Linux下的SELINUX
理解Linux下的SELinux
长久以来,每当遇到授权问题或者新安装的主机,我的第一反应是通过setenforce 0命令禁用SELinux,来减少产生的权限问题,但是这并不是一个良好的习惯。这篇文章尝试对SELinux的基本概念和用法进行简单介绍,并且提供一些更深入的资料。
Linux下默认的接入控制是DAC,其特点是资源的拥有者可以对他进行任何操作(读、写、执行)。当一个进程准备操作资源时,Linux内核会比较进程和资源的UID和GID,如果权限允许,就可以进行相应的操作。此种方式往往会带来一些问题,如果一个进程是以root的身份运行,也就意味着他能够对系统的任何资源进行操作,而且不被限制。 假如我们的软件存在漏洞呢?这个往往是一个灾难性的问题。因此,就引出了另外的一种安全接入控制机制MAC,Linux下的一种现实是SELinux,也就是我们将要讨论的内容。
基本概念
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
SELinux 属于MAC的具体实现,增强了Linux系统的安全性。MAC机制的特点在于,资源的拥有者,并不能决定谁可以接入到资源。具体决定是否可以接入到资源,是基于安全策略。而安全策略则是有一系列的接入规则组成,并仅有特定权限的用户有权限操作安全策略。
一个简单的例子,则是一个程序如果要写入某个目录下的文件,在写入之前,一个特定的系统代码,将会依据进程的Context和资源的Context查询安全策略,并且根据安全策略决定是否允许写入文件。
Flask Security Architecture
SELinux的软件设计架构是参照Flask,Flask是一种灵活的操作系统安全架构,并且在Fluke research operating system中得到了实现。Flask的主要特点是把安全策略执行代码和安全策略决策代码,划分成了两个组件。安全策略决策代码在Flask架构中称作Security Server。除了这两个组件以外,另外一个组件Vector Cache(AVC), 主要提供策略决策结果的缓存,以此提高Security Server的性能。其具体执行流程为,安全策略执行代码通过AVC查询Security Server的安全策略决策结果,并将其缓存以备下次使用。
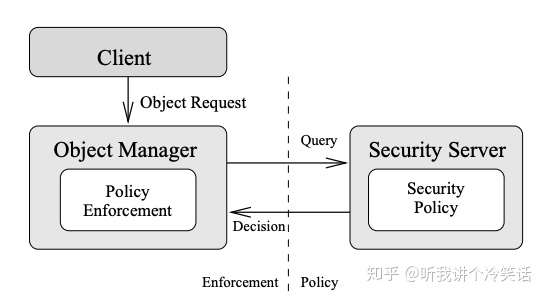 The Flask Security Architecture: System Support for Diverse Security Policies
The Flask Security Architecture: System Support for Diverse Security Policies
Linux Security Module
前面两部分介绍了MAC机制和Flask架构,最终SELinux的实现是依赖于Linux提供的Linux Security Module框架简称为LSM。其实LSM的名字并不是特别准确,因为他并不是Linux模块,而是一些列的hook,同样也不提供任何的安全机制。LSM的的重要目标是提供对linux接入控制模块的支持。
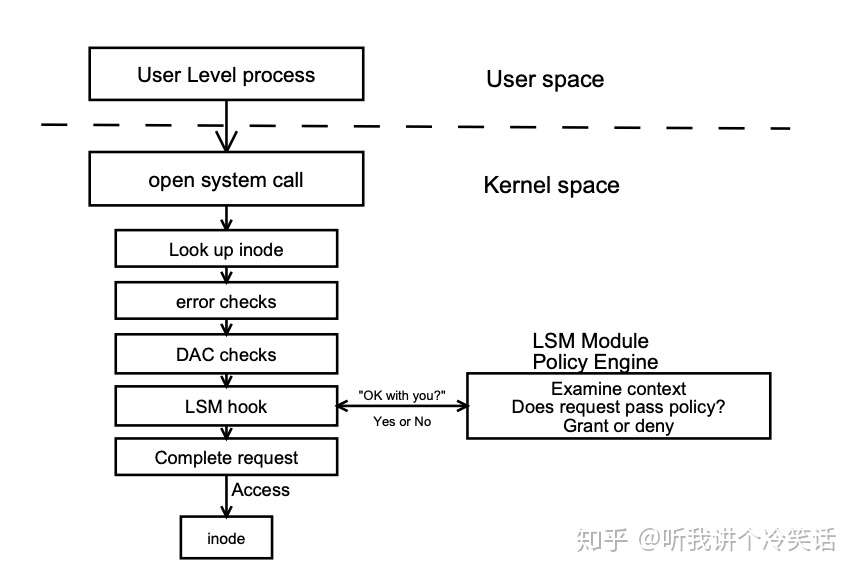 Linux Security Module Framework
Linux Security Module Framework
LSM 在内核数据结构中增加了安全字段,并且在重要的内核代码(系统调用)中增加了hook。可以在hook中注册回调函数对安全字段进行管理,以及执行接入控制。
SELinux
Security Enhanced Linux(SELinux) 为Linux 提供了一种增强的安全机制,其本质就是回答了一个“Subject是否可以对Object做Action?”的问题,例如 Web服务可以写入到用户目录下面的文件吗?其中Web服务就是Subject而文件就是Object,写入对应的就是Action。
依照上面的例子,我们引入了几个概念,分别是Subject、Object、Action、以及例子没有体现出来的Context:
- Subject: 在SELinux里指的就是进程,也就是操作的主体。
- Object: 操作的目标对象,例如 文件
- Action: 对Object做的动作,例如 读取、写入或者执行等等
- Context: Subject和Object都有属于自己的Context,也可以称作为Label。Context有几个部分组成,分别是SELinux User、SELinux Role、SELinux Type、SELinux Level,每个部分的具体含义,讲在下一章介绍。
用户程序执行的系统调用(例如读取文件),都要被SELinux依据安全策略进行检查。如果安全策略允许操作,则继续,否则将会抛出错误信息给应用程序。SELinux决策的同时还需要Subject和Object的Context信息,确定所属的User、Role和Type等信息,以此查询对应的安全策略进行决策。SELinux同样也使用了AVC机制用于缓存决策结果,以此来提高性能。
SELinux Context
进程和文件都有属于自己的Context信息,Context分为几个部分,分别是 SELinux User、Role、Type 和一个可选的Level信息。SELinux在运行过程中将使用这些信息查询安全策略进行决策。
- SELinux User:每一个Linux用户都会映射到SELinux用户,每一个SELinux User都会对应相应的Role。
- SELinux Role:每个Role也对应几种SELinux Type,并且充当了User和Type的‘中间人’
- SELinux Type:安全策略使用SELinux Type制定规则,定义何种Domian(Type)的Subject,可以接入何种Type的Object。
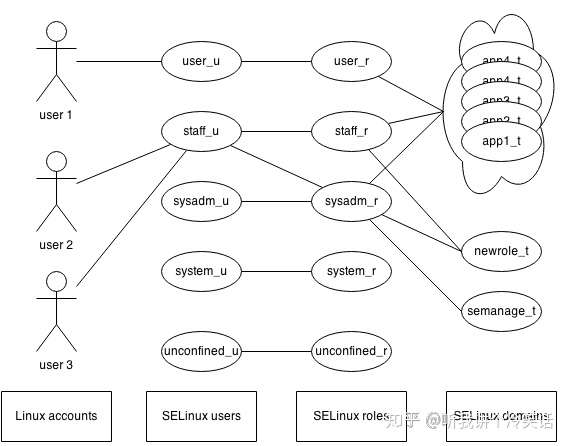
显示进程的Context
~]# ps -Z
LABEL PID TTY TIME CMD
unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 9509 pts/1 00:00:00 sudo
unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 9515 pts/1 00:00:00 su
unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 9516 pts/1 00:00:00 bash
unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 9544 pts/1 00:00:00 ps
显示文件的Context信息
~]# ls -Z
system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 anaconda-ks.cfg
临时修改文件的SELinux Type 为htttpd_sys_content_t
~]# chcon -t httpd_sys_content_t file-name
SELinux 的运行状态
SELinux 有三个运行状态,分别是disabled, permissive 和 enforcing
- Disable: 禁用SELinux,不会给任何新资源打Label,如果重新启用的话,将会给资源重新打上Lable,过程会比较缓慢。
- Permissive:如果违反安全策略,并不会真正的执行拒绝操作,替代的方式是记录一条log信息。
- Enforcing: 默认模式,SELinux的正常状态,会实际禁用违反策略的操作
查看当前的运行状态
~]# getenforce
Enforcing
临时改变运行状态为Permissive
~]# setenforce 0
~]# getenforce
Permissive
临时改变运行状态为 Enforcing
~]# setenforce 1
~]# getenforce
Enforcing
使用sestatus可以查看完整的状态信息
~]# sestatus
SELinux status: enabled
SELinuxfs mount: /sys/fs/selinux
SELinux root directory: /etc/selinux
Loaded policy name: targeted
Current mode: enforcing
Mode from config file: enforcing
Policy MLS status: enabled
Policy deny_unknown status: allowed
Max kernel policy version: 30
SELinux Log
SELinux 的Log日志默认记录在/var/log/audit/audit.log
~]# cat /var/log/audit/audit.log
type=AVC msg=audit(1223024155.684:49): avc: denied { getattr } for pid=2000 comm="httpd" path="/var/www/html/file1" dev=dm-0 ino=399185 scontext=unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 tcontext=system_u:object_r:samba_share_t:s0 tclass=file
/var/log/message 也会记录相应的信息,例如:
May 7 18:55:56 localhost setroubleshoot: SELinux is preventing httpd (httpd_t) "getattr" to /var/www/html/file1 (samba_share_t). For complete SELinux messages. run sealert -l de7e30d6-5488-466d-a606-92c9f40d316d
SELinux 配置文件
SELinux的配置文件位于/etc/selinux/config。默认配置文件主要两部分,一个是SELinux的运行状态和SELinuxType。直接在配置文件中修改SELinux将会在下次启动时生效。
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=enforcing
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
SELinux Booleans
Booleans允许在运行时修改SELinux安全策略。
列出所有的Booleans选项
~]# semanage boolean -l
SELinux boolean State Default Description
smartmon_3ware (off , off) Determine whether smartmon can...
mpd_enable_homedirs (off , off) Determine whether mpd can traverse...
临时修改httpd_can_network_connect_db状态为开启
~]# setsebool httpd_can_network_connect_db on
深入研究
Basic and advanced configuration of Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux)
Linux Security Module Framework
The Flask Security Architecture: System Support for Diverse Security Policies
[SELinux Notebook](



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 25岁的心里话