【小工具】XML解析器 —— XMLParser

需求 分析:
在我们使用框架的过程中,经常会看到 配置文件需要用XML文件格式进行配置
(譬如:log4j、mybatis等)
那么,在本篇博文中,本人就来提供一个 xml解析器,来方便我们理解这些框架的底层实现
实现 过程:
首先,本人还是以“学生信息”举例,首先,给出一个XML文件的代码:
student.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<students>
<student id="032312" name="右转哥的忠实粉丝" sex="男">
<hobby name="支持右转哥"></hobby>
<hobby name="学习右转哥"></hobby>
<hobby name="敬佩右转哥"></hobby>
</student>
<student id="032123" name="右转哥的病娇粉丝" sex="女">
<hobby name="喜欢右转哥"></hobby>
</student>
</students>
本人现在对于上面的语句进行一些说明:
1.第一行代码,是我们用编译器创建了*.xml文件时,自动写上去的,它的目的是帮助计算机识别我们的代码。所以,对于这段代码,我们不能更改,无需理解;
2.能够发现,除了第一行代码,其他的代码都是以
<标签名> 内容<\标签名>
的方式进行书写的。
至于左右的<标签名> 和 <\标签名>,我们可以理解为 左括号 和 右括号。有左必有右,成对出现,不能缺少;
3.代码的第3、8行:
<student id="032312" name="章安京" sex="男"> //上段代码第3行
<student id="032123" name="的那些九年" sex="女"> //上段代码第8行
这两行和别的行的书写格式有些不太一样,这里来做一下解释:
可以将 id 和 name 以及 sex 理解为键值对,可以将它们理解为标签的属性,这也是我们用来区分每一个student标签的手段;
4.在XML文件中,和我们以往所编写的代码一样,也是可以进行注释的,但是格式略有不同。格式如下:
<!-- 注释内容 -->
那么,了解了相关的基本写法之后,本人再来给出两种不同的书写格式的XML文件:
student.tag.xml(代码中,将大多数粉丝信息存放在不同的标签的内容中):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<students>
<student>
<id>2511515</id>
<name>右转哥的学徒</name>
<sex>男</sex>
<birtdhday>2002-10-3</birtdhday>
<hobbies>
<hobby>支持右转哥</hobby>
<hobby>学习右转哥</hobby>
<hobby>敬佩右转哥</hobby>
</hobbies>
<introduce>
一心单推右转哥,面入大厂不是梦!
</introduce>
</student>
<student>
<id>12155</id>
<name>右转哥的病娇粉丝</name>
<sex>女</sex>
<birtdhday>2000-12-26</birtdhday>
<hobbies>
<hobby>给右转哥博文点赞</hobby>
</hobbies>
<introduce>
喜欢右转哥
</introduce>
</student>
</students>
student.att.xml(将大部分学生信息存放在标签的属性中):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<students>
<student id="2511515" name="右转哥的学徒" sex="男" birtdhday="2002-10-3">
<hobby>支持右转哥</hobby>
<hobby>学习右转哥</hobby>
<hobby>敬佩右转哥</hobby>
<introduce>
一心单推右转哥,面入大厂不是梦!
