环境: SQL Server 2012
疑问:同样的一条语句,使用Profile跟踪出来的消耗与单独拿出来执行的消耗存在非常大的差距
语句如下:
declare @str nvarchar(max) ; set @str = ' SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE 1 = 1 and flag != 0 and t1.isRestore=0 and t1.flag = @flag and t1.mebId=@mebId and addSubBusType in ( select ListValue from dbo.fn_splitstr(@inAddSubBusType,'','') ) and t1.UsedBeginTime <= @usedBeginTimeLessThenOrEqual and (convert(datetime,convert(varchar,t1.UsedEndTime,112),112)+1-1.0/3600/24) >= @usedEndTimeMoreThenOrEqual and (select count(0) from t3 where t3.configid=t1ConfigID and t3.begintime <= @checkInDateInLimitDateRange_1 and @checkInDateInLimitDateRange_2<=(convert(datetime,convert(varchar,t3.endtime,112),112)+1-1.0/3600/24))<=0 and UsedWeekID in ( select ListValue from dbo.fn_splitstr(@inWeekIdsSql,'','') ) ' exec sp_executesql @str, N' @flag int, @mebId int, @inAddSubBusType nvarchar(max), @usedBeginTimeLessThenOrEqual datetime, @usedEndTimeMoreThenOrEqual datetime, @checkInDateInLimitDateRange_1 datetime, @checkInDateInLimitDateRange_2 datetime, @inWeekIdsSql nvarchar(max)', @flag=1, @mebId=222144787, @inAddSubBusType='0, 11, 12, 52', @usedBeginTimeLessThenOrEqual='2017-06-13 00:00:00', @usedEndTimeMoreThenOrEqual='2017-06-13 00:00:00', @checkInDateInLimitDateRange_1='2017-06-13 00:00:00', @checkInDateInLimitDateRange_2='2017-06-13 00:00:00', @inWeekIdsSql='2, 1000001, 1000003, 1000004, 3000006, 3000007, 3000008'
备注:先不要吐槽以下2个条件的写法
(convert(datetime,convert(varchar,t1.UsedEndTime,112),112)+1-1.0/3600/24) >= @usedEndTimeMoreThenOrEqual @checkInDateInLimitDateRange_2<=(convert(datetime,convert(varchar,t3.endtime,112),112)+1-1.0/3600/24)
使用Profile跟踪出来的语句的执行消耗如下:
