[LeetCode] 110. Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as:
a binary tree in which the left and right subtrees of every node differ in height by no more than 1.
Example 1:
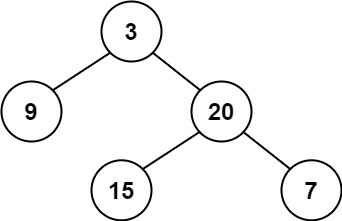
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: true
Example 2:
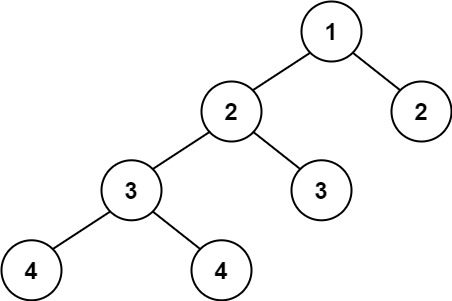
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] Output: false
Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: true
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -104 <= Node.val <= 104
平衡二叉树。
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
这个题我提供两种做法,一是通过后序遍历,判断高度是否符合条件。后序遍历的大致思路是先看左子树再看右子树再看当前节点。跑一下这个例子,
Given the following tree
[1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]:1 / \ 2 2 / \ 3 3 / \ 4 4
后序遍历先跑的是最底层的两个4,两者的高度都是1。再看上面一层的两个3,靠左的3因为有子树的关系所以高度是2,但是靠右的3高度是1,因为没有子树。同理,靠左的2的高度是3,靠右的2的高度是1。当遍历到这一层的时候因为两个2的高度差大于1了,会返回-1。因为树的高度一定是正数所以用-1来代表树的高度差不满足题意。
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
JavaScript实现
1 /** 2 * @param {TreeNode} root 3 * @return {boolean} 4 */ 5 var isBalanced = function (root) { 6 if (root === null) return true; 7 return helper(root) !== -1; 8 }; 9 10 var helper = function (root) { 11 if (root === null) return 0; 12 let left = helper(root.left); 13 let right = helper(root.right); 14 if (left == -1 || right == -1 || Math.abs(left - right) > 1) { 15 return -1; 16 } 17 return Math.max(left, right) + 1; 18 }
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { 12 if (root == null) { 13 return true; 14 } 15 return helper(root) != -1; 16 } 17 18 private int helper(TreeNode root) { 19 if (root == null) { 20 return 0; 21 } 22 int l = helper(root.left); 23 int r = helper(root.right); 24 if (l == -1 || r == -1 || Math.abs(l - r) > 1) { 25 return -1; 26 } 27 return Math.max(l, r) + 1; 28 } 29 }
第二种做法是类似104题的找树的最大高度的思路。如果左右子树的高度差大于1,则说明这个树不是balanced。时间空间复杂度都是O(n)。这个做法本质上也是后序遍历。
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 boolean balanced = true; 18 19 public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { 20 helper(root); 21 return balanced; 22 } 23 24 private int helper(TreeNode root) { 25 if (root == null) { 26 return 0; 27 } 28 int left = helper(root.left); 29 int right = helper(root.right); 30 if (Math.abs(right - left) > 1) { 31 balanced = false; 32 } 33 return Math.max(left, right) + 1; 34 } 35 }
相关题目
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree




