NO.1 2 章 评测技巧、C/C++入门
NO.1章 上机注意事项
AC Accept 答案正确 CE Compile Error 编译错误 WA Wrong Answer 答案错误 TLE Time Limit Exceeded 运行超时 //考虑时间复杂度+数据死循环情况 //段错误 浮点错误 递归爆栈(检查数组大小+除数为0+递归层数) RE Runtime Error 运行错误 MLE Memory Limit Exceeded 内存超限 //数组太大 PE Presentation Error 格式错误 OLE Output Limit Exceeded 输出超限 //大量调试信息+特殊数据导致的死循环输出
NO.2章 C/C++快速入门
1. 基本数据类型
1)变量

注:绝对值在109范围内的整数都可以定义为int型
碰到浮点型数据都用double来存储
ASCII码范围:0~127(0~9:48~57;A~Z:65~90)小写比大写的ASCII码大32
\0:空字符NULL,ASCII码为 0(不是空格,空格ASCII码:32)
%.1f:保留一位小数输出
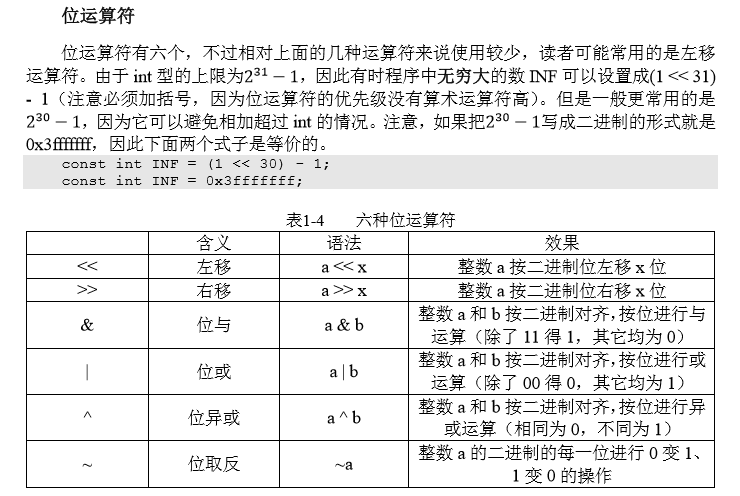
2)运算符

2. 输入输出
1)scanf()
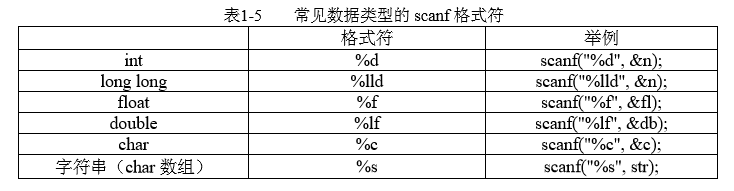
注:scanf中,除了char数组整个输入不加&,其他变量类型都要加&
除%c外,scanf对其他格式符的输入,以空白符(空格、Tab)为读入结束标志
%s,以(空格、换行)为读入结束标志
%c,可以读入(空格、换行)
2)printf()
实用的输出格式:
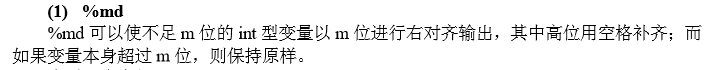



注:typedef long long LL; //避免程序中出现大量的 long long
3)getchar() putchar()

4)gets() puts()
gets():输入一行字符串,并存放于一维数组中
puts():将一维数组在屏幕上输出,并紧跟一个换行
3. 常用math函数
//都返回 double 型 fabs(double x) //取绝对值 floor(double x) //向下取整 ceil(double x) //向上取整 round(double x) //四舍五入取整 pow(double r, double p) //返回 r 的p次方 sqrt(double x) //取算术平方根 log(double x) //取以自然对数为底的对数 sin(double x) cos(double x) tan(double x) //参数均为弧度制 asin(double x) acos(double x) atan(double x) //反xx值

4. 数组
初始化:
memset(数组名, 值, sizeof(数组名)); //对数组初始化为0 -1(按字节赋值) fill(first, last, val); //first为容器的首迭代器,last为末迭代器,val为将要替换的值(任意)
string.h 头文件:
//strX:字符数组 strlen(str) //返回字符数组中第一个\0前的字符个数 strcmp(str1, str2) //返回字符串比较大小的结果(按字典序) strcpy(str1, str2) //把str2复制给str1(包括\0) strcat(str1, str2) //把str2接到str1后面 sscanf(str, "%d", &n); //把 str 的内容以"%d"的格式写到 n 中 sprintf(str, "%d", n); //把 n 以"%d"格式写到 str 中
5. 函数
swap():(指针 作为 函数参数)
void swap(int* a, int *b) { int temp = *a; *a = *b; *b = temp; }
错误写法一:
void swap(int* a, int* b) { int* temp; // 错在定义temp时没有初始化 *temp = *a; *a = *b; *b = *temp; }
错误写法二:
void swap(int* a, int* b) { int* temp = a; // 只交换了地址,没有改变变量值 a = b; b = temp; }
swap():(指针的引用 作为 函数参数)
void swap(int* &a, int* &b) { int* temp = a; a = b; b = temp; }
6. 结构体(初始化)
设置多个构造函数
struct Point { // 结构体 int x, y; Point() {} Point(int _x, int _y) : x(_x), y(_y) {} } pt[10];
在main函数里初始化
int num = 0; for(int i=0; i<3; i++) { for(int j=0; j<3; j++) { pt[num++] = Point(i, j); //直接使用构造函数 } }
7. 浮点数的比较
浮点数在计算机中计算并不总是准确,需要引入一个极小数eps来对这种误差进行修正
const double eps = 1e-8; const double Pi = acos(-1.0); // π #define Equ(a, b) ( fbs(a-b) < eps ) // 等于 #define More(a, b) ( (a-b) > eps ) // 大于 #define Less(a, b) ( (a-b) < (-eps) ) // 小于 #define MoreEqu(a, b) ( (a-b) > (-eps) ) // 大于等于 #define LessEqu(a, b) ( (a-b) < eps ) // 小于等于
8. 测试



