Python3练习
Hello Python3
1 print("Hello Python!") 2 #print("Hello, Python!"); 3 '''a=1 4 b=2 5 c=a+b 6 print(c) 7 ''' 8 9 #列表:存储多个元素的东西,列表里面的元素是可以重新赋值的 10 a=[1,"a"] 11 a[0]=2 12 #元组:存储多个元素的东西,元组里面的元素不可用重新赋值 13 b=(1,"b") 14 #字典 15 #{key1:value1, key2:value} 16 #集合 17 #去重 18 19 #if语句 20 a=10 21 b=1 22 if(a > 9): 23 print(a) 24 if(b < 9): 25 print(b) 26 27 age=18 28 if(age <= 10): 29 print("儿童") 30 elif(age > 10 and age <= 20): 31 print("青少年") 32 elif(age > 20): 33 print("青年") 34 else: 35 print("小伙子") 36 37 #while语句 38 a=0 39 while(a<10): 40 print("hello") 41 a += 1 42 43 #for语句:遍历列表 44 a=["aa", "bb", "cc", "dd"] 45 for i in a: 46 print(i) 47 #for语句:常规循环 48 for i in range(0, 10): 49 print(i) 50 for i in range(0, 10): 51 print("AAA") 52 #中断退出:continue,break 53 for i in a: 54 if(i=="cc"): 55 break 56 print(i) 57 for i in a: 58 if(i=="cc"): 59 continue 60 print(i) 61 #乘法口诀 62 #end=""表示不换行输出 63 for i in range(1, 10): 64 for j in range(1, i+1): 65 print(str(i) + "*" + str(j) + "=" + str(i*j), end=" ") 66 print() 67 print("-----------------------") 68 for i in range(9, 0, -1): 69 for j in range(1, i+1): 70 print(str(i) + "*" + str(j) + "=" + str(i*j), end=" ") 71 print() 72 73 ''' 74 #作用域 75 i=10 76 def func(): 77 j=20 78 print(j) 79 print(j) 80 ''' 81 82 #函数 83 #函数定义格式: 84 #def 函数名(参数): 85 # 函数体 86 87 def abc(): 88 print("abcdef") 89 #调用函数:函数名(参数) 90 abc() 91 92 def func2(a, b): 93 if(a > b): 94 print("a>b") 95 else: 96 print("a<=b") 97 func2(1,2) 98 func2(5,4) 99 100 #模块导入 101 import cgi 102 cgi.closelog() 103 from cgi import closelog 104 105 #文件操作 106 #打开 open(文件路径, 操作形式) 107 ''' 108 w:写 109 r:读 110 b:二进制 111 a:追加 112 ''' 113 file = open("D:/python/1.txt", "r") 114 data=file.read() 115 print(data) 116 data=file.readline() 117 print(data) 118 file.close() 119 #文件写入 120 data2="一起学python" 121 file2=open("D:/python/2.txt", "w") 122 file2.write(data2) 123 file2.close() 124 data2="Java" 125 file2=open("D:/python/2.txt", "a+") 126 file2.write(data2) 127 file2.close() 128 129 #异常处理 130 try: 131 a = 1 / 0 132 except Exception as ex: 133 print(ex) 134 135 #类 136 class User: 137 def __init__(self): 138 print("无参构造函数") 139 a=User() 140 141 class Person: 142 def __init__(self, name, age): 143 print("带参数的构造函数,name=" + name + ", age=" + age) 144 c1=Person("zhangsan", str(20)) 145 c2=Person("lisi", str(22)) 146 147 class Rabbit: 148 def __init__(self, name, color): 149 self.name = name 150 self.color = color 151 def func1(self): 152 print("aaa"); 153 def func2(self, age): 154 print("这个兔子已经" + str(age) + "岁了") 155 def toString(self): 156 print("Rabbit [name=" + self.name + ", color=" + self.color + "]") 157 r1 = Rabbit("流氓兔", "白色") 158 r1.func1() 159 r1.func2(3) 160 r1.toString() 161 162 #继承 163 class Father(): 164 def write(self): 165 print("写作") 166 class Son(Father): 167 pass 168 class Mother(): 169 def draw(self): 170 print("画画") 171 def makeDinner(self): 172 print("做饭") 173 class Daughter(Father, Mother): 174 def draw(self): 175 print("素描") 176 son = Son() 177 son.write() 178 daughter = Daughter() 179 daughter.write() 180 daughter.draw() 181 daughter.makeDinner() 182 183 184 print("Hello\n" * 3) 185 186 #str是关键字是函数名不能随便用 187 tmp = input("请输入一个数字:") 188 print(tmp) 189 190 #递归 191 def factorial(n): 192 if(n == 1): 193 return 1 194 else: 195 return n * factorial(n-1) 196 number = int(input("请输入一个正整数:")) 197 result = factorial(number) 198 print("%d的阶乘是%d"%(number, result)) 199 200 201 def fab(n): 202 if(n == 1 or n == 2): 203 return 1 204 else: 205 return fab(n-1) + fab(n-2) 206 number = int(input("请输入一个正整数:")) 207 result = fab(number) 208 print("总共" + str(result) + "对兔子")
数据类型以及传参