</introduce>
</student>
<student id="12155" name="右转哥的病娇粉丝" sex="女" birtdhday="2000-12-26">
<hobbies>
<hobby>给右转哥博文点赞</hobby>
</hobbies>
<introduce>
喜欢右转哥
</introduce>
</student>
</students>
那么,现在,本人为了之后输出的美观,再来给出一个处理学生信息的类:
package com.mec.about_xml.model;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentInfo {
private String id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private String birthday;
private String introduce;
private List<String> hobbies;
public StudentInfo() {
hobbies = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getIntroduce() {
return introduce;
}
public void setIntroduce(String introduce) {
this.introduce = introduce;
}
public List<String> getHobbies() {
return hobbies;
}
public void addHobby(String hobby) {
if (hobbies.contains(hobby)) {
return;
}
hobbies.add(hobby);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer();
res.append(id).append(" ")
.append(sex).append(" ")
.append(name).append(" ")
.append(birthday).append("\n简介:")
.append("\n\t")
.append(introduce).append("\n").append("爱好:\n");
for (String hobby : hobbies) {
res.append('\t').append(hobby).append("\n");
}
return res.toString();
}
}
那么,既然一切准备工作都做好了,本人就来显示一下最后那两个XML文件内的信息吧:
首先,本人来通过一个测试类 展示下 jdk原生方法 的解决方案:
package com.mec.about_xml.parse.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import com.mec.about_xml.model.StudentInfo;
public class TestParseAttribute {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
InputStream is = TestParseAttribute.class.getResourceAsStream("/student.att.xml"); //这行语句的参数一定要注意了:本人将student.att.xml文件放在了根目录下,所以路径是“/student.att.xml”
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document document = db.parse(is);
//上面这四行语句,是解析XML文件的四种方法之一的固定搭配,目前阶段的我们还没能力明白这四句的原理,本人将会在之后的专栏中对于这四条语句的原理进行详细地讲解
NodeList studentList = document.getElementsByTagName("student");
for (int i = 0; i < studentList.getLength(); i++) {
StudentInfo stu = new StudentInfo();
Element student = (Element) studentList.item(i);
String id = student.getAttribute("id");
String name = student.getAttribute("name");
String sex = student.getAttribute("sex");
String birthday = student.getAttribute("birtdhday");
NodeList hobbyList = student.getElementsByTagName("hobby");
for (int j = 0; j < hobbyList.getLength(); j++) {
Element hobby = (Element) hobbyList.item(j);
String hobbyString = hobby.getTextContent();
stu.addHobby(hobbyString);
}
stu.setId(id);
stu.setName(name);
stu.setSex(sex);
stu.setBirthday(birthday);
String introduce = student.getElementsByTagName("introduce")
.item(0).getTextContent().trim(); //这个方法的作用是:用来获取标签的内容
//上行代码的最后的trim()方法的作用是:忽略前导和尾随空格
stu.setIntroduce(introduce);
