Codeforces Round 941 (Div. 2) Div 1 cf941 A-D
A
感觉A比较复杂啊,相比较B简单明了。
way1
只要有相同的一个数,它的数目大于等于k,那么它就可以进行一次操作,接下来可以再摸k-1个数,那么对于无法凑成k个数的数字来说,无论现在它有多少个数(>=1),加上这k-1个数,都能凑成数目>=k。同时,这个操作可以无限循环下去。
所以这道题的出题设计还是比较精妙的。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define LL long long 4 #define ULL unsigned long long 5 6 const LL mod_1=1e9+7; 7 const LL mod_2=998244353; 8 9 const double eps_1=1e-5; 10 const double eps_2=1e-10; 11 12 const int maxn=2e5+10; 13 14 map<int,int> m; 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 int T,n,k,d,i,x,y,z,result; 19 scanf("%d",&T); 20 while (T--) 21 { 22 x=y=z=0; 23 result=0; 24 m.clear(); 25 26 scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); 27 for (i=0;i<n;i++) 28 { 29 scanf("%d",&d); 30 m[d]++; 31 } 32 33 for (auto par:m) 34 { 35 x += par.second / k * (k-1); 36 //y += (k-1) - (k - par.second%k); 37 y += max(par.second%k - 1, 0); 38 z += par.second; 39 } 40 41 if (x==0) 42 result=z; 43 else 44 { 45 result = x+y; 46 while (result>=k) 47 result = result%k + result/k*(k-1); 48 } 49 50 //printf("Case %d : ",T); 51 printf("%d\n",result); 52 } 53 54 return 0; 55 }
way2
A 数目大于等于k的数,记录可以执行变化的操作数目,对应可以摸的数目
B 数目小于k的数,从大到小排序,依次利用A摸到的数,增加这个数的数目,看能否数目到达k个,然后可以归类为A
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define LL long long 4 #define ULL unsigned long long 5 6 const LL mod_1=1e9+7; 7 const LL mod_2=998244353; 8 9 const double eps_1=1e-5; 10 const double eps_2=1e-10; 11 12 const int maxn=2e5+10; 13 14 map<int,int> m; 15 vector<int> vec(1005); 16 17 int main() 18 { 19 int T,n,k,d,i,rest,result; 20 scanf("%d",&T); 21 while (T--) 22 { 23 rest=0; 24 result=0; 25 m.clear(); 26 vec.clear(); 27 28 scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); 29 for (i=0;i<n;i++) 30 { 31 scanf("%d",&d); 32 m[d]++; 33 } 34 35 for (auto par:m) 36 { 37 rest += (par.second / k) * (k-1); 38 vec.push_back( par.second % k ); 39 } 40 41 sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); 42 reverse(vec.begin(), vec.end()); 43 //result += accumulate(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0); 44 45 for (auto v:vec) 46 if (rest >= k - v) 47 { 48 rest += k-1 - (k-v); 49 } 50 else 51 result+=v; 52 53 while (rest>=k) 54 rest = rest%k + rest/k*(k-1); 55 result+=rest; 56 57 //printf("Case %d : ",T); 58 printf("%d\n",result); 59 } 60 61 return 0; 62 }
B
对于某个颜色,
行的最小=1,最大=n
列的最小=1,最大=m
只要满足这个条件就行,无论黑色还是白色
好的代码写法能很快写完
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define LL long long 4 #define ULL unsigned long long 5 6 const LL mod_1=1e9+7; 7 const LL mod_2=998244353; 8 9 const double eps_1=1e-5; 10 const double eps_2=1e-10; 11 12 const int maxn=2e5+10; 13 14 int main() 15 { 16 int T,n,m,i,j,u1,u2,u3,u4,v1,v2,v3,v4; 17 char c; 18 //xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax 19 scanf("%d",&T); 20 while (T--) 21 { 22 u1=u2=u3=u4=v1=v2=v3=v4=0; 23 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 24 for (i=1;i<=n;i++) 25 { 26 scanf("%c",&c); 27 for (j=1;j<=m;j++) 28 { 29 scanf("%c",&c); 30 if (c=='W') 31 { 32 if (i==1) 33 u1=1; 34 if (i==n) 35 u2=1; 36 if (j==1) 37 u3=1; 38 if (j==m) 39 u4=1; 40 } 41 else 42 { 43 if (i==1) 44 v1=1; 45 if (i==n) 46 v2=1; 47 if (j==1) 48 v3=1; 49 if (j==m) 50 v4=1; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 //printf("Case %d : ",T); 55 if ((u1+u2+u3+u4==4) || (v1+v2+v3+v4==4)) 56 printf("YES\n"); 57 else 58 printf("NO\n"); 59 } 60 61 return 0; 62 }
C
cf的test case和最后才大数据评测比较搞人心态,也算是一种磨练了,多年没打,没意识到,打div1,没想到栽在了这上面。
好像没怎么看到人hack?感觉好hack?
