【比赛题解】CSP2022 提高组题解
T1. 假期计划
Solution
首先,从每个节点开始 bfs 一次,求出任意两个点之间的最少转车次数。
由于路径的形式为 1→A→B→C→D→1,考虑枚举路径当中的中转点 B,C,现在要找出满足条件且权值和最大的一对点 A,D。
可以对每个点 x,维护权值前三大的点 gx,1,gx,2,gx,3,使得 1→gx,i 与 gx,i→x 之间的最少转车次数 ≤k。至于为什么要维护前三大,是为了不和另外两个中转点重复。
找出满足条件且权值和最大的一对 A,D,只需枚举 i,j∈[1,3],分别尝试令 A=gB,i,D=gC,j 更新答案即可。
时间复杂度 O(n2+nm)。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
template <class T>
inline void read(T &x) {
static char s;
while (s = getchar(), s < '0' || s > '9');
x = s - '0';
while (s = getchar(), s >= '0' && s <= '9') x = x * 10 + s - '0';
}
typedef long long s64;
const int N = 2510, M = 10010;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, k;
s64 a[N];
int tot, head[N], ver[M * 2], Next[M * 2];
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
ver[++ tot] = v; Next[tot] = head[u]; head[u] = tot;
}
int d[N][N];
void bfs(int st) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) d[st][i] = inf;
d[st][st] = 0;
std::queue<int> q;
q.push(st);
while (q.size()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int v = ver[i];
if (d[st][v] == inf) {
d[st][v] = d[st][u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
bool ok(int i, int j) { return d[i][j] - 1 <= k; }
int g[N][3];
void attend(int x, int y) {
if (a[g[x][0]] <= a[y]) {
g[x][2] = g[x][1], g[x][1] = g[x][0], g[x][0] = y;
} else if (a[g[x][1]] <= a[y]) {
g[x][2] = g[x][1], g[x][1] = y;
} else if (a[g[x][2]] < a[y]) {
g[x][2] = y;
}
}
s64 ans;
void calc(int p, int q, int x, int y) {
if (p == y || q == x || x == y || !x || !y) return;
ans = std::max(ans, a[p] + a[q] + a[x] + a[y]);
}
int main() {
read(n), read(m), read(k);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)
read(a[i]);
for (int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; i ++) {
read(u), read(v);
add_edge(u, v), add_edge(v, u);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) bfs(i);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)
for (int j = 2; j <= n; j ++) {
if (i == j || !ok(1, j) || !ok(j, i)) continue;
attend(i, j);
}
for (int p = 2; p < n; p ++)
for (int q = p + 1; q <= n; q ++) {
if (!ok(p, q)) continue;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i ++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j ++)
calc(p, q, g[p][i], g[q][j]);
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
T2. 策略游戏
Solution
分类讨论(下面说的 最大值 / 最小值 指的是绝对值 最大 / 最小,0 可以同时归进正数和负数):
-
若小 L 选择的 A 为正数:
- 若小 Q 可以选择的 B 只有正数:小 L 会选择正数最大值,小 Q 会选择正数最小值。
- 否则:小 L 会选择正数最小值,小 Q 会选择负数最大值。
-
若小 L 选择的 A 为负数:
- 若小 Q 可以选择的 B 只有负数:小 L 会选择负数最大值,小 Q 会选择负数最小值。
- 否则:小 L 会选择负数最小值,小 Q 会选择正数最大值。
使用两棵线段树分别维护序列 A,B 的区间 正 / 负 最大值 / 最小值 即可。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
template <class T>
inline void read(T &x) {
static char s;
static bool opt;
while (s = getchar(), (s < '0' || s > '9') && s != '-');
x = (opt = s == '-') ? 0 : s - '0';
while (s = getchar(), s >= '0' && s <= '9') x = x * 10 + s - '0';
if (opt) x = ~x + 1;
}
