create NioEventLoopGroup Instance
![image]()
一、NioServerSocketChannel init
![image]()
note:Initializing ChannelConfig creates a WriteBufferWaterMark instance,Default low 32k,high 64k
作用: 防止ChannelOutboundBuffer 太大最终导致内存溢出,达到 High water值,
会传播ChannelHandler 的 channelWritabilityChanged method,但是依旧能 write to buffer
需要依据ChannelOutboundBuffer.isWritable 方法判断是否继续 write 处理.
方案:after write to buffer,调用 ChannelOutboundBuffer,isWritable 方法是否可写,不可写时候,
调用Channel config AutoRead 置为false,停止从Socket接收缓冲区读取到应用缓冲区
(利用Tcp协议栈的滑动窗口做流控),监听ChannelHandler.channelWritabilityChanged 方法处理是否
恢复AutoRead:true
![image]()
register0 method code int the AbstractChannel class:
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
// check
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
doRegister();//Selector register ServerSocketChannel
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// 传播 ChannelHandler 的 handlerAdded 方法(先执行 initChannel 方法)
// 之前在ServerBootstrap 类中定义的init 方法里将会触发ChannelInitializer 的执行
// performs complete, remove current ChannelHandler
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
safeSetSuccess(promise);//如果启用listener,callBacks Results
//传播 channelHandler 的 channelRegistered 方法
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
// 是否传播 ChannelHandler 的 channelActive 方法
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {//默认AutoRead:true(是否从Socket接收缓冲区读取数据)
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
note:sun Jdk的Selector选择是依据 OS 来挑选 select、poll、epoll.
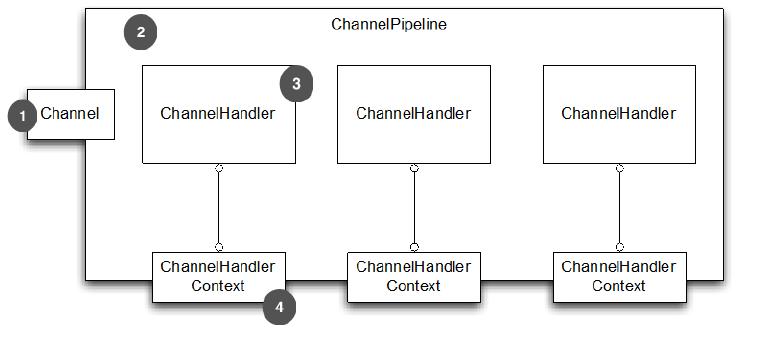
三、ChannelPipeline, Channel, ChannelHandler 和 ChannelHandlerContext 的关系
![image]()
1.Channel 绑定到 ChannelPipeline
2.ChannelPipeline 绑定到 包含 ChannelHandler 的 Channel
3.ChannelHandler
4.当添加 ChannelHandler 到 ChannelPipeline 时,ChannelHandlerContext 被创建
四、Client Connection to Server
![image]()
note:传播之前添加的ServerBootstrapAcceptor(ChannelHandler) 的 channelRead 方法
![image]()
note:ParentDefaultChannelPipeline -> NioServerSocketChannel
SubDefaultChannelPipeline -> NioSocketChannel(a TcpConnection map a NioSocketChannel)
流程和NioServerSocketChannel一致,对Multi NioScoketChannel采用分治思想,多线程去承担(IO Read/Write),
利用multi core cpu.
Core Code in the ServerBootstrap.ServerBootstrapAcceptor Class:
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;//Converted to NioSockerChannel
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);//Add Application setting childHandler
//添加Application 配置的相关属性和选项
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
//切换NioSocketChannel 到其他线程的Scheduling和Register
try {
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {//操作结果失败
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
五、Client transmits data to the Server
![image]()
Core Code in the AbstractNioByteChannel.NioByteUnsafe Class:
public final void read() {
final ChannelConfig config = config();//获取NioSocketChannel 配置
//检查是否可读
if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) {
clearReadPending();
return;
}
//接收缓存区分配器
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);//重置
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
//NioSocketChannel配置(AutoRead)是否可读,最大读取次数范围内是否读取数据流完毕
do {
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);//分配byteBuf
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));//读取数据流
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {//是否读取完毕
byteBuf.release();//释放资源
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);//递增一次读取次数
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);//Callbacks channelRead ChannelHandler
byteBuf = null;
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();//Callbacks channelReadComplete ChannelHandler
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
}
...
}
}
Flow:
I/O Request
Channel
|
+---------------------------------------------------+---------------+
| ChannelPipeline | |
| \|/ |
| +---------------------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| | Inbound Handler N | | Outbound Handler 1 | |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| /|\ | |
| | \|/ |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| | Inbound Handler N-1 | | Outbound Handler 2 | |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| /|\ . |
| . . |
| ChannelHandlerContext.fireIN_EVT() ChannelHandlerContext.OUT_EVT()|
| [ method call] [method call] |
| . . |
| . \|/ |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| | Inbound Handler 2 | | Outbound Handler M-1 | |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| /|\ | |
| | \|/ |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| | Inbound Handler 1 | | Outbound Handler M | |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| /|\ | |
+---------------+-----------------------------------+---------------+
| \|/
+---------------+-----------------------------------+---------------+
| | | |
| [ Socket.read() ] [ Socket.write() ] |
| |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
writeAndFlush流程:
Application --write--> ChannelOutboundBuffer --flush--> Socket发送缓冲区
六、Netty UDP Server is Single Thread Mode
note:不能阻塞IO线程,业务依靠业务线程池处理,否则Socket接收缓冲区溢出,会造成接收数据丢失,
数据可靠性问题,服务端设计方向利用 listen multi Network Interface 去处理,利用资源



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号