【八叉树:分割3D空间】
<1>目标:使用八叉树分割3D空间,实现创建函数和插入函数
<2>思路:

<3>代码:
以下树实现相关代码
//封装插入的obj结构(根据项目自己定义)
public class OCObj {
//Unity Obj引用 public GameObject gameObj;//
//物体半径(宽度) public float halfWidth; //center在obj身上取 //public Vector3 center = Vector3.zero; //引用到的树节点lst 用于移除 public Node linkNode;
//位置 public Vector3 center { get { return gameObj.transform.position; } } }
//节点定义(根据需求定义)
public class Node
{
//节点中心
public Vector3 center = Vector3.zero;
//节点宽度
public float halfWidth = 0;
//缓存插入的Obj
public List<OCObj> objLst = null;//需要再new
//子节点 需要再new
public List<Node> childs = new List<Node>();
}
//创建树函数 中心 半宽 深度
public static Node BuildOCTree(Vector3 center, float halfWidth, int stopDepth) { if (stopDepth < 0) return null; else { Node node = new Node(); node.center = center; node.halfWidth = halfWidth; //创建子节点 每个节点的3个轴偏移 即为+- halfWidth*0.5f Vector3 offset = Vector3.zero; float step = halfWidth * 0.5f; for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { //8个点 //上下排序 offset.y = i % 2 == 0 ? step : -step; offset.z = i <= 3 ? step : -step; offset.x = i <= 1 || i >= 6 ? step : -step; Node child = BuildOCTree(center + offset, step, stopDepth - 1); if (child != null) { node.childs.Add(child); } } return node; } }
//插入函数 树根节点 Obj
public static void Insert(Node root, OCObj obj) { int index = 0; int x = 0; int y = 0; int z = 0; bool isPress = false;//是否占用了节点的2个格子 Dictionary<int, int> map = new Dictionary<int, int>(); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { float delta = obj.center[i] - root.center[i]; if (Mathf.Abs(delta) < obj.halfWidth) { isPress = true; } if (i == 0) { x = delta > 0 ? 1 : -1; } else if (i == 1) { y = delta > 0 ? 1 : -1; } else { z = delta > 0 ? 1 : -1; } } index = indexMap[z * 100 + y * 10 + x]; //压线了 或者 没有再深的层次了 则加入到当前节点 if (isPress || root.childs.Count <= 0) { if (root.objLst == null) { root.objLst = new List<OCObj>(); } root.objLst.Add(obj); obj.linkNode = root; } else { Insert(root.childs[index], obj); } } static Dictionary<int, int> indexMap = new Dictionary<int, int>() { { 100+10+1,0 },//1 1 1 = 0 { 100-10+1,1 },//1 0 1 = 1 { 100+10-1,2 },//1 1 0 = 2 { 100-10-1, 3 },//1 0 0 = 3 { -100+10-1, 4 },//0 1 0 = 4 101 = 4 { -100-10 -1, 5 }, { -100+10 +1, 6 }, { -100-10 +1, 7 }, };
//打印周围obj.name
public static void PrintCloserObjs(Node node) {
if (node.objLst != null && node.objLst.Count > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < node.objLst.Count; i++)
{
Debug.Log("name: " + node.objLst[i].gameObj.name);
}
}
if (node.childs != null && node.childs.Count > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < node.childs.Count; i++)
{
PrintCloserObjs(node.childs[i]);
}
}
}
以下树创建测试代码
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using OCTree;
using System;
public class OCTreeMain : MonoBehaviour
{
public float halfWidth = 1000;
public int depth = 5;
public Vector3 center = Vector3.zero;
public GameObject gameObj;
Node root = null;
List<OCObj> ocLst = new List<OCObj>();
int uid = 0;
void Start()
{
root = OCTree.OCUtils.BuildOCTree(center, halfWidth, depth);
}
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
{
uid++;
OCObj obj = new OCObj();
obj.gameObj = new GameObject("empty"+ uid); //gameObj;
obj.gameObj.transform.position = gameObj.transform.position;
obj.halfWidth = gameObj.transform.localScale.x / 2;
OCUtils.Insert(root, obj);
ocLst.Add(obj);