这种题,类型多,按道理是挺容易出错的。如果是atcoder,就认真造样例检查了……虽然cf更加是如此……
div1的ac/wrong submisson率,高得有点吓人。
我觉得D比C,好写难说,但基本上D不容易出错。
回想,首先,保证0 wrong submisson,因为1wa,10mins罚时,而且不容易找到错误。在此基础上,怎么用时比较短。怎么让做这道题时,思路比较清晰?
我感觉我容易栽在这类题上,因为思路不清楚,很容易绕、晕……
去掉重复的数字,然后从小到大排序
如果第一个数大于1,无论怎么样,Alice总能使得当前最小的数是1,保证最后Alice能赢
如果一开始是1、2、3、……这样的序列,
a. 如果序列是1、2、3、……、k,如果k是奇数,Alice赢;否则Bob赢。因为每次都只能取一个数。
b. 如果序列是1、2、3、……、k,m(m>k+1),…… 如果k是奇数,Bob赢;否则Alice赢。因为一开始每次都只能取一个数,直到变成m-k(m-k>1),……这样的序列。如果k是奇数,对于m-k当前这个情况,是Bob开始拿,因为m-k>1,所以最后是Bob赢。同理k是偶数,Alice赢。
注意,去掉重复的数字后,数目不是n,不要下标写错了。真的是心态爆炸……
写成这样方便复制?:{printf("Alice\n"); continue;}
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cmath> 5 #include <cstdbool> 6 #include <string> 7 #include <algorithm> 8 #include <iostream> 9 #include <sstream> 10 #include <ctime> 11 #include <stack> 12 #include <vector> 13 #include <queue> 14 #include <set> 15 #include <map> 16 #include <array> 17 #include <bitset> 18 using namespace std; 19 #define LL long long 20 #define ULL unsigned long long 21 22 const LL mod_1=1e9+7; 23 const LL mod_2=998244353; 24 25 const double eps_1=1e-5; 26 const double eps_2=1e-10; 27 28 const int maxn=2e5+10; 29 30 set<int> s; 31 32 int a[maxn]; 33 34 int main() 35 { 36 int T,q,n,d,i,cond; 37 scanf("%d",&T); 38 while (T--) 39 { 40 s.clear(); 41 cond=0; 42 n=0; 43 44 scanf("%d",&q); 45 while (q--) 46 { 47 scanf("%d",&d); 48 if (s.find(d)==s.end()) 49 { 50 a[n++]=d; 51 s.insert(d); 52 } 53 } 54 sort(a,a+n); 55 56 a[n]=a[n-1]+1; 57 for (i=0;i<n;i++) 58 if (a[i]!=a[i+1]-1) 59 break; 60 if (i!=n) 61 cond=i & 1; 62 else 63 cond=n & 1; 64 65 if (a[0]!=1) 66 {printf("Alice\n"); continue;} 67 68 if (cond==1) 69 printf("Alice\n"); 70 else 71 printf("Bob\n"); 72 } 73 74 return 0; 75 } 76 /* 77 100 78 2 79 1 7 80 4 81 1 2 3 7 82 5 83 1 2 3 4 7 84 5 85 1 2 3 7 8 86 87 88 2 89 1 2 90 4 91 1 2 3 4 92 5 93 1 2 3 4 5 94 6 95 1 1 1 1 1 1 96 6 97 1 2 1 2 2 1 98 99 100 101 100 102 103 2 104 2 2 105 106 4 107 2 2 2 3 108 109 4 110 1 2 4 5 111 112 5 113 1 2 4 5 6 114 115 4 116 1 2 3 7 117 118 5 119 1 2 3 7 8 120 */
暴力打表验证
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define LL long long 4 #define ULL unsigned long long 5 6 const LL mod_1=1e9+7; 7 const LL mod_2=998244353; 8 9 const double eps_1=1e-5; 10 const double eps_2=1e-10; 11 12 const int maxn=2e5+10; 13 int print_1=0; 14 15 int dfs(vector<int> vec) 16 { 17 if (vec.size()==1) 18 return 1; 19 20 vector<int>::iterator it, next_it; 21 int value=vec[0], i, cur=0; 22 for (i=1;i<=value;i++) 23 { 24 for (it=vec.begin(); it!=vec.end(); it++) 25 *it = (*it)-1; 26 27 if (i==value) 28 { 29 /* 30 for (it=vec.begin();it!=vec.end();it++) 31 { 32 if ((*it)==0) 33 vec.erase(it); 34 } 35 */ 36 37 ///如果所有都是0,会删除错误 38 if (vec.back()==0) 39 return 1; 40 41 for (it=vec.begin();it!