select top 1000 TextData , Reads , Writes , CPU --单位:毫秒 , Duration Duration --Duration单位:微秒 , HostName , ClientProcessID , ApplicationName , LoginName , SPID , StartTime , EndTime , ServerName , ObjectName , DatabaseName , RowCounts from ::fn_trace_gettable('~path\ProfileMonitor_20170614-15.trc',default) where LoginName = 'xxxx' order by StartTime desc
Profile跟踪出来对CPU的消耗非常高,这样的一条语句,并发非常高,造成了服务器几乎卡死
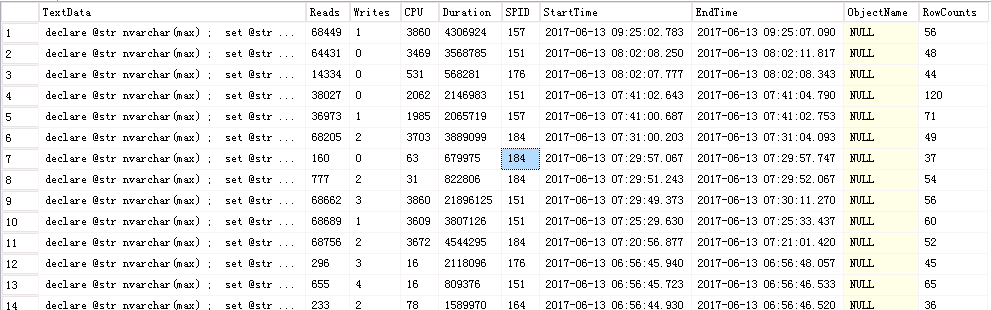
把语句拿出来单独执行,查看消耗情况
SQL Server 分析和编译时间: CPU 时间 = 0 毫秒,占用时间 = 0 毫秒。 SQL Server 执行时间: CPU 时间 = 0 毫秒,占用时间 = 0 毫秒。 SQL Server 分析和编译时间: CPU 时间 = 0 毫秒,占用时间 = 0 毫秒。 SQL Server 执行时间: CPU 时间 = 0 毫秒,占用时间 = 0 毫秒。 SQL Server 分析和编译时间: CPU 时间 = 0 毫秒,占用时间 = 0 毫秒。 (15 行受影响) 表 't3'。扫描计数 15,逻辑读取 38 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 表 '#B63AB884'。扫描计数 1,逻辑读取 15 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 表 'Workfile'。扫描计数 0,逻辑读取 0 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 表 'Worktable'。扫描计数 0,逻辑读取 0 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 表 'Worktable'。扫描计数 0,逻辑读取 0 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 表 't2'。扫描计数 1,逻辑读取 4 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 表 't4'。扫描计数 15,逻辑读取 15 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 46 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 表 't1'。扫描计数 1,逻辑读取 71 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 表 '#B72EDCBD'。扫描计数 1,逻辑读取 1 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。 (1 行受影响) SQL Server 执行时间: CPU 时间 = 15 毫秒,占用时间 = 59 毫秒。 SQL Server 执行时间: CPU 时间 = 15 毫秒,占用时间 = 60 毫秒。 SQL Server 分析和编译时间: CPU 时间 = 0 毫秒,占用时间 = 0 毫秒。 SQL Server 执行时间: CPU 时间 = 0 毫秒,占用时间 = 0 毫秒。
执行计划如下:
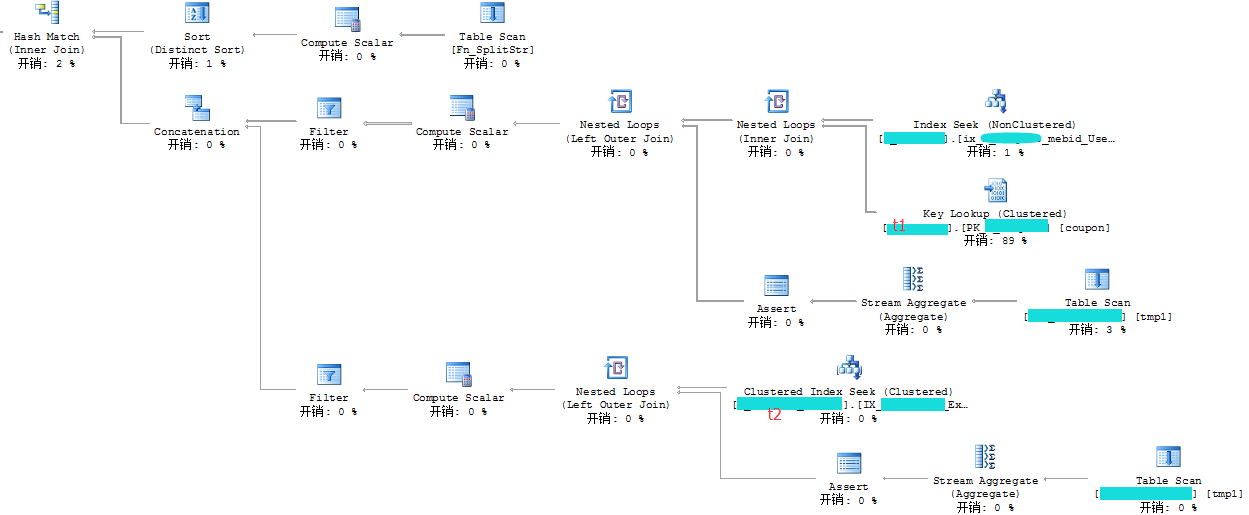
该用索引的地方已经使用了索引,而且消耗也不像Profile里跟踪出来的那么高。是什么原因造成在线上的程序中运行时消耗如此之大?
