[LeetCode] 513. Find Bottom Left Tree Value
Given the root of a binary tree, return the leftmost value in the last row of the tree.
Example 1:
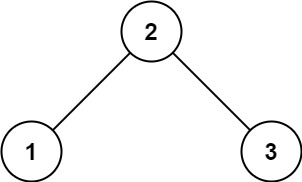
Input: root = [2,1,3]
Output: 1
Example 2:
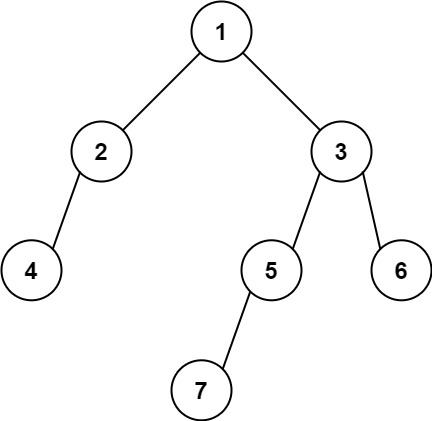
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
Output: 7
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
-231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
找树左下角的值。
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
思路 - BFS
首先 BFS 比较直观,只要按层序遍历的做法一层层把 node 塞进 queue。当遍历到最底层的时候,输出第一个塞进去的节点值即可。注意每层节点在塞入 queue 的时候应该是先塞右孩子再塞左孩子,原因是BFS的解法不看当前遍历到了第几层,只能通过这种方式才能保证最底层最靠左的叶子节点是最后被塞入 queue 的。如果按照第一个例子跑一遍,结果就是2 - 3 - 1而不是2 - 1 - 3.
复杂度
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
代码
Java实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
// corner case
if (root == null) {
return -1;
}
// normal case
int res = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
res = cur.val;
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
}
return res;
}
}
JavaScript实现
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var findBottomLeftValue = function (root) {
// corner case
if (root === null) {
return -1;
}
// normal case
let res = null;
let queue = [root];
while (queue.length > 0) {
let cur = queue.shift();
res = cur.val;
if (cur.right) {
queue.push(cur.right);
}
if (cur.left) {
queue.push(cur.left);
}
}
return res;
};
思路 - DFS
用DFS做的思路就稍微复杂一些。DFS 的做法会用到先序遍历,同时我们需要两个变量,height 记录当前遍历到的节点的深度,depth 记录当前遍历到的最大深度。当我们遍历到某个节点的时候,如果当前这个节点的深度 height 小于 depth,则说明当前这个节点一定不在最深层;否则这个节点是在最深层。同时因为我们是先遍历左子树的关系,所以当我们往某个左子树上走的时候,会记录第一个 height 被更新的左子树,这样深度最大的左孩子就会被记录下来了。
复杂度
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
代码
Java实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node. public class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode
* left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } }
*/
class Solution {
int res = 0;
int height = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return -1;
helper(root, 1);
return res;
}
public void helper(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (height < depth) {
res = root.val;
height = dpeth;
}
helper(root.left, depth + 1);
helper(root.right, depth + 1);
}
}



