HDU 1165 Eddy's research II (推公式)
Eddy's research II
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3122 Accepted Submission(s): 1137
Problem Description
As is known, Ackermann function plays an important role in the sphere of theoretical computer science. However, in the other hand, the dramatic fast increasing pace of the function caused the value of Ackermann function hard to calcuate.
Ackermann function can be defined recursively as follows:
![]()
Now Eddy Gives you two numbers: m and n, your task is to compute the value of A(m,n) .This is so easy problem,If you slove this problem,you will receive a prize(Eddy will invite you to hdu restaurant to have supper).
Ackermann function can be defined recursively as follows:
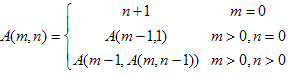
Now Eddy Gives you two numbers: m and n, your task is to compute the value of A(m,n) .This is so easy problem,If you slove this problem,you will receive a prize(Eddy will invite you to hdu restaurant to have supper).
Input
Each line of the input will have two integers, namely m, n, where 0 < m < =3.
Note that when m<3, n can be any integer less than 1000000, while m=3, the value of n is restricted within 24.
Input is terminated by end of file.
Note that when m<3, n can be any integer less than 1000000, while m=3, the value of n is restricted within 24.
Input is terminated by end of file.
Output
For each value of m,n, print out the value of A(m,n).
Sample Input
1 3
2 4
Sample Output
5
11
Author
eddy
Recommend
JGShining
看到这道题的0<m<=3,所以觉得可以分情况讨论推公式,试了几组数据才得出推得公式。

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 __int64 A(int m,int n) 7 { 8 if(n==0) return A(m-1,1); 9 else if(m==0) return n+1; 10 else if(m==1) return n+2; 11 else if(m==2) return 2*n+3; 12 else if(m==3) return 2*A(3,n-1)+3; 13 } 14 int main() 15 { 16 int m,n; 17 while(scanf("%d %d",&m,&n)!=EOF) 18 { 19 printf("%I64d\n",A(m,n)); 20 } 21 return 0; 22 }
这里我还没有推出m=3的时候的公式,后来比完赛GJ告诉我他推得,瞬间觉得可以更加优化

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 __int64 A(int m,int n) 7 { 8 if(m==0) return n+1; 9 if(m==1) return n+2; 10 if(m==2) return 2*n+3; 11 if(m==3) return (1<<(n+3))-3; 12 } 13 int main() 14 { 15 int m,n; 16 while(scanf("%d %d",&m,&n)!=EOF) 17 { 18 printf("%I64d\n",A(m,n)); 19 } 20 return 0; 21 }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号