spring-restTemplate-网络请求
1,引言
现如今的 IT 项目,由服务端向外发起网络请求的场景,基本上处处可见!
传统情况下,在服务端代码里访问 http 服务时,一般会使用 JDK 的 HttpURLConnection 或者 Apache 的 HttpClient,不过这种方法使用起来太过繁琐,而且 api 使用起来非常的复杂,还得操心资源回收。
RestTemplate是一个执行HTTP请求的同步阻塞式工具类,它仅仅只是在 HTTP 客户端库(例如 JDK HttpURLConnection,Apache HttpComponents,okHttp 等)基础上,封装了更加简单易用的模板方法 API,方便程序员利用已提供的模板方法发起网络请求和处理,能很大程度上提升我们的开发效率
2,环境配置
1,Spring 环境下
RestTemplate 在 spring-web 包中,需要引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2,SpringBoot 环境下
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
从 spring 某个版本开始,默认不生成 RestTemplate bean,需要我们自己注入
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfig {
/**
* 没有实例化RestTemplate时,初始化RestTemplate
* @return
*/
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(RestTemplate.class)
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
return restTemplate;
}
}
3,RestTemplate 底层实现
1. 源码分析
RestTemplate 有一个非常重要的基类叫做 HttpAccessor,可以理解为用于HTTP接触访问的基础类。
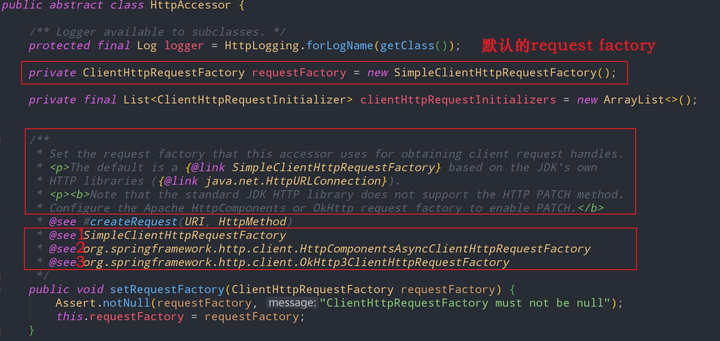
总结:
-
RestTemplate 支持至少三种HTTP客户端库,也就是 ClientHttpRequestFactory 的子类。
- SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory。对应的HTTP库是java JDK自带的HttpURLConnection。
- HttpComponentsAsyncClientHttpRequestFactory。对应的HTTP库是Apache HttpComponents。
- OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory。对应的HTTP库是OkHttp
-
java JDK自带的HttpURLConnection是默认的底层HTTP实现客户端
-
SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory,即java JDK自带的HttpURLConnection不支持HTTP协议的Patch方法,如果希望使用Patch方法,需要将底层HTTP客户端实现切换为Apache HttpComponents 或 OkHttp
-
可以通过设置 setRequestFactory 方法,来切换 RestTemplate 的底层HTTP客户端实现类库。
2. 切换底层实现方法
1. 切换为 OKHttp
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.squareup.okhttp3/okhttp -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3</groupId>
<artifactId>okhttp</artifactId>
<version>3.12.0</version>
</dependency>
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(getClientHttpRequestFactory());
return restTemplate;
}
private ClientHttpRequestFactory getClientHttpRequestFactory(){
OkHttpClient okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.writeTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.readTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
return new OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory(okHttpClient);
}
要注意一下版本。
2. 切换为 Apache HttpClient
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.httpcomponents/httpclient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.10</version>
</dependency>
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(getClientHttpRequestFactory());
return restTemplate;
}
/**
* 使用 appach 的 HttpClient 作为底层客户端
* @return
*/
private ClientHttpRequestFactory getClientHttpRequestFactory() {
int timeout = 1_000;
RequestConfig config = RequestConfig.custom()
.setConnectTimeout(timeout)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(timeout)
.setSocketTimeout(timeout)
.build();
CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder
.create()
.setDefaultRequestConfig(config)
.build();
return new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(client);
}
据说 OkHttp > Apache HttpComponents > HttpURLConnection
4. 拦截器设置
1. 定义一个拦截器
public class RestTemplateInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
System.out.println("拦截器!!!");
ClientHttpResponse response = execution.execute(request, body);
return response;
}
}
2. 给 restTemplate 设置拦截器
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(getClientHttpRequestFactory());
restTemplate.setInterceptors(Collections.singletonList(new RestTemplateInterceptor()));
return restTemplate;
}
5. RestTemplate Api
1. get 请求
-
getForObject():返回值是HTTP协议的响应体内容
-
getForEntity():返回的是ResponseEntity,ResponseEntity是对HTTP响应的封装,除了包含响应体,还包含HTTP状态码、contentType、contentLength、Header等信息
getForObject 方法
<T> T getForObject(URI url, Class<T> responseType) throws RestClientException;
/** url 请求路径,responseType 返回类型,uriVariables URL 上参数 */
<T> T getForObject(String url, Class<T> responseType, Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/** url 请求路径,responseType 返回类型,uriVariables 请求参数*/
<T> T getForObject(String url, Class<T> responseType, Map<String, ?> uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/**
* 无参
* */
Dog dog = restTemplate.getForObject(url + "/get", Dog.class);
System.out.println(dog);
/**
* path 参数
* */
Dog dog1 = restTemplate.getForObject(url + "/get/path/{code}", Dog.class, "不太聪明");
System.out.println(dog1);
/**
* restful 参数
* */
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "张飞");
map.put("color", "green");
