[LeetCode] 2192. All Ancestors of a Node in a Directed Acyclic Graph
You are given a positive integer n representing the number of nodes of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive).
You are also given a 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [fromi, toi] denotes that there is a unidirectional edge from fromi to toi in the graph.
Return a list answer, where answer[i] is the list of ancestors of the ith node, sorted in ascending order.
A node u is an ancestor of another node v if u can reach v via a set of edges.
Example 1:
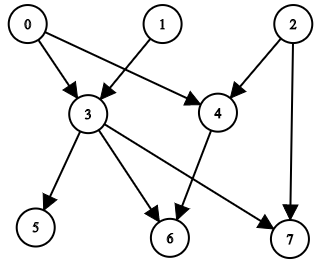
Input: n = 8, edgeList = [[0,3],[0,4],[1,3],[2,4],[2,7],[3,5],[3,6],[3,7],[4,6]]
Output: [[],[],[],[0,1],[0,2],[0,1,3],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,2,3]]
Explanation:
The above diagram represents the input graph.
- Nodes 0, 1, and 2 do not have any ancestors.
- Node 3 has two ancestors 0 and 1.
- Node 4 has two ancestors 0 and 2.
- Node 5 has three ancestors 0, 1, and 3.
- Node 6 has five ancestors 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- Node 7 has four ancestors 0, 1, 2, and 3.
Example 2:
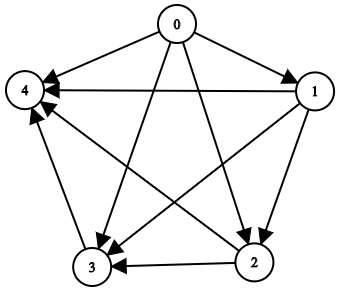
Input: n = 5, edgeList = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[3,4]]
Output: [[],[0],[0,1],[0,1,2],[0,1,2,3]]
Explanation:
The above diagram represents the input graph.
- Node 0 does not have any ancestor.
- Node 1 has one ancestor 0.
- Node 2 has two ancestors 0 and 1.
- Node 3 has three ancestors 0, 1, and 2.
- Node 4 has four ancestors 0, 1, 2, and 3.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000
0 <= edges.length <= min(2000, n * (n - 1) / 2)
edges[i].length == 2
0 <= fromi, toi <= n - 1
fromi != toi
There are no duplicate edges.
The graph is directed and acyclic.
有向无环图中一个节点的所有祖先。
给你一个正整数 n ,它表示一个 有向无环图 中节点的数目,节点编号为 0 到 n - 1 (包括两者)。给你一个二维整数数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [fromi, toi] 表示图中一条从 fromi 到 toi 的单向边。
请你返回一个数组 answer,其中 answer[i]是第 i 个节点的所有 祖先 ,这些祖先节点 升序 排序。
如果 u 通过一系列边,能够到达 v ,那么我们称节点 u 是节点 v 的 祖先 节点。
思路
这里我用一个类似反向 DFS 的方法解决这道题。题意是找图中每个节点的祖先。因为图本身是有向无环图(DAG),每条边是有方向的,所以为了找祖先,我们可以在建图的时候把每条边反过来理解。比如如果有一条边是从 A 到 B 的,那么我们在建图的时候可以把 A 加到 B 的邻接表上,意思是如果从 B 出发,能走到他的祖先 A。
下面的步骤就跟一般的图的遍历很类似了,我们还是需要一个 boolean 数组记录遍历过程中每个点是否被访问到,具体参见代码。
复杂度
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
代码
Java实现
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> getAncestors(int n, int[][] edges) { List<Integer>[] graph = new List[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { graph[i] = new ArrayList<>(); } // 反向建图 for (int[] edge : edges) { graph[edge[1]].add(edge[0]); } List<Integer>[] res = new List[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { res[i] = new ArrayList<>(); } boolean[] visited = new boolean[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Arrays.fill(visited, false); dfs(graph, visited, i); visited[i] = false; // res[i] 不含 i for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (visited[j]) { res[i].add(j); } } } return Arrays.asList(res); } private void dfs(List<Integer>[] graph, boolean[] visited, int u) { visited[u] = true; for (int v : graph[u]) { if (!visited[v]) { dfs(graph, visited, v); } } } }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
2020-04-07 [LeetCode] 200. Number of Islands
2020-04-07 [LeetCode] 72. Edit Distance