阶段性复习与应用——复数的四则运算
看到这篇博文的同学们,大多数都学习了之前的博文了,那么,现在,我们通过 “复数的实现” 这一项目,来复习一下之前所有博文中的重要知识点!
首先,我们现在来构建一个类,来存储这个复数的 实部 和 虚部:
package com.mec.complex;
public class Complex {
private double real;
private double vir;
}
现在,我们来构造方法,并且编写 Getter() 和 Setter() 方法:
package com.mec.complex;
public class Complex {
private double real;
private double vir;
public Complex(double real, double vir) {
this.real = real;
this.vir = vir;
}
public Complex() {
this(0.0, 0.0);
}
public Complex(Complex c) {
this(c.real, c.vir);
}
public double getReal() {
return real;
}
public void setReal(double real) {
this.real = real;
}
public double getVir() {
return vir;
}
public void setVir(double vir) {
this.vir = vir;
}
}
基本的录入、输出方法,我们就编写完成了。
现在我们来编写加、减、乘、除方法:
1.加方法:
public Complex add(Complex c) {
this.real += c.real;
this.vir += c.vir;
return this;
}
public Complex add(Complex one, Complex another) {
return new Complex (one).add(another);
}
我们在这里,定义了两种加法的实现方法,以满足用户不同的输入,或者我们之后的代码的需求。
2.取相反数方法:
private static Complex opposite(Complex c) {
return new Complex(-c.real, -c.vir);
}
(因为这个方法,我们是为了完成减法操作才创造的,并不想外类调用,所以用private修饰)
3.减方法:
public Complex sub(Complex c) {
return this.add(opposite(c));
}
public static Complex sub(Complex one, Complex another) {
return new Complex(one).add(opposite(another));
}
4.乘方法:
public Complex mul(Complex one) {
double real = this.real;
this.real = real * one.real - this.vir * one.vir;
this.vir = real * one.vir - this.vir * one.real;
return this;
}
public static Complex mul(Complex one, Complex another) {
return new Complex (one).mul(another);
}
5.取倒数方法:
private static Complex reciprocal(Complex c) { //这里我们通过参考公式可得:倒数=原复数*共轭数/模长
double model = c.real * c.real + c.vir * c.vir; //复数的模长
if(Math.abs(model) < 1e-6) {
return null;
} //因为double的精度为1e-6,所以,小于1e-6时,可以忽略不计
return new Complex(c.real / model, -c.vir / model);
}
(因为这个方法,我们是为了完成除法操作才创造的,并不想外类调用,所以用private修饰)
6.除方法:
public static Complex div(Complex one, Complex another) {
Complex rec = reciprocal(another);
return rec == null ? null : new Complex(one).mul(rec);
}
注意:本人上面的四则运算方法,有的有 static修饰符 修饰,有的却没有,这里做下解释:
(1)有static修饰符修饰的方法,是我们之后的 Demo.java类 (即:测试类)所要调用的方法,而且这些方法的调用也更符合我们的认知(即:四则运算 的 参数是两个 “复数”);
(2)没有 static修饰符 修饰的方法,则是为了辅助我们完成 有 static修饰符 修饰的方法。
那么,我们总结下所有成员 和 方法:
Complex.java:
package com.mec.complex;
public class Complex {
private double real;
private double vir;
public Complex(double real, double vir) {
this.real = real;
this.vir = vir;
}
public Complex() {