typedef long long s64;
const int N = 100100;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, Q;
int a[N], b[N];
struct dat {
int Pmax, Pmin;
int Qmax, Qmin;
dat() { Pmax = -inf, Pmin = inf, Qmax = inf, Qmin = -inf; }
dat operator + (const dat &rhs) {
dat self;
self.Pmax = std::max(Pmax, rhs.Pmax);
self.Pmin = std::min(Pmin, rhs.Pmin);
self.Qmax = std::min(Qmax, rhs.Qmax);
self.Qmin = std::max(Qmin, rhs.Qmin);
return self;
}
};
struct SGT {
struct node {
int l, r;
dat h;
} t[N * 4];
void build(int p, int l, int r, bool state) {
t[p].l = l, t[p].r = r;
if (l == r) {
int x = state ? b[l] : a[l];
if (x >= 0) t[p].h.Pmax = t[p].h.Pmin = x;
if (x <= 0) t[p].h.Qmax = t[p].h.Qmin = x;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(p * 2, l, mid, state), build(p * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r, state);
t[p].h = t[p * 2].h + t[p * 2 + 1].h;
}
dat ask(int p, int l, int r) {
if (l <= t[p].l && t[p].r <= r) return t[p].h;
int mid = (t[p].l + t[p].r) >> 1;
if (l <= mid && mid < r)
return ask(p * 2, l, r) + ask(p * 2 + 1, l, r);
else if (l <= mid)
return ask(p * 2, l, r);
else
return ask(p * 2 + 1, l, r);
}
} A, B;
int main() {
read(n), read(m), read(Q);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) read(a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) read(b[i]);
A.build(1, 1, n, 0);
B.build(1, 1, m, 1);
while (Q --) {
int L1, R1, L2, R2;
read(L1), read(R1), read(L2), read(R2);
s64 ans = -1e18;
dat row = A.ask(1, L1, R1), col = B.ask(1, L2, R2);
if (row.Pmax > -inf) {
if (col.Qmax == inf)
ans = std::max(ans, 1ll * row.Pmax * col.Pmin);
else
ans = std::max(ans, 1ll * row.Pmin * col.Qmax);
}
if (row.Qmax < inf) {
if (col.Pmax == -inf)
ans = std::max(ans, 1ll * row.Qmax * col.Qmin);
else
ans = std::max(ans, 1ll * row.Qmin * col.Pmax);
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
T3. 星战
Solution
反攻时刻条件 1:从任意一个点开始,都可以走入一个环中。
反攻时刻条件 2:每个点的出度均为 1。
显然条件 2 是条件 1 的充分条件。
设集合 S 表示当前时刻每条有向边的起点组成的可重集,则当前时刻为反攻时刻当且仅当 S={1,2,⋯,n}。
可以考虑 hash,维护集合 S 所有数的和、平方和。判断 S 的和是否为 n(n+1)2,S 的平方和是否为 n(n+1)(2n+1)6。
操作 1 与 操作 3,都是往集合 S 里 加 / 删 一个数,直接维护即可。
操作 2 与 操作 4,预处理出每个点的所有入边起点的和、平方和,把原先的贡献删掉,加进新的贡献即可。
时间复杂度 O(n)。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
template <class T>
inline void read(T &x) {
static char s;
while (s = getchar(), s < '0' || s > '9');
x = s - '0';
while (s = getchar(), s >= '0' && s <= '9') x = x * 10 + s - '0';
}
typedef long long s64;
const int N = 500100;
int n, m, Q;
int tot, head[N], ver[N], Next[N];
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
ver[++ tot] = v; Next[tot] = head[u]; head[u] = tot;
}
s64 base1, base2;
s64 all1, all2;
s64 sum1[N], sum2[N];
s64 cur1[N], cur2[N];
int main() {
read(n), read(m);
for (int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; i ++) {
read(u), read(v);
add_edge(v, u);
}
base1 = 1ll * n * (n + 1) / 2;
base2 = 1ll * n * (n + 1) * (2 * n + 1) / 6;
for (int v = 1; v <= n; v ++)