System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch stopwatch = new System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
OCUtils.Remove(obj);
OCUtils.Insert(root, obj);
}
stopwatch.Stop();
Debug.Log("插入耗时: "+stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
}
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.P)) {
int max = ocLst.Count;
int idx = UnityEngine.Random.Range(0, max);
if (idx > 0) {
OCObj obj = ocLst[idx];
Debug.LogError("打印: " + obj.gameObj.name + " 周围的物体");
OCUtils.PrintCloserObjs(obj.linkNode);
}
}
}
int gizFrameNum = 0;
int gizShowNum = 0;
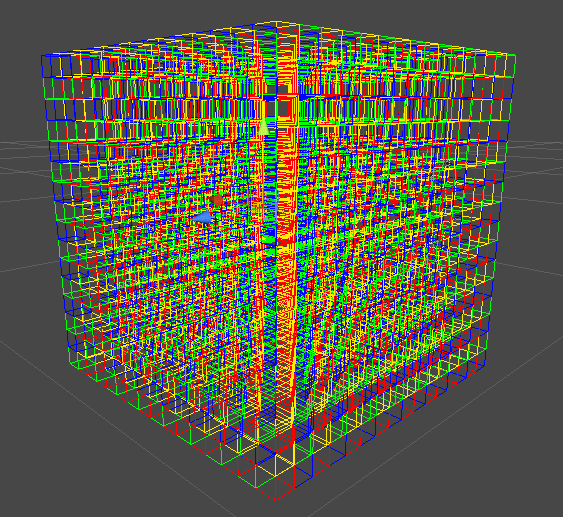
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
gizShowNum++;
if (gizShowNum >= 100)
{
gizShowNum = 0;
if (gizFrameNum >= 8) gizFrameNum = 0;
gizFrameNum++;
}
//展示所有
if (root != null)
{
drawOCTree(root);
}
//一层一层展示
//8个叶子分别展示
//int idx = gizFrameNum % 8;
//if (root != null) {
// Node node = root.childs[idx];
// if (node != null) {
// drawOCTree(node);
// }
//}
}
void drawOCTree(Node node)
{
//绘制里面的物体
if (node.objLst != null && node.objLst.Count > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < node.objLst.Count; i++)
{
OCObj obj = node.objLst[i];
Gizmos.DrawCube(obj.center, new Vector3(obj.halfWidth * 2, obj.halfWidth * 2, obj.halfWidth * 2));
}
}
//绘制线框
List<Node> childs = node.childs;
if (childs != null && childs.Count > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < childs.Count; i++)
{
Node child = childs[i];
drawOCTree(child);
if (child.childs.Count <= 0)
{
//绘制8个
Gizmos.color = getColor(i);
//8个顶点
float halfWidth = child.halfWidth;
Vector3 p0 = child.center + new Vector3(halfWidth, halfWidth, halfWidth);
Vector3 p2 = child.center + new Vector3(-halfWidth, halfWidth, halfWidth);
Vector3 p4 = child.center + new Vector3(-halfWidth, halfWidth, -halfWidth);
Vector3 p6 = child.center + new Vector3(halfWidth, halfWidth, -halfWidth);
Vector3 p1 = child.center + new Vector3(halfWidth, -halfWidth, halfWidth);
Vector3 p3 = child.center + new Vector3(-halfWidth, -halfWidth, halfWidth);
Vector3 p5 = child.center + new Vector3(-halfWidth, -halfWidth, -halfWidth);
Vector3 p7 = child.center + new Vector3(halfWidth, -halfWidth, -halfWidth);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p0, p2);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p2, p4);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p4, p6);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p6, p0);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p1, p3);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p3, p5);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p5, p7);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p7, p1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p0, p1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p2, p3);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p4, p5);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p6, p7);
}
}
}
}
Color getColor(int index)
{
Color color = Color.white;
int idx = index % 4;
switch (idx)
{
case 0:
color = Color.blue;
break;
case 1:
color = Color.yellow;
break;
case 2:
color = Color.green;
break;
case 3:
color = Color.red;
break;
case 4:
color = Color.red;
break;
}
return color;
}
}
<4>核心
创建函数中,2种创建方式,最终我们选取第二种方式创建子节点,因为我们需要更高效的插入
1.红色代码计算8个节点中心 容易理解:8个节点在3D空间中分为2层,从上层第一象限Index=0到第二层第一象限Index=1到第一层第二象限到第二层第二象限到...
