[LeetCode] 662. Maximum Width of Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum width of the given tree.
The maximum width of a tree is the maximum width among all levels.
The width of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes that would be present in a complete binary tree extending down to that level are also counted into the length calculation.
It is guaranteed that the answer will in the range of a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
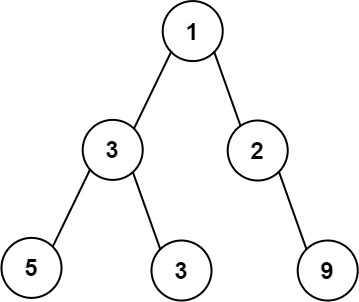
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] Output: 4 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the third level with length 4 (5,3,null,9).
Example 2:
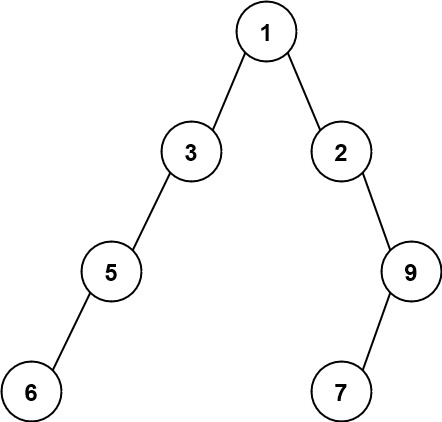
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7] Output: 7 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the fourth level with length 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7).
Example 3:
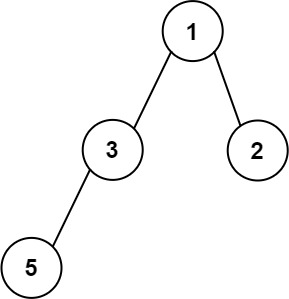
Input: root = [1,3,2,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the second level with length 2 (3,2).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
二叉树的最大宽度。
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。
树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。
每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些延伸到这一层的 null 节点,这些 null 节点也计入长度。
题目数据保证答案将会在 32 位 带符号整数范围内。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
题意是给一个结构近似于满二叉树 complete binary tree 的二叉树,请你返回他的最大宽度是多少。
题目中有一句话非常关键,这个树近似于一棵满二叉树。我们需要回忆满二叉树的特点,满二叉树除了最底层,每一层都是满的,如果最后一层不满足,那么也一定是从左往右尽量排满的。对于一棵满二叉树,对于任意一个父节点,如果这个父节点的 index = n 的话,这个节点的两个孩子的 index 则分别是 2n 和 2n + 1。这个画一下就知道了。
那么这道题的具体思路是,在进行常规的 BFS 遍历的同时,我们还需要另外一个 queue 来记录每个节点的 index。遍历每一层的时候,我们需要计算一下当前层的第一个节点和最后一个节点的index的差,这个差值就是题目所求的最大宽度。
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { 12 // corner case 13 if (root == null) { 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 // normal case 18 Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); 19 LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); 20 int res = 1; 21 queue.offer(root); 22 list.add(1); 23 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 24 int count = queue.size(); 25 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 26 TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); 27 int curIndex = list.removeFirst(); 28 if (cur.left != null) { 29 queue.offer(cur.left); 30 list.offer(curIndex * 2); 31 } 32 if (cur.right != null) { 33 queue.offer(cur.right); 34 list.offer(curIndex * 2 + 1); 35 } 36 } 37 if (list.size() >= 2) { 38 res = Math.max(res, list.peekLast() - list.peekFirst() + 1); 39 } 40 } 41 return res; 42 } 43 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号