Dog dog2 = restTemplate.getForObject(url + "/get/restful?name={name}&color={color}", Dog.class, map);
System.out.println(dog2);
getForEntity 方法
//无参
<T> ResponseEntity<T> getForEntity(URI url, Class<T> responseType) throws RestClientException;
//路径参数
<T> ResponseEntity<T> getForEntity(String url, Class<T> responseType, Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
//restful 参数
<T> ResponseEntity<T> getForEntity(String url, Class<T> responseType, Map<String, ?> uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/**
* 无参
* */
ResponseEntity<Dog> res = restTemplate.getForEntity(url + "/get", Dog.class);
System.out.println( res.getStatusCode());
System.out.println( res.getBody() );
/**
* path 参数
* */
ResponseEntity<Dog> res1 = restTemplate.getForEntity(url + "/get/path/{code}", Dog.class, "不太聪明");
System.out.println( res1.getStatusCode());
System.out.println( res1.getBody() );
/**
* restful 参数
* */
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "张飞");
map.put("color", "green");
ResponseEntity<Dog> res2 = restTemplate.getForEntity(url + "/get/restful?name={name}&color={color}", Dog.class, map);
System.out.println( res2.getStatusCode());
System.out.println( res2.getBody() );
2. post 请求
- postForObject():返回值是HTTP协议的响应体body内容
- postForEntity():返回的是ResponseEntity,ResponseEntity是对HTTP响应的封装,除了包含响应体,还包含HTTP状态码、contentType、contentLength、Header等信息
- postForLocation:使用POST创建一个新资源,返回UTI对象,可以从响应中返回Location报头。
postForObject 方法
/** url 请求路径,request 请求体,responseType 返回类型 */
<T> T postForObject(URI url, @Nullable Object request, Class<T> responseType) throws RestClientException;
/** uriVariables 路劲里的参数 */
<T> T postForObject(String url, @Nullable Object request, Class<T> responseType,
Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/** uriVariables 请求参数 */
<T> T postForObject(String url, @Nullable Object request, Class<T> responseType,
Map<String, ?> uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/**
* 无参
* */
Dog dog = restTemplate.postForObject(url + "/api", null, Dog.class);
System.out.println(dog);
/**
* path 参数
* */
Dog dog1 = restTemplate.postForObject(url + "/api/path/{code}", null, Dog.class, "不太聪明");
System.out.println(dog1);
/**
* 表单 参数 表单参数(专用map)
* */
MultiValueMap<String,String> map = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
map.add("name", "张飞");
map.add("color", "green");
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED);
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String,String>> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(map,httpHeaders);
Dog dog2 = restTemplate.postForObject(url + "/api/restful", requestEntity, Dog.class);
System.out.println(dog2);
/**
* json
* */
Dog d = new Dog("李白", "得瑟");
Dog dog3 = restTemplate.postForObject(url + "/api/json", d, Dog.class);
System.out.println(dog3);
postForEntity 方法
/** url 请求路径,request 请求体,responseType 返回类型 */
<T> ResponseEntity<T> postForEntity(URI url, @Nullable Object request, Class<T> responseType)
throws RestClientException;
/** uriVariables 路劲里的参数 */
<T> ResponseEntity<T> postForEntity(String url, @Nullable Object request, Class<T> responseType,
Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/** uriVariables 请求参数 */
<T> ResponseEntity<T> postForEntity(String url, @Nullable Object request, Class<T> responseType,
Map<String, ?> uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/**
* 无参
* */
ResponseEntity<Dog> entity = restTemplate.postForEntity(url + "/api", null, Dog.class);
System.out.println(entity.getBody());
/**
* path 参数
* */
ResponseEntity<Dog> entity1 = restTemplate.postForEntity(url + "/api/path/{code}", null, Dog.class, "不太聪明");
System.out.println(entity1.getBody());
/**
* 表单 参数
* */
//表单参数(专用map)
MultiValueMap<String,String> map = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String,String>();
map.add("name", "张飞");
map.add("color", "green");
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED);
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String,String>> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(map,httpHeaders);
ResponseEntity<Dog> entity2 = restTemplate.postForEntity(url + "/api/restful", requestEntity, Dog.class);
System.out.println(entity2.getBody());
/**
* json
* */
Dog d = new Dog("李白", "得瑟");
ResponseEntity<Dog> entity3 = restTemplate.postForEntity(url + "/api/json", d, Dog.class);
System.out.println(entity3.getBody());
/**
* json 封装请求体
* */
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