2.蓝色代码用一种比较特殊的方式计算出8个节点中心
8个节点的Index区间[0-7],而0-7可以用二进制表示为8个象限轴方向
1,2,4的二进制可以表示三条坐标轴
在遍历0-7的时候,每个数字的二进制与1,2,4求 & 运算
可以求出每个节点的轴方向:我们下面以1计算X轴 2计算Y轴 4计算Z轴 1=0001 2=0010 4=0100
例如节点index=0与 1,2,4 做&运算 0=0000 求出的三种&运算都为0000 所以index=0的节点坐标=父节点坐标 + Vector3(-step,-step,-step) 即位于第二层的第三象限
例如节点index=1与 1,2,4 做&运算 0=0001 X轴为正 所以index=1的节点坐标=父节点坐标 + Vector3(step,-step,-step) 即位于第二层的第四象限
例如节点index=2与 1,2,4 做&运算 0=0010 Y轴为正 所以index=1的节点坐标=父节点坐标 + Vector3(-step,step,-step) 即位于第一层的第三象限
例如节点index=3与 1,2,4 做&运算 0=0011 XY轴为正 所以index=1的节点坐标=父节点坐标 + Vector3(step,step,-step) 即位于第一层的第四象限
例如节点index=4与 1,2,4 做&运算 0=0100 Z轴为正 所以index=1的节点坐标=父节点坐标 + Vector3(-step,-step,step) 即位于第二层的第二象限
例如节点index=5与 1,2,4 做&运算 0=0101 XZ轴为正 所以index=1的节点坐标=父节点坐标 + Vector3(step,-step,step) 即位于第二层的第一象限
例如节点index=6与 1,2,4 做&运算 0=0110 YZ轴为正 所以index=1的节点坐标=父节点坐标 + Vector3(-step,step,step) 即位于第一层的第二象限
例如节点index=7与 1,2,4 做&运算 0=0111 XYZ轴为正 所以index=1的节点坐标=父节点坐标 + Vector3(step,step,step) 即位于第一层的第一象限
//0 0/2 = 00 0000 //XYZ轴为负 //1 1/2 = 01 0001 //Z轴为正 也可以当做X轴 //2 10 01 0010 //Y轴为正 //3 11 01 0011 //YZ为正 //4 20 10 01 0100 //X轴为正 也可以当做Z轴 //5 21 10 01 0101 //XZ为正 //6 30 11 01 0110 //XY为正 //7 31 11 01 0111 //XYZ为正
//创建子节点 每个节点的3个轴偏移 即为+- halfWidth*0.5f
Vector3 offset = Vector3.zero;
float step = halfWidth * 0.5f;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
//8个点
//上下排序
offset.y = i % 2 == 0 ? step : -step;
offset.z = i <= 3 ? step : -step;
offset.x = i <= 1 || i >= 6 ? step : -step;
//offset.x = (i & 1) > 0 ? step : -step;
//offset.y = (i & 2) > 0 ? step : -step;
//offset.z = (i & 4) > 0 ? step : -step;
Node child = BuildOCTree(center + offset, step, stopDepth - 1);
if (child != null)
{
node.childs.Add(child);
}
}
插入函数
public static void Insert(Node root, OCObj obj)
{
int index = 0;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int z = 0;
bool isPress = false;//是否占用了节点的2个格子
Dictionary<int, int> map = new Dictionary<int, int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
float delta = obj.center[i] - root.center[i];
if (Mathf.Abs(delta) < obj.halfWidth)
{
isPress = true;
}
if (i == 0)
{
x = delta > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
else if (i == 1)
{
y = delta > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
else
{
z = delta > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
}
index = indexMap[z * 100 + y * 10 + x];
//压线了 或者 没有再深的层次了 则加入到当前节点
if (isPress || root.childs.Count <= 0)
{
if (root.objLst == null)
{
root.objLst = new List<OCObj>();
}
root.objLst.Add(obj);
obj.linkNode = root;
}
else
{
Insert(root.childs[index], obj);
}
}
static Dictionary<int, int> indexMap = new Dictionary<int, int>() {
{ 100+10+1,0 },//1 1 1 = 0
{ 100-10+1,1 },//1 0 1 = 1
{ 100+10-1,2 },//1 1 0 = 2
{ 100-10-1, 3 },//1 0 0 = 3
{ -100+10-1, 4 },//0 1 0 = 4 101 = 4
{ -100-10 -1, 5 },
{ -100+10 +1, 6 },
{ -100-10 +1, 7 },
};
public static void Insert(Node root, OCObj obj)
{
int index = 0;
bool isPress = false;//是否占用了节点的2个格子
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
float delta = obj.center[i] - root.center[i];
if (Mathf.Abs(delta) < obj.halfWidth)
{
isPress = true;
break;
}
if (delta > 0.0f) index |= (1 << i);
}
//压线了 或者 没有再深的层次了 则加入到当前节点
if (isPress || root.childs.Count <= 0)
{
if (root.objLst == null)
{
root.objLst = new List<OCObj>();
}
root.objLst.Add(obj);
obj.linkNode = root;
}
else
{
Insert(root.childs[index], obj);
}
}
上面的2种插入函数对应了2种创建函数
第一种插入函数比较容易理解:根据插入obj的坐标与节点坐标进行对比,确定XYZ的正负,组合成key = Z*100+Y*10+X,然后再字典中取对应的index
第一种10000次测试,深度为4,平均开销为25ms(new字典 3次遍历 if else3次判断)
第二种10000次测试,深度为4,平均开销为5ms(至多3次遍历,如果压线就break插入当前节点,两种方式中读取了gameObject的transform这个可以统一优化todo)
第二种函数函数最难理解的是确定obj的index
思路:
遍历3次 i区间[0-2]
默认index=0 使用二进制表示为 0000三个轴都为负
每次都进行了 1<<i 运算 可以发现三次运算结果是 1<<0 = 0001 1<<1 = 1*2^1 = 2 = 0010 1<<2 = 1*2^2 = 4 = 0100 即为XYZ三个轴
当i=0切obj.x-node.x > 0,index = 0000 | (1<<0) = 0000 | (1*2^0) = 0000 | 1 = 0000 | 0001 = 0001 = 1
第一次可以确定X 第二次可以确定Y 第三次可以确定Z 三次的index都是在与之前的index做 | 运算,可以求出并集,最终确定index