this(0.0, 0.0);
}
public Complex(Complex c) {
this(c.real, c.vir);
}
public double getReal() {
return real;
}
public void setReal(double real) {
this.real = real;
}
public double getVir() {
return vir;
}
public void setVir(double vir) {
this.vir = vir;
}
public Complex add(Complex c) {
this.real += c.real;
this.vir += c.vir;
return this;
}
public static Complex add(Complex one, Complex another) {
return new Complex (one).add(another);
}
private static Complex opposite(Complex c) {
return new Complex(-c.real, -c.vir);
}
private static Complex reciprocal(Complex c) {
double model = c.real * c.real + c.vir * c.vir;
if(Math.abs(model) < 1e-6) {
return null;
}
return new Complex(c.real / model, -c.vir / model);
}
public Complex sub(Complex c) {
return this.add(opposite(c));
}
public static Complex sub(Complex one, Complex another) {
return new Complex(one).add(opposite(another));
}
public Complex mul(Complex one) {
double real = this.real;
this.real = real * one.real - this.vir * one.vir;
this.vir = real * one.vir - this.vir * one.real;
return this;
}
public static Complex mul(Complex one, Complex another) {
return new Complex (one).mul(another);
}
public static Complex div(Complex one, Complex another) {
Complex rec = reciprocal(another);
return rec == null ? null : new Complex(one).mul(rec);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + real + "," + vir + ")";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(null == obj) {
return false;
}
if(this == obj) {
return true;
}
if(!(obj instanceof Complex)) {
return false;
}
Complex c = (Complex) obj;
return Math.abs(this.real - c.real) < 1e-6
&& Math.abs(this.vir - c.vir) < 1e-6;
}
}
现在,我们来编写一个主函数的类来调用这些“工具”吧:
Demo.java:
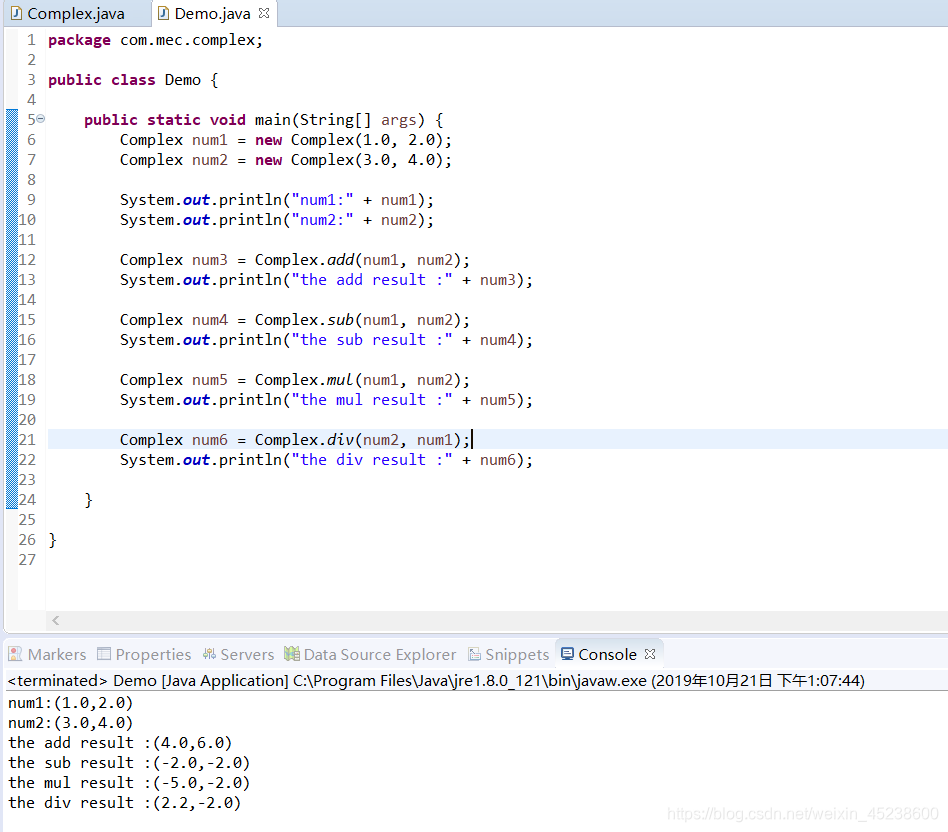
package com.mec.complex;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Complex num1 = new Complex(1.0, 2.0);
Complex num2 = new Complex(3.0, 4.0);
System.out.println("num1:" + num1);
System.out.println("num2:" + num2);
Complex num3 = Complex.add(num1, num2);
System.out.println("the add result :" + num3);
Complex num4 = Complex.sub(num1, num2);
System.out.println("the sub result :" + num4);
Complex num5 = Complex.mul(num1, num2);
System.out.println("the mul result :" + num5);
Complex num6 = Complex.div(num2, num1);
System.out.println("the div result :" + num6);
}
}
那么,测试结果如下:
那么,对于复数的基本操作的“工具”我们就做好了,我们之前所学习的重要知识点,差不多到此,就全部复习完了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号