for (int i = head[v]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int u = ver[i];
sum1[v] += u, sum2[v] += 1ll * u * u;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cur1[i] = sum1[i], cur2[i] = sum2[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
all1 += sum1[i], all2 += sum2[i];
read(Q);
while (Q --) {
int opt, u, v;
read(opt), read(u);
if (opt == 1) {
read(v);
cur1[v] -= u, cur2[v] -= 1ll * u * u;
all1 -= u, all2 -= 1ll * u * u;
} else if (opt == 2) {
all1 -= cur1[u], cur1[u] = 0;
all2 -= cur2[u], cur2[u] = 0;
} else if (opt == 3) {
read(v);
cur1[v] += u, cur2[v] += 1ll * u * u;
all1 += u, all2 += 1ll * u * u;
} else {
all1 -= cur1[u], cur1[u] = sum1[u], all1 += sum1[u];
all2 -= cur2[u], cur2[u] = sum2[u], all2 += sum2[u];
}
puts(all1 == base1 && all2 == base2 ? "YES" : "NO");
}
return 0;
}
T4. 数据传输
Solution
先讨论 k=3 的情况。
对于每个从 s 到 t 的询问,不妨以 t 为根,将从 s 到 t 的路径提取出来。设从 s 到 t 的路径上的第 i 个点为 seqi。
从 s 到 t 的过程中,有四种走法:
- 转移 1:向 t 的方向走 1 步。
- 转移 2:向 t 的方向走 2 步。
- 转移 3:向 t 的方向走 3 步。
- 转移 4:向 t 的方向走 2 步,再向它的某个儿子走 1 步。
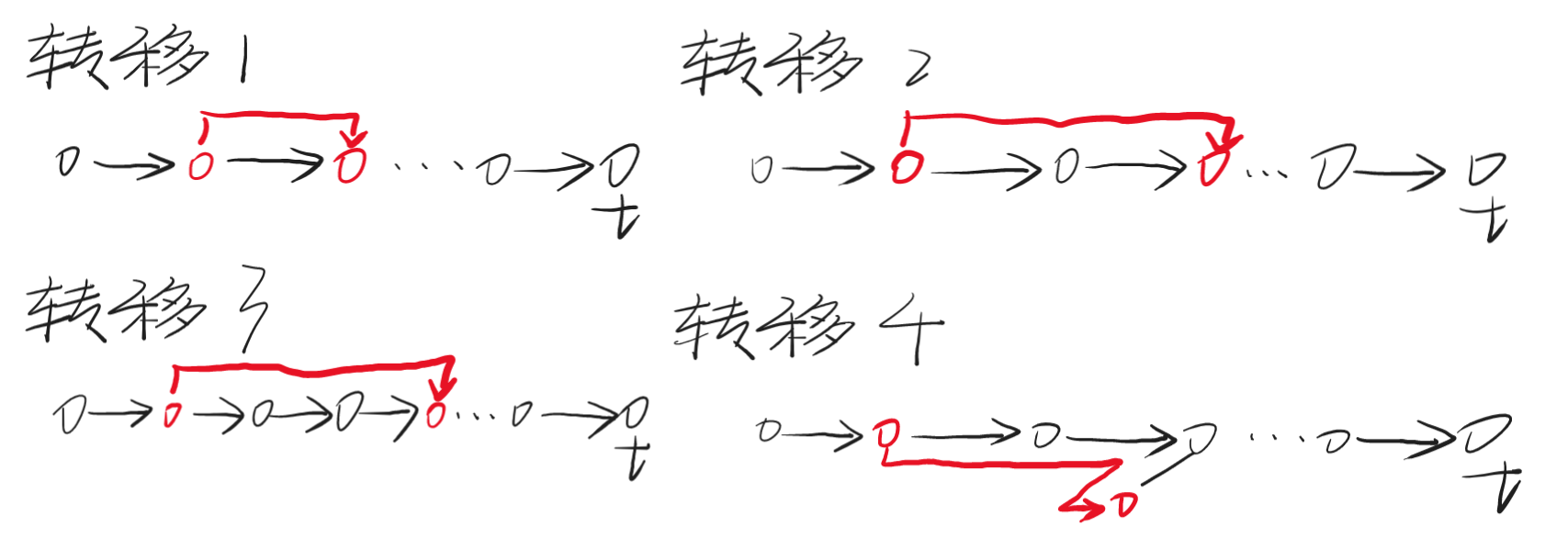
至于为什么不能从当前点向 t 的方向走 1 步,再向它的子树内走 2 步。这是因为使用这种转移后的下一步转移,被从当前点出发的所有下一步转移包含,而这种转移多走了一个点,显然是更劣的。
注意到在转移 4 中,向 t 的方向走 2 步,再向它的某个儿子走 1 步,则走向的这个儿子的权值要尽量小。故记录 greatu 表示 u 的点权最小的出点的权值,即 min(u,v)∈E{av}。
设 fi,0/1/2 分别表示到从起点 s 出发,与 seqi 距离为 0/1/2 的点的代价和最小值,则:
注意到这个转移可以看成是(这里的矩阵乘法是 min,+ 广义矩阵乘法):
考虑动态 dp。有两种写法:
- 运用树上倍增自下而上地维护矩阵积。回答询问时,将 s→LCA(s,t) 的链信息与 t→LCA(s,t) 的链信息分别求出来,分类讨论合并信息。
- 运用树上倍增自下而上、自上而下地维护矩阵积。回答询问时,将 s→LCA(s,t) 的链信息与 LCA(s,t)→t 的链信息分别求出来,合并信息。
至于 k=1,2 的情况就很简单了,这里留给读者。
时间复杂度 O(nk3logn)。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
template <class T>
inline void read(T &x) {
static char s;
while (s = getchar(), s < '0' || s > '9');
x = s - '0';
while (s = getchar(), s >= '0' && s <= '9') x = x * 10 + s - '0';
}
template <class P, class Q>
void relax(P &x, const Q &y) {
if (x > y) x = y;
}
typedef long long s64;
const int N = 200100;
const s64 inf = 1e18;
int n, Q, k;
int a[N];
int great_son[N];
int tot, head[N], ver[N * 2], Next[N * 2];
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
ver[++ tot] = v; Next[tot] = head[u]; head[u] = tot;
}
struct mat {
s64 num[3][3];
mat() { memset(num, 0x3f, sizeof(num)); }
void init(int u, int v) {
if (k == 1) {
num[0][0] = a[u];
} else if (k == 2) {
num[0][0] = a[u], num[0][1] = 0;
num[1][0] = a[u], num[1][1] = inf;
} else {
num[0][0] = a[u], num[0][1] = 0, num[0][2] = inf;
num[1][0] = a[u], num[1][1] = great_son[u], num[1][2] = 0;
num[2][0] = a[u], num[2][1] = inf, num[2][2] = great_son[v];
}
}
mat operator * (const mat &rhs) const {
mat self;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i ++)
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++)
for (int p = 0; p < k; p ++)
relax(self.num[i][j], num[i][p] + rhs.num[p][j]);
return self;
}
};
struct vec {
s64 num[3];
vec() { memset(num, 0x3f, sizeof(num)); }
vec(int x) { num[0] = x; num[1] = num[2] = inf; }
