【Java】Java8-1
Stream、Optional、try-with-resources、 AutoClosable
§ 一、Stream
1、得到流:Arrays.asStream(); 2、中间操作; 3、终端操作:

§ 二、Optional
https://www.cnblogs.com/Kevin-ZhangCG/p/14852547.htm 推荐
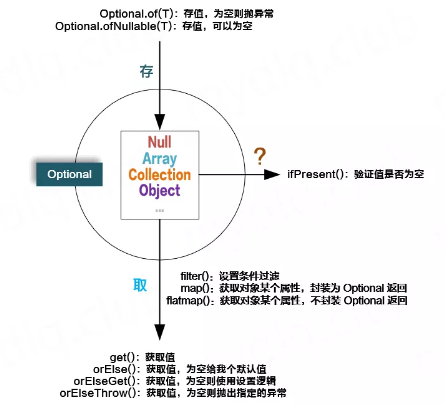
- 非空断言:JDK的Objects.requireNonNull
// 简单检查 Objects.requireNonNull(t); // 带Message的检查:若失败则抛java.lang.NullPointerException: Param t should not be null Objects.requireNonNull(t, "Param t should not be null"); // 断言+赋值,一步到位 this.id = Objects.requireNonNull(idVal); // 带Message的断言:若失败则抛java.lang.NullPointerException: Param t should not be null this.id = Objects.requireNonNull(idVal, "Param idVal should not be null");
- 入参检查与操作
this.name = Optional.ofNullable(inputName).orElse("SOME_DEFAULT_NAME"); 基于Guava // 简单断言 Preconditions.checkArgument(param.endsWith("abc")); // 带Message的断言 Preconditions.checkArgument(param.endsWith("abc"), "Para doesn't end with abc"); // 带Message format的断言 Preconditions.checkArgument(param.endsWith("abc"), "Para %s doesn't end with %s", param, "abc");
- lombok.NonNull、javax.annotation.Nonnull和javax.validation.constraints.NotNull
- @NonNull用在强制入参非空、属性非空的场景下,编译时会生成空指针检查的代码,如果不满足,则会抛出NullPointerException。
- @Nonnull用在返回结果不为空的场景,主要由IDE识别并给出告警提示。
- @NotNull主要用在Validator校验场景下,限制参数非空,如果不满足,则校验失败。
void setId(@NonNull String id) { if (id.contains("xxx")) { // ... } }
// info不为null才执行,null场景并不报错 Optional.ofNullable(info).ifPresent(System.out::println);
- 简化多级判空:使用Optional的多次map,可以依次逐级get对象的子对象,一定程度上替代多级if判空。
Optional.ofNullable(result) .map(DResult::getDevice) .map(Device::getGroup) .map(Group::getId) .ifPresent(Dummy::doSomething); 对比: // 多级if判空 if (result != null && result.getDevice() != null && result.getDevice().getGroup() != null) { String groupId = result.getDevice().getGroup().getId(); if (groupId != null) { Dummy.doSomething(groupId); } } // 对比,有返回值场景:返回 result.getDevice().getGroup().getName() 或 unknown return Optional.ofNullable(result) .map(DResult::getDevice) .map(Device::getGroup) .map(Group::getName) .orElse("Unknown"); return Optional.ofNullable(device).map(Device::getName).orElse("Unknown"); return Optional.ofNullable(device).map(Device::getName).orElseGet(this::getDefaultName); return Optional.ofNullable(result).map(DResult::getDevice).orElseThrow(() -> new DummyException("No device")); // 获得device对应的Group Optional.ofNullable(device).map(dvc -> dvc.getGroup()).ifPresent(grp -> Dummy.doSomething(grp)); // FunctionalInterface部分的内容,推荐使用方法引用方式,提升编码简洁度 Optional.ofNullable(device).map(Device::getGroup).ifPresent(Dummy::doSomething); Optional.ofNullable(device) .filter(d -> d.getName() != null) // 如果device.getName为null,则提前结束 .ifPresent(Dummy::doSomething);
§ 三、try-with-catch
针对流的使用和关闭:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (BufferedInputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("test.txt")));
BufferedOutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("out.txt")))) {
int b;
while ((b = bin.read()) != -1) {
bout.write(b);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
背后的原因探究:try-with-resources 要求关闭的资源必须实现AutoCloseable接口
Test1:基础测试
public class Connection implements AutoCloseable {
public void doTask() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Connection doTask");
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Connection close()");
}
}
调用的写法
public class TryWithResource {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Connection conn = new Connection()) {
conn.doTask();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
执行结果:
Connection doTask
Connection close()
反编译的结果:自动生成了之前手写的try-catch-finally复杂逻辑
public class TryWithResource {
public TryWithResource() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Connection conn = new Connection();
Throwable var2 = null;
try {
conn.doTask();
} catch (Throwable var12) {
var2 = var12;
throw var12;
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
if (var2 != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (Throwable var11) {
var2.addSuppressed(var11);
}
} else {
conn.close();
}
}
}
} catch (Exception var14) {
var14.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Test2:异常测试,Connection主动抛出异常
public class Connection implements AutoCloseable {
public void doTask() throws Exception {
throw new Exception("doTask()");
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
throw new Exception("close()");
}
}
测试结果:可以抛出出问题地方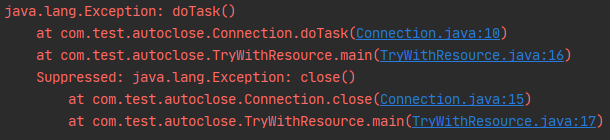
原因是反编译时 var2.addSuppressed(var11) 作用(上面反编译结果红色字体部分)
注意:在使用try-with-resource的过程中,一定需要了解资源的close方法内部的实现逻辑。否则还是可能会导致资源泄露。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(new File("input.txt"));
GZIPOutputStream out = new GZIPOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("out.txt")))) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int read;
while ((read = fin.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, read);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
因为采用了装饰器模式,在调用GZIPOutputStream::close可能发生异常,而无法继续调用FileOutputStream::close方法
正确做法:应该在try-with-resource中单独声明最底层的资源,保证对应的close方法一定能够被调用。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(new File("input.txt"));
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(new File("out.txt"));
GZIPOutputStream out = new GZIPOutputStream(fout)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int read;
while ((read = fin.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, read);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)