,数值在 1 到 99,999 之间,表示该索引相对于其他索引字段的得分权重。 |
| default_language | string | 对于文本索引,该参数决定了停用词及词干和词器的规则的列表。 默认为英语 |
| language_override | string | 对于文本索引,该参数指定了包含在文档中的字段名,语言覆盖默认的language,默认值为 language. |
单字段索引创建示例
//对userid创建索引
db.comment.createIndex({userid:1})
//结果
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically": false,
"numIndexesBefore": NumberInt("1"),
"numIndexesAfter": NumberInt("2"),
"ok": 1
}
复合索引创建示例:
//对userid和nickname同时创建复合索引
db.comment.createIndex({userid:1,nickname:-1})
//返回结果
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 2,
"numIndexesAfter" : 3,
"ok" : 1
}
移除索引
移除指定索引
//指定要删除的索引。可以通过索引名称或索引规范文档指定索引。若要删除文本索引,请指定索引名称。
db.collection.dropIndex(index)
示例
//删除comment集合中userid字段上的升序索引
db.comment.dropIndex({userid:1})
//返回结果
{ "nIndexesWas" : 3, "ok" : 1 }
移除所有索引
db.collection.dropIndexes()
索引的使用
执行计划
分析查询性能(Analyze Query Performance)通常使用执行计划(解释计划、Explain Plan)来查看查询的情况,如查询耗费的时间、是否基于索引查询等。
通常,我们想知道,建立的索引是否有效,效果如何,都需要通过执行计划查看。
db.collection.find(query,options).explain(options)
比如:
根据userid查询
db.comment.find({userid:"1003"}).explain()
//返回结果
{
"queryPlanner" : {
"plannerVersion" : 1,
"namespace" : "articledb.comment",
"indexFilterSet" : false,
"parsedQuery" : {
"userid" : {
"$eq" : "1003"
}
},
"winningPlan" : {
"stage" : "COLLSCAN",
"filter" : {
"userid" : {
"$eq" : "1003"
}
},
"direction" : "forward"
},
"rejectedPlans" : [ ]
},
"serverInfo" : {
"host" : "9ef3740277ad",
"port" : 27017,
"version" : "4.0.10",
"gitVersion" : "c389e7f69f637f7a1ac3cc9fae843b635f20b766"
},
"ok" : 1
}
关键点看:"stage" : "COLLSCAN",表示全集合扫描
然后对userid建立索引db.comment.createIndex({userid:1})
再次执行上面的查询可以看到:"stage" : "IXSCAN",基于索引的扫描。
涵盖查询(Covered Queries)
当查询条件和查询的投影仅包含索引字段时,MongoDB直接从索引返回结果,而不扫描任何文档或将文档带入内存。 这些覆盖的查询可以非常有效。

Spring结合MongoDB
现有数据库:articledb
articledb
| 专栏文章评论 | comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 字段名称 | 字段含义 | 字段类型 | 备注 |
| _id | ID | ObjectId或String | Mongo的主键的字段 |
| articleid | 文章ID | String | |
| content | 评论内容 | String | |
| userid | 评论人ID | String | |
| nickname | 评论人昵称 | String | |
| createdatetime | 评论的日期时间 | Date | |
| likenum | 点赞数 | Int32 | |
| replynum | 回复数 | Int32 | |
| state | 状态 | String | 0:不可见;1:可见; |
| parentid | 上级ID | String | 如果为0或置空表示文章的顶级评论 |
技术选型
选择使用SpringDataMongoDB,SpringData家族成员之一,用于操作MongoDB的持久层框架,封装了底层的mongodb-driver(相当于mysql的jdbc)。
创建SpringBoot工程
首先创建一个maven工程,引入依赖如下:
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>article</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
然后创建启动类以及application.yml文件:
启动类和application.yml
package com.example.article;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ArticleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ArticleApplication.class, args);
}
}
spring:
#数据源配置
data:
mongodb:
# 主机地址
host: localhost
# 数据库
database: articledb
# 默认端口是27017
port: 27017
#也可以使用uri连接
#uri: mongodb://192.168.40.134:27017/articledb
然后创建实体类:
Comment
package com.example.article.po;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.Indexed;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Field;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 文章评论实体类
*/
//把一个java类声明为mongodb的文档,可以通过collection参数指定这个类对应的文档。
//@Document(collection="mongodb 对应 collection 名")
// 若未加 @Document ,该 bean save 到 mongo 的 comment collection
// 若添加 @Document ,则 save 到 comment collection
@Document(collection="comment")//可以省略,如果省略,则默认使用类名小写映射集合
//复合索引
@CompoundIndex( def = "{'userid': 1, 'nickname': -1}")
@Data
public class Comment implements Serializable {
//主键标识,该属性的值会自动对应mongodb的主键字段"_id",如果该属性名就叫“id”,则该注解可以省略,否则必须写
@Id
private String id;//主键
//该属性对应mongodb的字段的名字,如果一致,则无需该注解
@Field("content")
private String content;//吐槽内容
private Date publishtime;//发布日期
//添加了一个单字段的索引
@Indexed
private String userid;//发布人ID
private String nickname;//昵称
private LocalDateTime createdatetime;//评论的日期时间
private Integer likenum;//点赞数
private Integer replynum;//回复数
private String state;//状态
private String parentid;//上级ID
private String articleid;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Comment{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", publishtime=" + publishtime +
", userid='" + userid + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
", createdatetime=" + createdatetime +
", likenum=" + likenum +
", replynum=" + replynum +
", state='" + state + '\'' +
", parentid='" + parentid + '\'' +
", articleid='" + articleid + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
其中可以在MongoDB中添加字段索引。
然后创建repository接口:
CommentRepository
package com.example.article.dao;