ResponseEntity<Dog> entity4 = restTemplate.postForEntity(url + "/api/json", new HttpEntity<>(d,headers), Dog.class);
System.out.println(entity4.getBody());
3. exchange 请求
exchange 通用请求类型方法,可以自己组装各种各样的请求。
/**
* url 请求地址
* method 请求方式,get、post 等
* requestEntity 请求体
* responseType 返回类型
* uriVariables 路径中的参数
*/
<T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(String url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable HttpEntity<?> requestEntity,
Class<T> responseType, Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/**
* uriVariables 请求参数
*/
<T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(String url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable HttpEntity<?> requestEntity,
Class<T> responseType, Map<String, ?> uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
<T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(URI url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable HttpEntity<?> requestEntity,
Class<T> responseType) throws RestClientException;
<T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(String url,HttpMethod method, @Nullable HttpEntity<?> requestEntity,
ParameterizedTypeReference<T> responseType, Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
/**
* responseType 返回 List<T> 这种类型的时候,要用这个, Class<T> 表示不了
*/
<T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(String url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable HttpEntity<?> requestEntity,
ParameterizedTypeReference<T> responseType, Map<String, ?> uriVariables) throws RestClientException;
<T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(URI url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable HttpEntity<?> requestEntity,
ParameterizedTypeReference<T> responseType) throws RestClientException;
<T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(RequestEntity<?> requestEntity, Class<T> responseType)
throws RestClientException;
<T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(RequestEntity<?> requestEntity, ParameterizedTypeReference<T> responseType)
throws RestClientException;
//无参
ResponseEntity<Dog> e1 = restTemplate.exchange(url + "/api", HttpMethod.GET, null, Dog.class);
System.out.println( e1.getBody() );
//path 参数
ResponseEntity<Dog> e2 = restTemplate.exchange(url + "/api/path/{code}", HttpMethod.GET, null, Dog.class, "啥子");
System.out.println( e2.getBody() );
//表单参数
MultiValueMap<String,String> map = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String,String>();
map.add("name", "张飞");
map.add("color", "green");
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED);
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String,String>> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(map,httpHeaders);
ResponseEntity<Dog> e3 = restTemplate.exchange(url + "/api/restful", HttpMethod.POST, requestEntity, Dog.class);
System.out.println(e3.getBody());
//json 参数
Dog d1 = new Dog("尸鬼", "李贺");
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<Dog> dogHttpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(d1, headers);
ResponseEntity<Dog> e4 = restTemplate.exchange(url + "/api/json", HttpMethod.POST, dogHttpEntity, Dog.class);
System.out.println(e4.getBody());
//返回结果是 list<T> 这种格式
ResponseEntity<List<Dog>> e5 = restTemplate.exchange(url + "/api/list", HttpMethod.GET, null, new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<Dog>>() {
@Override
public Type getType() {
return super.getType();
}
});
System.out.println( e5.getBody() );
4. 文件上传下载
@RequestMapping("/file/upload")
public void fileDemo(){
// 请求头设置,multipart/form-data格式的数据
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA);
//提交参数
String path = "C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\local-file\\jsStream.js";
MultiValueMap<String, Object> param = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
param.add("file", new FileSystemResource(new File(path)));
param.add("name", "小三子");
// 组装请求体
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, Object>> request = new HttpEntity<>(param, headers);
ResponseEntity<Dog> exchange = restTemplate.postForEntity("http://localhost:8080/file/upload", request, null);
System.out.println(exchange.getStatusCode());
}
/**
* 下载
* */
@RequestMapping("/file/download")
public void fileDemo1() throws IOException {
//发起请求(响应内容为字节文件)
ResponseEntity<byte[]> response = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8080/file/download", byte[].class);
System.out.println( response.getStatusCode() );
Files.write(Paths.get( "C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\local-file\\dd"), response.getBody() );
