[LeetCode] 314. Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal
Given the root of a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from top to bottom, column by column).
If two nodes are in the same row and column, the order should be from left to right.
Example 1:
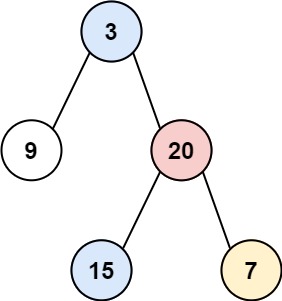
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Example 2:
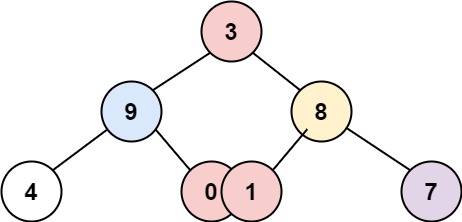
Input: root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7]
Output: [[4],[9],[3,0,1],[8],[7]]
Example 3:
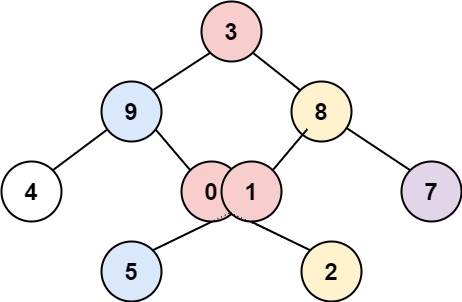
Input: root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7,null,null,null,2,5]
Output: [[4],[9,5],[3,0,1],[8,2],[7]]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
二叉树的垂直遍历。
给你一个二叉树的根结点,返回其结点按 垂直方向(从上到下,逐列)遍历的结果。
如果两个结点在同一行和列,那么顺序则为 从左到右。
思路
例子应该解释的很清楚了,思路是 BFS 层序遍历,需要用到一个 index 变量记录子节点相对于根节点的偏移量,同时需要用 hashmap<偏移量,相同偏移量的节点组成的list> 把相同偏移量的节点放在一起。
首先 BFS 层序遍历还是跟一般的 BFS 差不多,但是这里我做了两个 queue,一个存放节点,一个存放每个节点的偏移量(注意这里实际只存了 X 坐标的偏移量,这个题是有 followup 的,987题),这样 BFS 遍历的时候,可以同时得到被遍历节点的偏移量。min 和 max 的存在是记录最左和最右的偏移量,这样最后输出 res 的时候就可以从左往右按顺序输出了。
复杂度
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
代码
Java实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> verticalOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// corner case
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
// normal case
HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 记录节点之于根节点的偏移距离
Queue<Integer> dis = new LinkedList<>();
int min = 0;
int max = 0;
queue.offer(root);
dis.offer(0);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
int col = dis.poll();
if (!map.containsKey(col)) {
map.put(col, new ArrayList<>());
}
map.get(col).add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
dis.offer(col - 1);
min = Math.min(min, col - 1);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
dis.offer(col + 1);
max = Math.max(max, col + 1);
}
}
for (int i = min; i <= max; i++) {
res.add(map.get(i));
}
return res;
}
}
JavaScript实现
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var verticalOrder = function (root) {
let res = [];
// corner case
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
// normal case
let map = new Map();
let queue = [];
queue.push([root, 0]);
let min = 0;
let max = 0;
while (queue.length > 0) {
let cur = queue.shift();
let node = cur[0];
let col = cur[1];
if (!map.has(col)) {
map.set(col, []);
}
map.get(col).push(node.val);
if (node.left) {
queue.push([node.left, col - 1]);
min = Math.min(min, col - 1);
}
if (node.right) {
queue.push([node.right, col + 1]);
max = Math.max(max, col + 1);
}
}
for (let i = min; i <= max; i++) {
res.push(map.get(i));
}
return res;
};
相关题目
314. Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal
987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree


