HDU 2169 Computer[树形dp]
Computer
时限:1000ms
Problem Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.

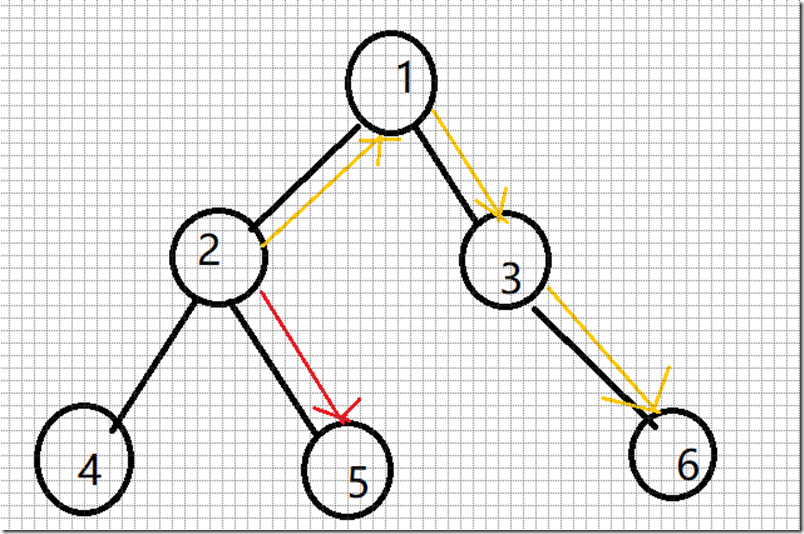
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
题意:
给你一个树状的电脑网络,求出每个点到其他点的最短距离。
思路:
我做搜索的时候做过这道题,当时用三个bfs过掉了,树的直径过掉的,今天练习数位dp,所以用数位dp写。思路很清晰,从u点出发有两个状态,一个是向下的最短,一个是过父亲节点,向上的最短距离。对于向下的很好解决,先从根节点一层一层的推上去。但是对于过父亲节点的情况,当u为其父亲节点向下的最远路径上的一点的时候,可能是u->u的父亲节点->u->u的子节点。所以要记录u的子树的次远距离,这样就当上面的情况发生的时候我们选择次远的距离作为从该点出发的最远距离。
dp[u][0]表示u向下走的最远距离,dp[u][1]表示u向下走的次远距离,dp[u][2]表示向上走的最远距离。
对于这棵树上的节点2来说,2经过子树的最远距离是dp[2][0](红颜色的),利用dfs每次向上更新节点的就能记录。
对于节点2经过父亲节点的最远距离,要更麻烦点。首先已经跑完了第一个dfs知道了每个点到它子树下的最远距离。通过观察可以发现2过他父亲节点的最远距离就是2到1的距离加上1到它子树的叶子的最远距离。但是这样会出现一个问题,如果最远距离是(1-2-4)就会得到最远的距离是(2-1-2-4)很明显是错误的。因为如此,要用一个dp[2][1]记录次远的距离,当第一个dfs更新到1节点的时候,记录下次远的距离。1的节点是2和3,要是2被选中为最远的距离,那么3就是次远的,这样当2向上访问的判断他是不是最长的那个(dp[v][0] + edge[i].val == dp[u][0]) ,要是最长的就换用次长的边
#include "stdio.h" #include "vector" #include "string.h" #include "algorithm" using namespace std; const int maxn = 10000 + 10; int head[maxn]; struct node { int to, next, val; } edge[maxn]; int tot = 0; int dp[maxn][3]; void add_edge(int u,int v,int w) { edge[tot].to = v; edge[tot].val = w; edge[tot].next = head[u]; head[u] = tot++; } void dfs1(int u) { for (int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) { int v = edge[i].to; dfs1(v); int sval = dp[v][0] + edge[i].val; if (sval >= dp[u][0]) { dp[u][1] = dp[u][0]; dp[u][0] = sval; } else if (sval > dp[u][1]) dp[u][1] = sval; } } void dfs2(int u) { for (int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) { int v = edge[i].to; if (dp[v][0] + edge[i].val == dp[u][0]) dp[v][2] = max(dp[u][2], dp[u][1]) + edge[i].val; else dp[v][2] = max(dp[u][2], dp[u][0]) + edge[i].val; dfs2(v); } } void init() { memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp)); tot = 0; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { int n; while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { init(); for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { int u, w; scanf("%d%d", &u, &w); add_edge(u, i, w); } dfs1(1); dfs2(1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { printf("%d\n", max(dp[i][0], dp[i][2])); } } return 0; }
再附上曾经用树的直径A掉的代码。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define MAXN 10010 using namespace std; struct node{ int from, to, val, next; } edge[MAXN*2]; int dist1[MAXN], head[MAXN], edgenum, s, dist2[MAXN]; int ans; bool vis[MAXN]; void init() { memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); edgenum = 0; } void addEdge(int x, int y, int z) { edge[edgenum].from = x; edge[edgenum].to = y; edge[edgenum].val = z; edge[edgenum].next = head[x]; head[x] = edgenum++; } void bfs1(int x) { queue<int> que; ans = 0; memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis)); memset(dist1, 0, sizeof(dist1)); while (!que.empty()) que.pop(); que.push(x); vis[x] = true; while (que.size()) { int a = que.front(); que.pop(); for (int i = head[a]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) { int b = edge[i].to; if (!vis[b] && dist1[b] < dist1[a] + edge[i].val) { dist1[b] = dist1[a] + edge[i].val; if(ans < dist1[b]) { ans = dist1[b]; s = b; } vis[b] = true; que.push(b); } } } }void bfs2(int x) { queue<int> que; ans = 0; memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis)); memset(dist2, 0, sizeof(dist2)); while (!que.empty()) que.pop(); que.push(x); vis[x] = true; while (que.size()) { int a = que.front(); que.pop(); for (int i = head[a]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) { int b = edge[i].to; if (!vis[b] && dist2[b] < dist2[a] + edge[i].val) { dist2[b] = dist2[a] + edge[i].val; if(ans < dist2[b]) { ans = dist2[b]; s = b; } vis[b] = true; que.push(b); } } } } int main() { int a, b, c, n, m; while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { init(); for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); addEdge(i, a, b); addEdge(a, i, b); } bfs1(1); bfs1(s); bfs2(s); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { printf("%d\n", max(dist1[i], dist2[i])); } } return 0; }
本文作者: zprhhs
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/cniwoq/p/7246997.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· [AI/GPT/综述] AI Agent的设计模式综述