}
上述文件下载的方式,是一次性将响应内容加载到客户端内存中,然后再从内存中将文件写入到磁盘中,这种方式适用于一些小文件的下载。如果遇到大的文件,可能会爆内存。之后我们使用 execute 方法处理。
5. execute 方法
其内部调用的 doExecute 方法,是几乎所有方法最终的走向
/** requestCallback 对请求的处理,responseExtractor 对响应的处理 */
<T> T execute(URI url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable RequestCallback requestCallback,
@Nullable ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor) throws RestClientException;
<T> T execute(String url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable RequestCallback requestCallback,
@Nullable ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor, Map<String, ?> uriVariables)
throws RestClientException;
<T> T execute(String url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable RequestCallback requestCallback,
@Nullable ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor, Object... uriVariables)
throws RestClientException;
doExecute 方法源码:
@Nullable
protected <T> T doExecute(URI url, @Nullable HttpMethod method, @Nullable RequestCallback requestCallback, @Nullable ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor) throws RestClientException {
Assert.notNull(url, "URI is required");
Assert.notNull(method, "HttpMethod is required");
ClientHttpResponse response = null;
Object var14;
try {
//1.生成请求
ClientHttpRequest request = this.createRequest(url, method);
if (requestCallback != null) {
//2.设置header
requestCallback.doWithRequest(request);
}
//3.执行请求
response = request.execute();
//4.处理响应
this.handleResponse(url, method, response);
//5.返回执行结果
var14 = responseExtractor != null ? responseExtractor.extractData(response) : null;
} catch (IOException var12) {
String resource = url.toString();
String query = url.getRawQuery();
resource = query != null ? resource.substring(0, resource.indexOf(63)) : resource;
throw new ResourceAccessException("I/O error on " + method.name() + " request for \"" + resource + "\": " + var12.getMessage(), var12);
} finally {
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
}
return var14;
}
此方法并没有对外暴露,只能通过继承调用。可以看到我们每次请求的时候内部会发生这几个步骤:
- 生成请求
- 设置header
- 执行请求
- 处理响应
- 返回执行结果
RequestCallback 接口 官方介绍
RequestCallback用于操作ClientHttpRequest的代码的回调接口。允许操作请求头,并写入请求体。
在RestTemplate内部使用,但对应用程序代码也很有用。有以下两个实现类:
- AcceptHeaderRequestCallback:只处理请求头回调,用于restTemplate.getXXX()方法;
- HttpEntityRequestCallback:继承AcceptHeaderRequestCallback,可以处理请求头和body,用于restTemplate.putXXX()、restTemplate.postXXX()和restTemplate.exchange()等方法。
ResponseExtractor 接口
响应提取器,主要就是用来从Response中提取数据。RestTemplate请求完成后,都是通过它来从ClientHttpResponse提取出指定内容,比如:请求头、请求body等。
ResponseExtractor有三个实现类:
- HeadersExtractor:用于提取请求头
- HttpMessageConverterExtractor:用于提取响应body体内容
- ResponseEntityResponseExtractor:内部借助HttpMessageConverterExtractor提取body体(委托模式),然后将body和响应头、状态封装成ResponseEntity对象返回调用者。
下载大文件
/**
* 下载
* */
@RequestMapping("/file/download")
public void fileDemo1() throws Exception {
//请求地址
String url = "http://localhost:8080/file/download";
//定义请求头的接收类型
RequestCallback requestCallback = clientHttpRequest
-> clientHttpRequest.getHeaders()
.setAccept(Arrays.asList(MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM,MediaType.ALL));
//下载文件保存路径
File savePath = new File("C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\local-file\\");
if (!savePath.isDirectory()){
savePath.mkdirs();
}
Path path = Paths.get(savePath.getPath() + File.separator + "ssss.zip");
try {
//对响应结果进行流式处理,而不是一次性将响应结果全部加载到内存
restTemplate.execute(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestCallback,clientHttpResponse
-> {
//每响应一次就写入磁盘一次,不在内存中逗留
Files.copy(Objects.requireNonNull(clientHttpResponse.getBody(),"下载文件失败!"), path);
return null;
});
}catch (Exception e){
throw new Exception("文件下载异常或已经存在!");
}
}
6. 负载均衡的 restTemplate
RestTemplate 可以跟服务注册一同实现负载均衡调用。
1. 使用 @LoadBalanced 修饰 RestTemplate
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
2. 接口
@RequestMapping("/c2")
public String c2(){
//服务名
String server_name = "eureka-product";
//组装请求 这里一个巨坑:@LoadBalanced RestTemplate 严格(推荐连字符) 统一改为 eureka-product
ResponseEntity<String> forEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://"+ server_name +"/product/test/i1", String.class, new HashMap<>());
System.out.println( "调用服务结果:" + forEntity.getBody());
return forEntity.getBody();
}
参考文献
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/166214440
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52596258/article/details/127604909


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号