二维数组
动态初始化

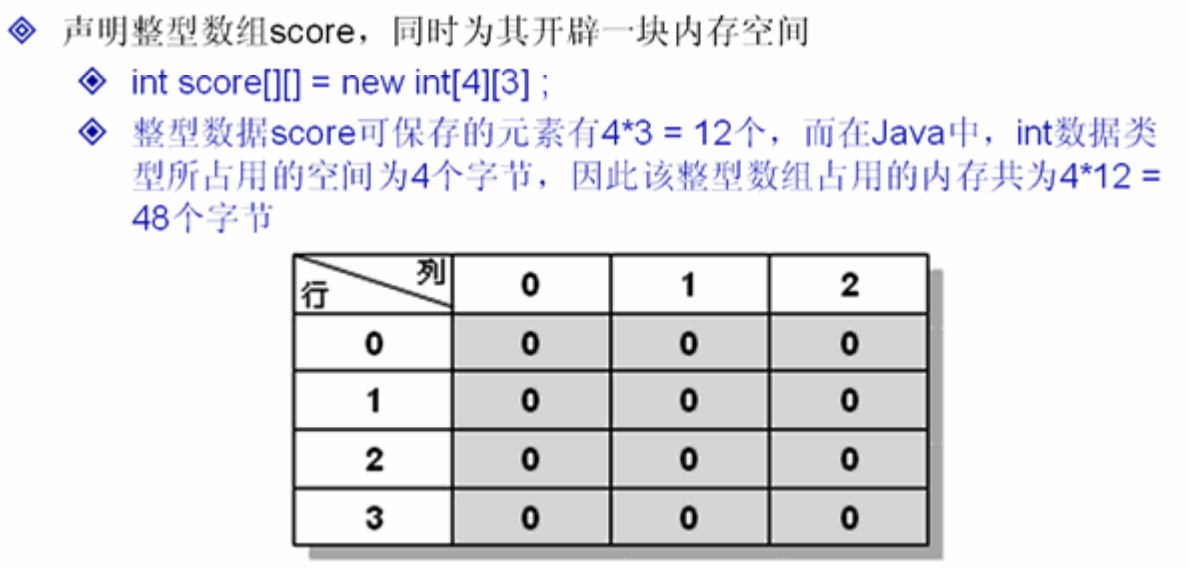
例1:
/* 二维数组动态初始化:声明、分配内存、赋值 */ public class ArrayDemo08 { public static void main(String[] args) { int score[][] = new int[4][3]; //声明并实例化二维数组(4行3列,可以理解成4个一维数组,每个数组中有3个元素) score[0][1] = 30; //为数组中的部分内容赋值 score[1][0] = 31; //为数组中的部分内容赋值 score[2][2] = 32; //为数组中的部分内容赋值 score[3][1] = 33; //为数组中的部分内容赋值 score[1][1] = 30; //为数组中的部分内容赋值 System.out.println("数组有几行?" + score.length); System.out.println("每行有几列?" + score[0].length); for(int i=0;i<score.length;i++){ //外层循环 for(int j=0;j< score[i].length;j++){ //内层循环 System.out.println(score[i][j] + "\t"); } System.out.println(""); //换行 } } }
运行结果:
数组有几行?4
每行有几列?3
0
30
0
31
30
0
0
0
32
0
33
0
静态初始化
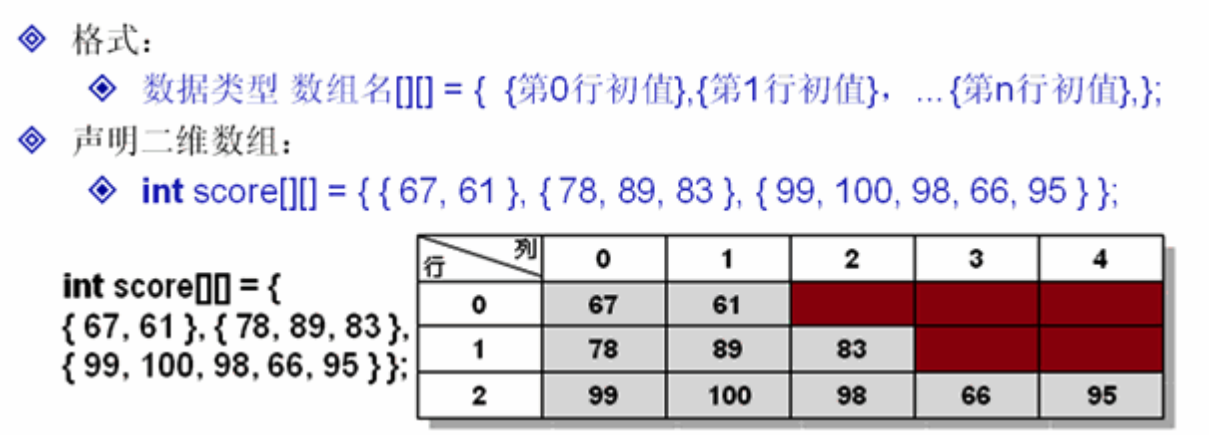
/* 二维数组静态初始化 */ public class ArrayDemo09 { public static void main(String[] args) { int score[][] = { {67,61},{78,89,83},{99,100,98,66,95} }; //静态初始化完成,每行的数组元素个数不一样 System.out.println("数组有几行?" + score.length); System.out.println("第0行有几列?" + score[0].length); System.out.println("第1行有几列?" + score[1].length); System.out.println("第2行有几列?" + score[2].length); for(int i=0;i< score.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<score[i].length;j++){ System.out.println(score[i][j] + "\t"); } System.out.println(""); } } }
运行结果:
数组有几行?3 第0行有几列?2 第1行有几列?3 第2行有几列?5 67 61 78 89 83 99 100 98 66 95



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号