找不到原因, 只好试着把原来的执行缓存清除掉,让其重新生成
select decp.plan_handle , decp.usecounts , dest.[text] , deqp.query_plan from sys.dm_exec_cached_plans decp cross apply sys.dm_exec_sql_text(decp.plan_handle) dest cross apply sys.dm_exec_query_plan(decp.plan_handle) deqp where dest.[text] like '%@flag%' order by usecounts desc
根据以上语句得到的plan_handle,再执行
dbcc freeproccache(0x0600070057A88E01B0BC9E0D2600000001000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000)
plan_handle的值为0x0600070057A88E01B0BC9E0D2600000001000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000,之后再观察Profile,竟然没有发现没有跟踪到这条语句了。把Duration的值调整为10ms,之后,跟踪到的结果是这样的
select top 1000 TextData , Reads , Writes , CPU --单位:毫秒 , Duration/1000 Duration --Duration单位:微秒;Duration/1000单位:毫秒 , StartTime , EndTime , ServerName , ObjectName , DatabaseName , RowCounts from ::fn_trace_gettable('~path\ProfileMonitor_20170620-15.trc',default) where TextData not like '%sp_prepare%' order by StartTime desc
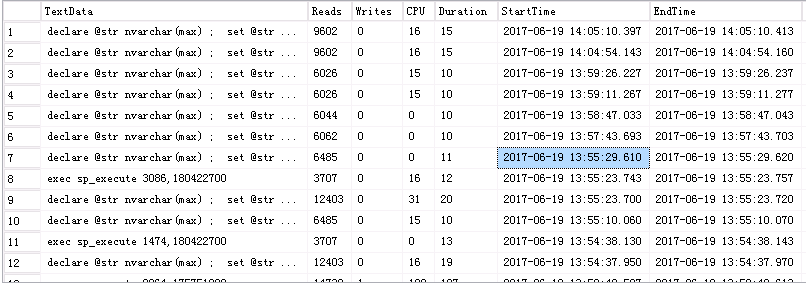
Reads虽然高,但是CPU却下降非常明显,而且,执行计划也发生了改变
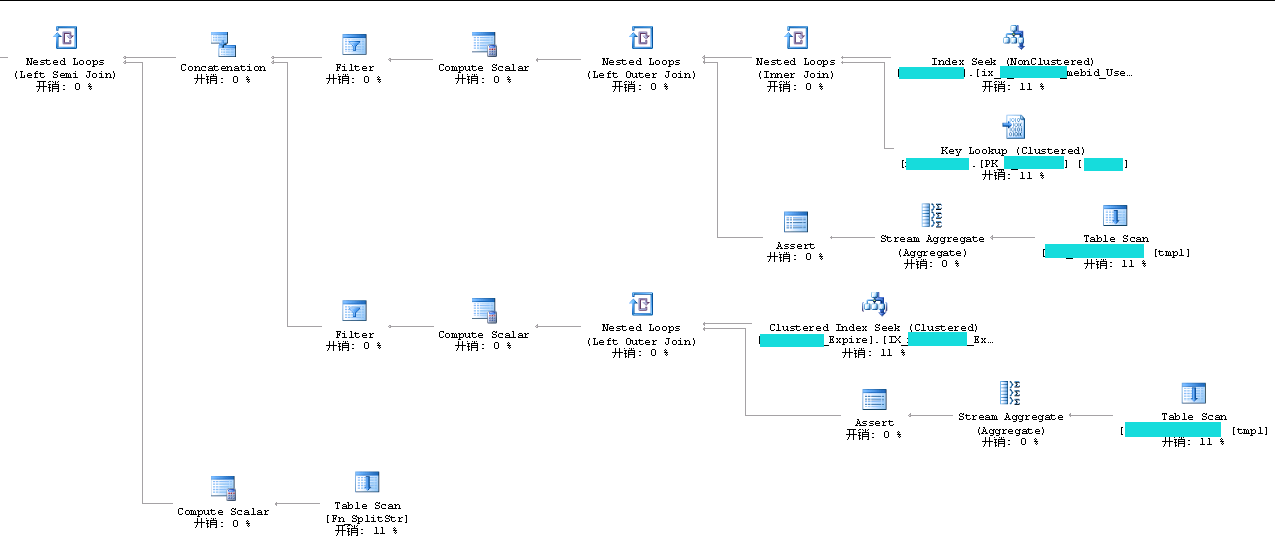
总结:当发现理想的执行效果与实际的执行效果存在很大差异的时候,可能就得要先确认缓存的执行计划是不是正确的。若不是,就需要做一下清空处理了。注意,在生产环境中,不能直接执行
dbcc freeporccache ;
否则会出现严重的性能问题。
以上,如有错谬,请不吝指正。