vec operator * (const mat &rhs) const {
vec self;
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++)
for (int p = 0; p < k; p ++)
relax(self.num[j], num[p] + rhs.num[p][j]);
return self;
}
};
int Fa[N];
int dep[N];
int anc[18][N];
mat f[18][N];
void dfs(int u) {
dep[u] = dep[Fa[u]] + 1;
great_son[u] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int v = ver[i];
if (v == Fa[u]) continue;
relax(great_son[u], a[v]);
}
if (Fa[u]) {
anc[0][u] = Fa[u], f[0][u].init(Fa[u], u);
for (int i = 1; i <= 17; i ++) {
anc[i][u] = anc[i - 1][anc[i - 1][u]]; if (!anc[i][u]) break;
f[i][u] = f[i - 1][u] * f[i - 1][anc[i - 1][u]];
}
}
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int v = ver[i];
if (v == Fa[u]) continue;
Fa[v] = u;
dfs(v);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (dep[x] > dep[y]) std::swap(x, y);
for (int i = 17; i >= 0; i --)
if (dep[x] <= dep[anc[i][y]]) y = anc[i][y];
if (x == y) return x;
for (int i = 17; i >= 0; i --)
if (anc[i][x] != anc[i][y]) x = anc[i][x], y = anc[i][y];
return anc[0][x];
}
vec calc(int x, int up) {
vec v = vec(a[x]);
for (int i = 17; i >= 0; i --)
if (up >> i & 1) v = v * f[i][x], x = anc[i][x];
return v;
}
int main() {
read(n), read(Q), read(k);
a[0] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) read(a[i]);
for (int i = 1, u, v; i < n; i ++) {
read(u), read(v);
add_edge(u, v), add_edge(v, u);
}
dfs(1);
while (Q --) {
int x, y, z;
read(x), read(y), z = lca(x, y);
if (k == 1) {
if (y == z) { printf("%lld\n", calc(x, dep[x] - dep[y]).num[0]); continue; }
if (x == z) { printf("%lld\n", calc(y, dep[y] - dep[x]).num[0]); continue; }
printf("%lld\n", calc(x, dep[x] - dep[z] - 1).num[0] + calc(y, dep[y] - dep[z] - 1).num[0] + a[z]);
} else if (k == 2) {
if (y == z) { printf("%lld\n", calc(x, dep[x] - dep[y]).num[0]); continue; }
if (x == z) { printf("%lld\n", calc(y, dep[y] - dep[x]).num[0]); continue; }
vec dx = calc(x, dep[x] - dep[z] - 1), dy = calc(y, dep[y] - dep[z] - 1);
s64 ans = inf;
relax(ans, std::min(dx.num[0], dx.num[1]) + std::min(dy.num[0], dy.num[1]) + a[z]);
relax(ans, dx.num[0] + dy.num[0]);
printf("%lld\n", ans);
} else {
if (y == z) { printf("%lld\n", calc(x, dep[x] - dep[y]).num[0]); continue; }
if (x == z) { printf("%lld\n", calc(y, dep[y] - dep[x]).num[0]); continue; }
vec dx = calc(x, dep[x] - dep[z] - 1), dy = calc(y, dep[y] - dep[z] - 1);
s64 tx = inf, ty = inf;
relax(tx, dx.num[0]), relax(tx, dx.num[1]), relax(tx, dx.num[2]);
relax(ty, dy.num[0]), relax(ty, dy.num[1]), relax(ty, dy.num[2]);
s64 ans = inf;
relax(ans, tx + ty + a[z]);
relax(ans, dx.num[0] + dy.num[0]);
relax(ans, dx.num[1] + dy.num[0]);
relax(ans, dx.num[0] + dy.num[1]);
relax(ans, dx.num[1] + dy.num[1] + std::min(great_son[z], a[Fa[z]]));
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
template <class T>
inline void read(T &x) {
static char s;
while (s = getchar(), s < '0' || s > '9');
x = s - '0';