import com.example.article.po.Comment;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
//评论的持久层接口
public interface CommentRepository extends MongoRepository<Comment,String> {
}
然后是service层
CommentService
package com.example.article.service;
import com.example.article.dao.CommentRepository;
import com.example.article.po.Comment;
import com.example.article.utils.IdWorker;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
//评论的业务层
@Service
public class CommentService {
//注入dao
@Autowired
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
/**
* 保存一个评论
* @param comment
*/
public void saveComment(Comment comment){
//如果需要自定义主键,可以在这里指定主键;如果不指定主键,MongoDB会自动生成主键
//设置一些默认初始值。。。
//调用dao
commentRepository.save(comment);
}
/**
* 更新评论
* @param comment
*/
public void updateComment(Comment comment){
//调用dao
commentRepository.save(comment);
}
/**
* 根据id删除评论
* @param id
*/
public void deleteCommentById(String id){
//调用dao
commentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
/**
* 查询所有评论
* @return
*/
public List<Comment> findCommentList(){
//调用dao
return commentRepository.findAll();
}
/**
* 根据id查询评论
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Comment findCommentById(String id){
//调用dao
return commentRepository.findById(id).get();
}
}
然后在service类上使用idea快捷键Ctrl + Shift + T可以快速创建测试类:
测试类
package com.example.article.service;
import com.example.article.ArticleApplication;
import com.example.article.po.Comment;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
//测试评论的业务层
//SpringBoot的Junit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
//SpringBoot的测试环境初始化,参数:启动类
@SpringBootTest(classes = ArticleApplication.class)
public class CommentServiceTest {
//注入Service
@Autowired
private CommentService commentService;
/**
* 保存一个评论
*/
@Test
public void testSaveComment(){
Comment comment=new Comment();
comment.setArticleid("100000");
comment.setContent("测试添加的数据");
comment.setCreatedatetime(LocalDateTime.now());
comment.setUserid("1003");
comment.setNickname("凯撒大帝");
comment.setState("1");
comment.setLikenum(0);
comment.setReplynum(0);
commentService.saveComment(comment);
}
/**
* 查询所有数据
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
List<Comment> list = commentService.findCommentList();
System.out.println(list);
}
/**
* 测试根据id查询
*/
@Test
public void testFindCommentById(){
Comment comment = commentService.findCommentById("5d6a27b81b8d374798cf0b41");
System.out.println(comment);
}
}
接着便可以进行简单的查询测试。
根据上级ID查询文章评论的分页列表
CommentRepository新增方法定义
分页方法
//根据父id,查询子评论的分页列表
Page<Comment> findByParentid(String parentid, Pageable pageable);//Page、Pageable都是spring.data.domain下的类
CommentService新增方法
调用分页方法
/**
* 根据父id查询分页列表
* @param parentid
* @param page
* @param size
* @return
*/
public Page<Comment> findCommentListPageByParentid(String parentid,int page ,int size){
//为什么要page-1?因为参数穿进去的是zero-based page index.,基于0开始的索引的页码
return commentRepository.findByParentid(parentid, PageRequest.of(page-1,size));
}
测试类中添加测试方法:
测试方法
/**
* 测试根据父id查询子评论的分页列表
*/
@Test
public void testFindCommentListPageByParentid(){
Page<Comment> pageResponse = commentService.findCommentListPageByParentid("3", 1, 2);
System.out.println("----总记录数:"+pageResponse.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("----当前页数据:"+pageResponse.getContent());
}
插入一条测试数据:
插入测试数据
db.comment.insert({"id":"33", "content":"你年轻,火力大", "publishtime":null, "userid":"1003", "nickname":"凯撒大帝", "createdatetime":null, "likenum":null, "replynum":null, "state":"null", "parentid":"3", "articleid":"100001"})
执行测试。
MongoTemplate实现评论点赞
简单实现(效率低):
/**
* 点赞-效率低
* @param id
*/
public void updateCommentThumbupToIncrementingOld(String id){
Comment comment = CommentRepository.findById(id).get();
comment.setLikenum(comment.getLikenum()+1);
CommentRepository.save(comment);
}
但是我们只需要将点赞数加1就可以了,没必要查询出所有字段修改后再更新所有字段。
可以使用MongoTemplate来实现:
CommentService:
//注入MongoTemplate
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
/**
* 点赞数+1
* @param id
*/
public void updateCommentLikenumThumbup(String id){
//查询对象
Query query=Query.query(Criteria.where("_id").is(id));
//更新对象
Update update=new Update();
//局部更新,相当于$set
//update.set(key,value)
//递增$inc
//update.inc("likenum",1);
update.inc("likenum");
//参数1:查询对象
//参数2:更新对象
//参数3:集合的名字或实体类的类型Comment.class
mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query,update,"comment");
}
添加测试方法:
/**
* 点赞数+1
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateCommentLikenumThumbup(){
//对3号文档的点赞数+1
commentService.updateCommentLikenumThumbup("3");
}
即可发现测试成功。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号