System.out.println(stu);
}
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
那么,我们来观看一下运行结果:
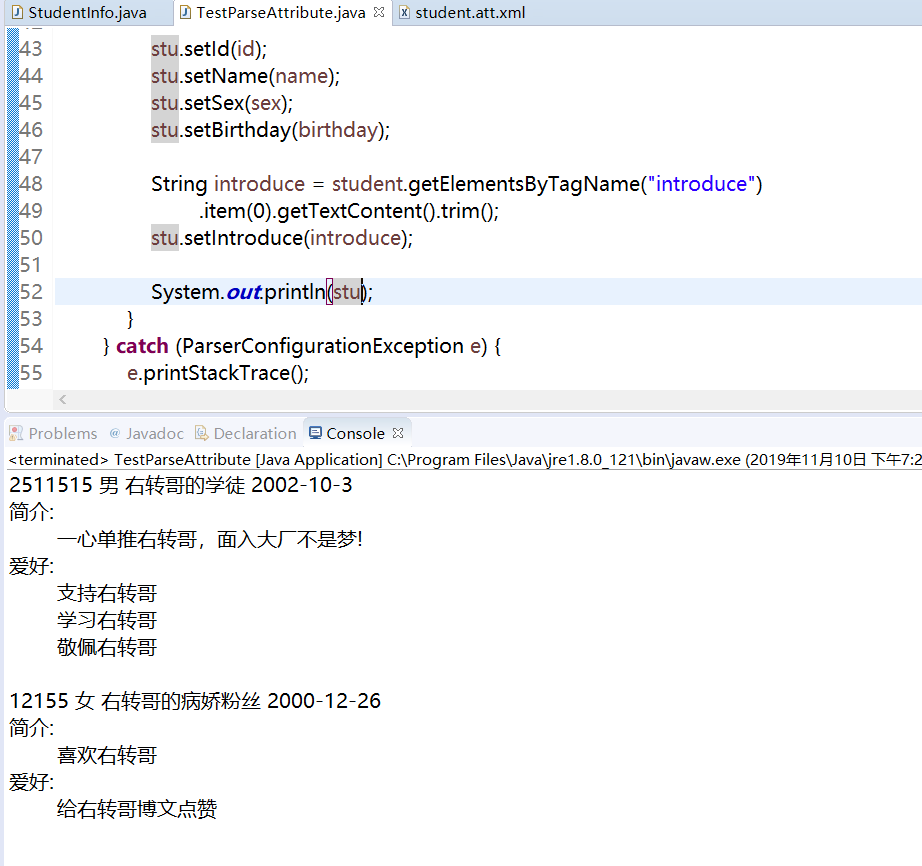
那么,接下来是另一个 jdk原生方法 的解决方案:
package com.mec.about_xml.parse.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
public class TestParseTag {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
InputStream is = TestParseTag.class.getResourceAsStream("/student.tag.xml");
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document document = db.parse(is);
NodeList studentList = document.getElementsByTagName("student"); //这个方法的作用是:用来获取标签的属性
for (int index = 0; index < studentList.getLength(); index++) {
Element student = (Element) studentList.item(index);
Element idElement = (Element) student.getElementsByTagName("id").item(0);
String id = idElement.getTextContent();
Element nameElement = (Element) student.getElementsByTagName("name").item(0);
String name = nameElement.getTextContent();
Element introduceElement = (Element) student.getElementsByTagName("introduce").item(0);
String introduce = introduceElement.getTextContent();
System.out.println(id + ", " + name);
System.out.println("[" + introduce.trim() + "]");
}
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
下面,我们来看一下运行结果:
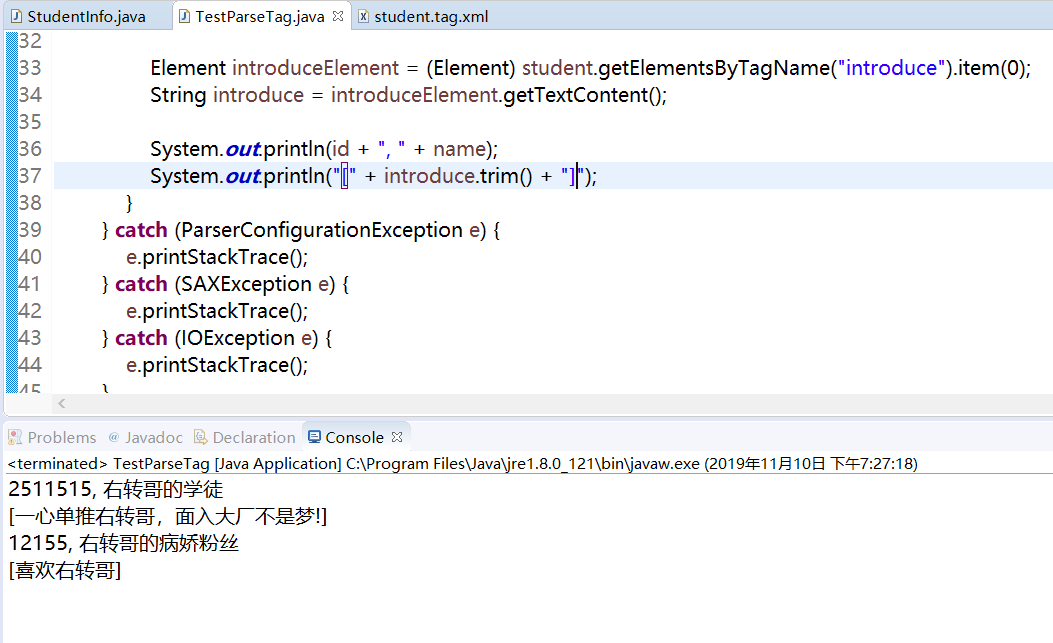 我们能够看到,和前一种结果相比,没有显示“爱好”的信息,本人在这里做一下解释:
我们能够看到,和前一种结果相比,没有显示“爱好”的信息,本人在这里做一下解释:
因为本人的两种XML文件中的爱好都是存放在了标签的内容中,而并非属性中,所以,显示这两个文件中的“爱好”的信息的代码是一样的,所以,本人为了简明扼要地讲解完内容,就没有进行重复代码段的书写。
我们可以看到:使用jdk原生的方法去解析XML配置文件的内容,过程过于繁杂
因此,在这里,本人提供一个 小工具,来简化我们的解析:
代码 实现:
首先是 指定路径下,xml文件不存在异常
XMLIsInexistentException 异常:
package edu.youzg.util.exceptions;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* xml配置文件不存在 异常
*
* @author Youzg
*/
public class XMLIsInexistentException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5631612417525749262L;
public XMLIsInexistentException() {
super();
}
public XMLIsInexistentException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public XMLIsInexistentException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public XMLIsInexistentException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
接下来是 XML解析器:
XMLParser:
package edu.youzg.util;
import edu.youzg.util.exceptions.XMLIsInexistentException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* XML文件解析器
*
* @author Youzg
*/
public abstract class XMLParser {
private static volatile DocumentBuilder db;
public XMLParser() {
}
private static DocumentBuilder getDocumentBuilder() throws ParserConfigurationException {
if (db == null) {
synchronized (XMLParser.class) {
if (db == null) {
db = DocumentBuilderFactory
.newInstance()
.newDocumentBuilder();
}
}
}