=vec.end();it=next_it) 42 { 43 next_it=it+1; 44 if ((*it)==0) 45 vec.erase(it); 46 } 47 48 /* 49 if (vec.empty()) 50 return 1; 51 */ 52 } 53 54 if (print_1) 55 { 56 printf("array: "); 57 for (auto d:vec) 58 printf("%d ",d); 59 printf("\n"); 60 printf("\n"); 61 } 62 63 cur |= (dfs(vec)^1); 64 } 65 return cur; 66 } 67 68 int main() 69 { 70 vector<int> v; 71 int mode=1,a,n,i; 72 if (mode==1) 73 { 74 while (1) 75 { 76 v.clear(); 77 78 scanf("%d",&n); 79 for (i=1;i<=n;i++) 80 { 81 scanf("%d",&a); 82 v.push_back(a); 83 } 84 sort(v.begin(), v.end()); 85 86 //printf("%d\n", dfs(v)); ///1 Alice ; 0 Bob 87 printf("%s\n", dfs(v)==1 ? "Alice" : "Bob" ); 88 89 } 90 91 92 } 93 94 return 0; 95 } 96 /* 97 98 99 3 100 1 2 3 101 102 4 103 1 2 3 4 104 105 5 106 1 2 3 4 5 107 108 6 109 1 2 3 4 5 6 110 111 3 112 2 3 4 113 114 4 115 2 3 4 5 116 117 5 118 2 3 4 5 6 119 120 6 121 2 3 4 5 6 7 122 123 124 125 126 result: 127 3 128 1 2 3 129 Alice 130 131 4 132 1 2 3 4 133 Bob 134 135 5 136 1 2 3 4 5 137 Alice 138 139 6 140 1 2 3 4 5 6 141 Bob 142 143 3 144 2 3 4 145 Alice 146 147 4 148 2 3 4 5 149 Alice 150 151 5 152 2 3 4 5 6 153 Alice 154 155 6 156 2 3 4 5 6 7 157 Alice 158 159 160 161 162 一段 163 164 165 从1开始 双数: Bob;单数:Alice 166 从2开始 都是Alice 167 168 169 170 ====== 171 172 173 6 174 1 2 3 4 6 7 175 176 7 177 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 178 179 8 180 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 181 182 183 5 184 1 2 3 6 7 185 186 6 187 1 2 3 6 7 8 188 189 7 190 1 2 3 6 7 8 9 191 192 193 194 195 result: 196 6 197 1 2 3 4 6 7 198 Alice 199 200 7 201 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 202 Alice 203 204 8 205 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 206 Alice 207 5 208 1 2 3 6 7 209 Bob 210 211 6 212 1 2 3 6 7 8 213 Bob 214 215 7 216 1 2 3 6 7 8 9 217 Bob 218 219 220 ====== 221 222 223 224 225 8 226 1 2 3 4 6 7 9 10 227 228 9 229 1 2 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 230 231 10 232 1 2 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 12 233 234 235 236 6 237 1 2 3 6 7 10 238 239 7 240 1 2 3 6 7 10 11 241 242 8 243 1 2 3 6 7 10 11 12 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 result: 251 252 8 253 1 2 3 4 6 7 9 10 254 Alice 255 256 9 257 1 2 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 258 Alice 259 260 10 261 1 2 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 12 262 Alice 263 264 265 266 6 267 1 2 3 6 7 10 268 Bob 269 270 7 271 1 2 3 6 7 10 11 272 Bob 273 274 8 275 1 2 3 6 7 10 11 12 276 Bob 277 278 279 280 281 282 ====== 283 284 8 285 1 2 3 6 7 8 9 11 286 287 9 288 1 2 3 6 7 8 9 11 12 289 290 10 291 1 2 3 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 292 293 294 8 295 1 2 3 6 7 8 9 11 296 Bob 297 298 9 299 1 2 3 6 7 8 9 11 12 300 Bob 301 302 10 303 1 2 3 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 304 Bob 305 306 307 