[LeetCode] 787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] indicates that there is a flight from city fromi to city toi with cost pricei.
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return -1.
Example 1:
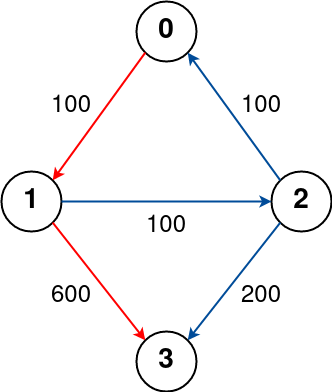
Input: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1
Output: 700
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 3 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 600 = 700.
Note that the path through cities [0,1,2,3] is cheaper but is invalid because it uses 2 stops.
Example 2:
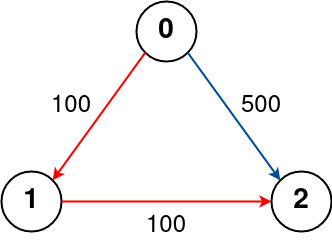
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
Output: 200
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 100 = 200.
Example 3:
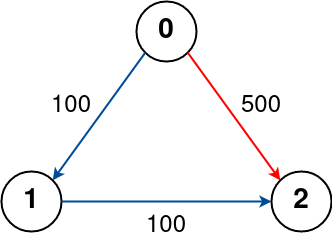
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with no stops from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 500.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 100
0 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)
flights[i].length == 3
0 <= fromi, toi < n
fromi != toi
1 <= pricei <= 104
There will not be any multiple flights between two cities.
0 <= src, dst, k < n
src != dst
K 站中转内最便宜的航班。
有 n 个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组 flights ,其中 flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] ,表示该航班都从城市 fromi 开始,以价格 pricei 抵达 toi。现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过 k 站中转的路线,使得从 src 到 dst 的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出 -1。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路一 - dijkstra, 超时
这个思路对,但是现在会超时。
大致思路是 dijkstra 算法。首先创建一个邻接矩阵,记录每两个城市之间的 price。然后创建一个关于 price 的最小堆,把(目前所花费的cost,下一个要去到的城市,剩余步数)放入这个最小堆,同时一开始的时候放入的初始值是(0, 起点city, K + 1)。这样遍历的时候,每次从最小堆 pop 出来一个元素,查看这个元素的下一个遍历到的 city 是否是最终的 dst,如果是,则返回 price;如果不是,同时剩余步数 > 0 的话,则遍历邻接表里面所有跟当前这个 city 有连通的部分,加入最小堆。
复杂度
时间O(nlogn)
空间O(n^2)
代码
Java实现
class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
int[][] g = new int[n][n];
for (int[] f : flights) {
g[f[0]][f[1]] = f[2];
}
PriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
// <price, source, stop>
// 因为K是允许中转的次数所以实际可以遍历到K + 1个城市
queue.offer(new int[] { 0, src, K + 1 });
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
int price = cur[0];
int city = cur[1];
int remainStops = cur[2];
if (city == dst) {
return price;
}
if (remainStops > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (g[city][i] != 0) {
queue.offer(new int[] { price + g[city][i], i, remainStops - 1 });
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
思路二 - Dijkstra + 剪枝
二刷我再提供一个不会超时的 BFS 的思路。既然是超时那么一定需要剪枝。我们思考一下对什么情况是可以剪枝的。我们可以创建一个额外的数组,记录走到每个 city 的 cost 是多少。我们还是正常创建图和做 BFS 遍历。当我们发现一条路径 from - to 的时候,我们看一下 to 这个城市是否已经被访问过,如果被访问过,看一下他之前记录的 cost 是多少,如果目前的 cost 大于之前记录的 cost,或者目前的 cost 甚至都大于走到 dst 的 cost 了,则不需要再看了,这条路径一定不是最优解。这个思路就相当于是在满足只能经过 k 个城市的同时,我们要看一下经过这 k 个城市的代价是多少,比如如果有任何一个方案走到某个中间城市的代价大于之前的方案的话,则当前这个方案就不需要再看了。
复杂度
时间O(V + E)
空间O(n)
代码
Java实现
class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
// 建立邻接表
int[][] g = new int[n][n];
for (int[] flight : flights) {
int from = flight[0];
int to = flight[1];
int cost = flight[2];
g[from][to] = cost;
}
// 记录结果
int[] res = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(res, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[] { src, 0 });
// 经过K个站点 = 经过K + 1条边
while (!queue.isEmpty() && k + 1 > 0) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
int from = cur[0];
int cost = cur[1];
for (int to = 0; to < n; to++) {
if (g[from][to] != 0) {
int newCost = cost + g[from][to];
if (newCost < res[to] && newCost < res[dst]) {
res[to] = newCost;
if (to != dst) {
queue.offer(new int[] { to, newCost });
}
}
}
}
}
k--;
}
return res[dst] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res[dst];
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号