return db;
}
public static Document getDocument(String xmlPath) throws XMLIsInexistentException {
InputStream is = XMLParser.class.getResourceAsStream(xmlPath);
if (is == null) {
throw new XMLIsInexistentException("路径[" + xmlPath + "]不存在xml文件!");
}
return getDocument(is);
}
private static Document getDocument(InputStream is) {
Document document = null;
try {
document = getDocumentBuilder().parse(is);
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return document;
}
public abstract void dealElement(Element element, int index);
public void parseTag(Document document, String tagName) {
NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName(tagName);
for (int index = 0; index < nodeList.getLength(); index++) {
Element ele = (Element) nodeList.item(index);
dealElement(ele, index);
}
}
public void parseTag(Element element, String tagName) {
NodeList nodeList = element.getElementsByTagName(tagName);
for (int index = 0; index < nodeList.getLength(); index++) {
Element ele = (Element) nodeList.item(index);
dealElement(ele, index);
}
}
public void parseRoot(Document document) {
Element root = (Element) document.getChildNodes().item(0);
dealElement(root, 0);
}
public void parseElement(Element element) {
NodeList nodeList = element.getChildNodes();
for (int index = 0; index < nodeList.getLength(); index++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(index);
if (node instanceof Element) {
dealElement((Element) node, index);
}
}
}
}
接下来,本人来测试下是否 可以正常读取XML配置文件:
测试:
package com.mec.parse_xml.test;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import com.mec.about_xml.model.StudentInfo;
import com.mec.util.XMLParser;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new XMLParser() {
@Override
public void dealElement(Element element, int index) {
StudentInfo stu = new StudentInfo();
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
stu.setId(id);
String name = element.getAttribute("name");
stu.setName(name);
String sex = element.getAttribute("sex");
stu.setSex(sex);
String birthday = element.getAttribute("birtdhday");
stu.setBirthday(birthday);
new XMLParser() {
@Override
public void dealElement(Element element, int index) {
String hobbyString = element.getTextContent();
stu.addHobby(hobbyString);
}
}.parseTag(element, "hobby");
new XMLParser() {
@Override
public void dealElement(Element element, int index) {
String introduce = element.getTextContent().trim();
stu.setIntroduce(introduce);
}
}.parseTag(element, "introduce");
System.out.println(stu);
}
}.parseTag(XMLParser.getDocument("/student.att.xml"), "student");
}
}
下面是运行结果:
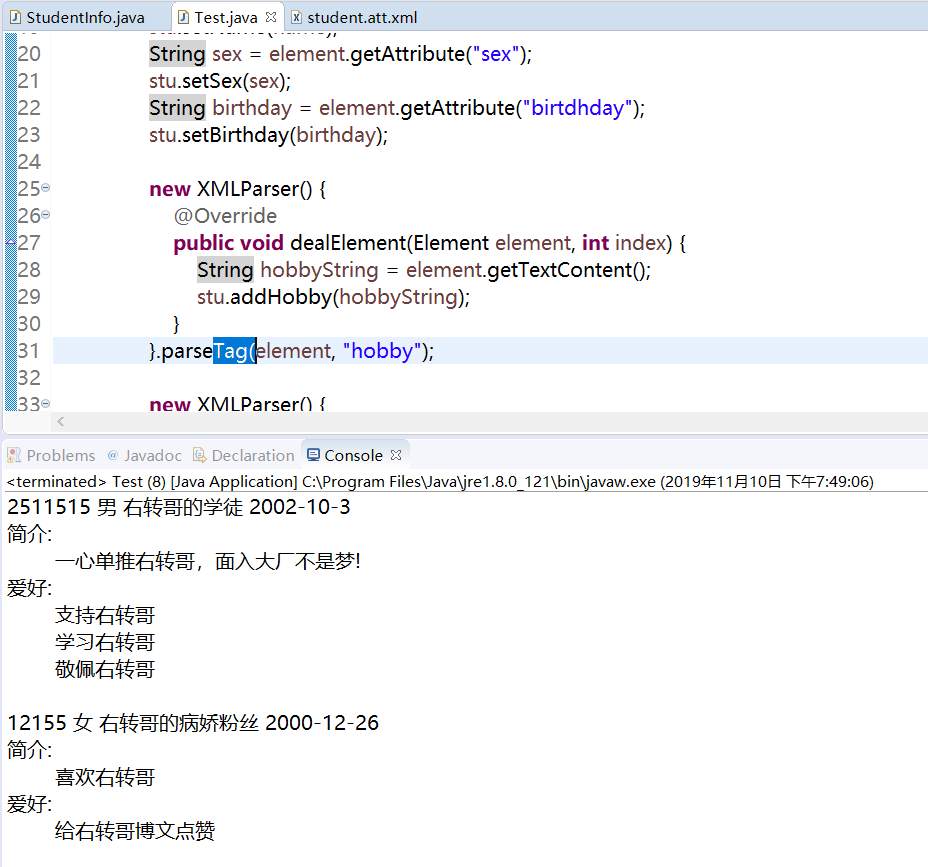