while (s = getchar(), s >= '0' && s <= '9') x = x * 10 + s - '0';
}
void relax(int &x, const int &y) {
if (x > y) x = y;
}
typedef long long s64;
const int N = 200100;
const s64 inf = 1e18;
int n, Q, k;
int a[N], great[N];
int tot, head[N], ver[N * 2], Next[N * 2];
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
ver[++ tot] = v; Next[tot] = head[u]; head[u] = tot;
}
struct mat {
int r, c;
s64 num[3][3];
mat() {}
mat(int _r, int _c) {
r = _r, c = _c;
for (int i = 0; i < r; i ++)
for (int j = 0; j < c; j ++)
num[i][j] = inf;
}
void init(int u, int pre) {
r = c = k;
if (k == 1) {
num[0][0] = a[u];
} else if (k == 2) {
num[0][0] = a[u], num[0][1] = 0;
num[1][0] = a[u], num[1][1] = inf;
} else {
num[0][0] = a[u], num[0][1] = 0, num[0][2] = inf;
num[1][0] = a[u], num[1][1] = great[u], num[1][2] = 0;
num[2][0] = a[u], num[2][1] = inf, num[2][2] = great[pre];
}
}
mat operator * (const mat &rhs) const {
mat cur(r, rhs.c);
for (int i = 0; i < r; i ++)
for (int j = 0; j < rhs.c; j ++)
for (int p = 0; p < c; p ++)
cur.num[i][j] = std::min(cur.num[i][j], num[i][p] + rhs.num[p][j]);
return cur;
}
};
mat up[18][N], dn[18][N];
int dep[N];
int anc[18][N];
void dfs(int u, int fu) {
dep[u] = dep[fu] + 1;
anc[0][u] = fu;
for (int i = 1; i <= 17; i ++) anc[i][u] = anc[i - 1][anc[i - 1][u]];
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int v = ver[i];
if (v == fu) continue;
up[0][v].init(u, v), dn[0][v].init(v, u);
dfs(v, u);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (dep[x] > dep[y]) std::swap(x, y);
for (int i = 17; i >= 0; i --)
if (dep[x] <= dep[y] - (1 << i)) y = anc[i][y];
if (x == y) return x;
for (int i = 17; i >= 0; i --)
if (anc[i][x] ^ anc[i][y]) x = anc[i][x], y = anc[i][y];
return anc[0][x];
}
void calc_up(int x, int k, mat &cur) {
for (int i = 17; i >= 0; i --)
if (k >> i & 1) cur = cur * up[i][x], x = anc[i][x];
}
void calc_dn(int x, int k, mat &cur) {
static int seq[18];
for (int i = 0; i <= 17; i ++)
if (k >> i & 1) seq[i] = x, x = anc[i][x];
for (int i = 17; i >= 0; i --)
if (k >> i & 1) cur = cur * dn[i][seq[i]];
}
int main() {
read(n), read(Q), read(k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
read(a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) great[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for (int i = 1, u, v; i < n; i ++) {
read(u), read(v);
add_edge(u, v), add_edge(v, u);
relax(great[u], a[v]);
relax(great[v], a[u]);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for (int j = 1; j <= 17; j ++)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
up[j][i] = up[j - 1][i] * up[j - 1][anc[j - 1][i]],
dn[j][i] = dn[j - 1][anc[j - 1][i]] * dn[j - 1][i];
while (Q --) {
int x, y, z;
read(x), read(y), z = lca(x, y);
mat cur(1, k);
cur.num[0][0] = a[x], cur.num[0][1] = cur.num[0][2] = inf;
calc_up(x, dep[x] - dep[z], cur);
calc_dn(y, dep[y] - dep[z], cur);
printf("%lld\n", cur.num[0][0]);
}
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探