308 309 ====== 310 311 312 7 313 1 2 4 5 6 8 9 314 315 316 317 318 //三段 319 320 A 321 322 ====== 323 324 7 325 2 3 5 6 7 9 10 326 //三段 327 328 A 329 330 ====== 331 332 4 333 1 2 4 5 334 A 335 336 4 337 1 2 4 5 6 338 A 339 340 //二段 341 342 343 ====== 344 345 10 346 1 2 3 10 12 13 20 21 22 30 347 B 348 349 11 350 1 2 3 10 12 13 20 21 22 30 31 351 B 352 353 12 354 1 2 3 10 12 13 20 21 22 30 31 32 355 B 356 357 358 ====== 359 360 361 362 11 363 1 2 3 10 12 13 20 21 22 25 30 364 B 365 366 12 367 1 2 3 10 12 13 20 21 22 25 30 31 368 B 369 370 371 13 372 1 2 3 10 12 13 20 21 22 25 30 31 32 373 B 374 375 ====== 376 377 10 378 2 3 4 11 13 14 21 22 23 31 379 A 380 381 11 382 2 3 4 11 13 14 21 22 23 31 32 383 A 384 385 12 386 2 3 4 11 13 14 21 22 23 31 32 33 387 A 388 389 390 8 391 2 3 4 5 6 10 11 12 392 A 393 394 395 8 396 397 398 399 ====== 400 401 402 403 404 */
D
n的要求才1e6,所以可以大开大合的构造:
对于不能为k
a. 1、2、4、... 相加,直到小于等于(k-1)。 这些数的和为A。
b. (k-1)-A。 使得a、b这两类数的和为(k-1),同时,可以任意数相加和可以为1~(k-1)。
c. k+1、k+2、k+3 三个数。a、b、c这三类数,可以任意数相加和可以为1~(2*k-1)。 这个就是大致构造,大致感觉可以就行。
d. k*2、k*4、k*8、... 剩余凑齐25个数。
设计理念:
a 1~k-1要有:若干个,1、2、...,直到不能满足任意数相加和为k
b 不能有2i,否则加上a里的数,任意数相加可以为k
c 要有k+1 否则无法使得任意数相加和为k+1
d 经过处理后,1~r除去k,任意数相加都可以变为它们
e 在d的基础上,2r,4r,8r,…… 凑够25个数
不要对于比较小的k,都制定一组数,这样工作量大,很累,很容易出错,浪费大量时间。n<=1e6太小了,完全有很多选择,浪费多一两个数,也能构造出成功、设计很简单的例子。
通过k=1~15,看结果,判断是否可以。assert(最后一个数>=5e5)
看了题解,这个数字上的描述,就很简洁明了:
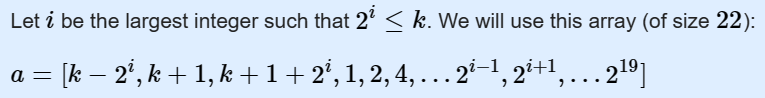
1~ 2i-1 包含 1~ 2i-1
再加上k-2i 包含 1~ k-1
再加上k+1 包含 1~k+1 除去k
k+1+2i 包含 1~k+1+2i 除去k。这一步是为了使得满足1~2i+1-1
然后就是再加上 2i+1,2i+2,……
设计理念:
当满足1~x后,加上2i(2i<=x),满足1~x+2i
当满足1~x+2i后,加上2i+1(2i+1<=x+2i),满足1~x+2i+1
依次类推
就是1~x,加上2i,2i+1……2j 满足x+2j
对于0,加上20,20+1……2j 满足2j+1
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define LL long long 4 #define ULL unsigned long long 5 6 const LL mod_1=1e9+7; 7 const LL mod_2=998244353; 8 9 const double eps_1=1e-5; 10 const double eps_2=1e-10; 11 12 const int maxn=2e5+10; 13 14 int er[100],result[100]; 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 int T,n,k,m,i,j,maxs=25; 19 er[0]=1; 20 for (i=1;er[i-1]<=1e7;i++) 21 er[i]=er[i-1]<<1; 22 scanf("%d",&T); 23 while (T--) 24 { 25 scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); 26 m=k-1; 27 i=0; 28 j=0; 29 while (m>=er[i]) 30 { 31 result[j++]=er[i]; 32 m-=er[i]; 33 i++; 34 } 35 if (m>0) 36 result[j++]=m; 37 result[j++]=k+1; 38 result[j++]=k+2; 39 result[j++]=k+3; 40 41 result[j++]=k*2; 42 while (j<maxs) 43 { 44 result[j]=result[j-1]*2; 45 j++; 46 } 47 48 //assert(result[maxs-1]>1e6); 49 50 printf("%d\n",maxs); 51 52 for (i=0;i<maxs;i++) 53 { 54 printf("%d",result[i]); 55 if (i==maxs-1) 56 printf("\n"); 57 else 58 printf(" "); 59 } 60 } 61 62 return 0; 63 } 64 /* 65 15 66 1 1 67 1 2 68 1 3 69 1 4 70 1 5 71 1 6 72 1 7 73 1 8 74 1 9 75 1 10 76 1 11 77 1 12 78 1 13 79 1 14 80 1 15 81 */