可以看到:xml文件内容 读取正常!
完整代码:
首先是 指定路径下,xml文件不存在异常
XMLIsInexistentException 异常:
package edu.youzg.util.exceptions;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* xml配置文件不存在 异常
*
* @author Youzg
*/
public class XMLIsInexistentException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5631612417525749262L;
public XMLIsInexistentException() {
super();
}
public XMLIsInexistentException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public XMLIsInexistentException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public XMLIsInexistentException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
接下来是 XML解析器:
XMLParser:
package edu.youzg.util;
import edu.youzg.util.exceptions.XMLIsInexistentException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* XML文件解析器
*
* @author Youzg
*/
public abstract class XMLParser {
private static volatile DocumentBuilder db;
public XMLParser() {
}
private static DocumentBuilder getDocumentBuilder() throws ParserConfigurationException {
if (db == null) {
synchronized (XMLParser.class) {
if (db == null) {
db = DocumentBuilderFactory
.newInstance()
.newDocumentBuilder();
}
}
}
return db;
}
public static Document getDocument(String xmlPath) throws XMLIsInexistentException {
InputStream is = XMLParser.class.getResourceAsStream(xmlPath);
if (is == null) {
throw new XMLIsInexistentException("路径[" + xmlPath + "]不存在xml文件!");
}
return getDocument(is);
}
private static Document getDocument(InputStream is) {
Document document = null;
try {
document = getDocumentBuilder().parse(is);
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return document;
}
public abstract void dealElement(Element element, int index);
public void parseTag(Document document, String tagName) {
NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName(tagName);
for (int index = 0; index < nodeList.getLength(); index++) {
Element ele = (Element) nodeList.item(index);
dealElement(ele, index);
}
}
public void parseTag(Element element, String tagName) {
NodeList nodeList = element.getElementsByTagName(tagName);
for (int index = 0; index < nodeList.getLength(); index++) {
Element ele = (Element) nodeList.item(index);
dealElement(ele, index);
}
}
public void parseRoot(Document document) {
Element root = (Element) document.getChildNodes().item(0);
dealElement(root, 0);
}
public void parseElement(Element element) {
NodeList nodeList = element.getChildNodes();
for (int index = 0; index < nodeList.getLength(); index++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(index);
if (node instanceof Element) {
dealElement((Element) node, index);
}
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号