1 # 数据类型 2 num = 123 3 print(type(num)) 4 f = 2.0 5 f = 5.0 / 2 6 print(f) 7 str1 = 'hello world' 8 print(str1) 9 str2 = "hello world" 10 print(str2) 11 str3 = "hello \"world\"" 12 str4 = "hello 'world'" 13 print(str3) 14 print(str4) 15 str5 = "Jack: \nI love you" 16 print(str5) 17 mail = """ 18 Rose: 19 I'am Jack 20 goodbye 21 """ 22 print(mail) 23 str6 = "abcdef" 24 print(str6[0]) 25 print(str6[1]) 26 print(str6[0] + str6[1]) 27 print(str6[1:4]) 28 print(str6[4:]) 29 print(str6[:4]) 30 print(str6[2:]) 31 print(str6[::2]) 32 print(str6[-1]) 33 print(str6[-4:-1]) 34 str7 = "1234" 35 print(id(str7)) 36 str7 = "1234" 37 print(id(str7)) 38 39 # 元组 40 t = ("Jack", 19, "male") 41 print(t) 42 print(t[0]) 43 print(type(t)) 44 t2 = (3,) 45 print(type(t2)) 46 print(len(t2)) 47 print(len(str6)) 48 a,b,c=(1,2,3) 49 print(a) 50 print(b) 51 print(c) 52 a,b,c=t 53 print(a) 54 print(b) 55 print(c) 56 57 # 列表 58 list1 = ["jack", 21, True, [1,2,3]] 59 print(list1[0]) 60 print(type(list1)) 61 print(list1[3]) 62 print(len(list1)) 63 list1[0]="rose" 64 list1[1]="jerry" 65 print(list1) 66 list1.append(3) 67 print(list1) 68 list1.remove(3) 69 del(list1[2]) 70 print(list1) 71 list2 = [1,2,3] 72 list2.append(4) 73 74 # 查看帮助 75 help(list) 76 help(list.remove) 77 help(len) 78 79 # 字典 80 dict1 = {"name":"jack", "age":25, "gender":"male"} 81 print(dict1["name"]) 82 print(dict1.keys()) 83 print(dict1.values()) 84 dict1["phone"] = "13712345678" 85 dict1["phone"] = "15923423455" 86 print(dict1) 87 del dict1["phone"] 88 print(dict1) 89 print(dict1.pop("age")) 90 91 # 条件语句 92 if 1 < 2: 93 print(1234) 94 if(2 > 1): 95 print("hhh") 96 if(True): 97 print("ok") 98 if(1+1): 99 print("yes") 100 101 102 # for循环 103 print(range(1,10)) 104 print(range(1, 10, 2)) 105 print(range(5)) 106 arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] 107 for i in arr: 108 print(i) 109 for i in range(len(arr)): 110 print(arr[i]) 111 num = 0 112 for i in range(101): 113 num += i 114 print(num) 115 116 for i in range(3): 117 print(i) 118 else: 119 print("finish") 120 121 # 遍历字典 122 d = {1:111, 2:222, 3:333} 123 for x in d: 124 print(d[x]) 125 for k,v in d.items(): 126 print(k) 127 print(v) 128 d2 = {"name":"zhangsan", "age":20} 129 for k,v in d2.items(): 130 print(k) 131 print(v) 132 133 # 函数 134 def func(): 135 print("123") 136 func() 137 138 def func2(x, y): 139 print(x) 140 print(y) 141 func2(3,4) 142 143 # 参数的默认值 144 def func3(x=5,y=6): 145 print("x=" + str(x) + ", y=" + str(y)) 146 func3() 147 func3(7,8) 148 149 def func4(x, y=9): 150 print("x=" + str(x) + ", y=" + str(y)) 151 func4(10) 152 func4(11, 12) 153 154 def func5(): 155 x = input("Please Enter A Number: ") 156 print(x) 157 func5() 158 159 160 def func6(): 161 global a 162 a = "good" 163 func6() 164 print(a) 165 166 # 传参:元组 167 # 传元组 168 def f(x,y): 169 print("x=%s, y=%s" % (x,y)) 170 f(1,2) 171 f(*(3,4)) 172 t = ("Tom", "Jerry") 173 f(*t) 174 175 def f1(x, y): 176 print("x=%s, y=%s" % (x, y)) 177 t = (20, "Jack") 178 f1(*t) 179 180 # 传字典 181 def f2(name, code, age): 182 print("name=%s, code=%s, age=%s" % (name, code, age)) 183 d = {"name": "zhangsan", "code": "10001", "age": 22} 184 f2(**d) 185 d["age"] = 28 186 f2(**d) 187 f2(d["name"], d["code"], d["age"]) 188 189 # 参数冗余 190 # 多余的实参 191 def f3(x, *args): 192 print(x) 193 print(args) 194 f3(1) 195 f3(1,2) 196 f3(1,2,3,4) 197 def f4(x, *args, **kwargs): 198 print(x) 199 print(args) 200 print(kwargs) 201 f4(1) 202 f4(1, 2) 203 f4(1, 2, 3) 204 f4(1, y=3, z=4) 205 f4(1, **d) 206 f4(1, 2, 3, 4, y=6, z=7, xy=8) 207 208 # lambda表达式 209 f6 = lambda x,y:x*y 210 print(f6(3, 4)) 211 212
内置函数
1 # Python内置函数 2 print(abs(2)) 3 print(abs(-2)) 4 r = range(11) 5 print(max(r)) 6 print(min(r)) 7 print(max([3,2,1,9])) 8 print(len(r)) 9 print(divmod(5,3)) 10 print(pow(2,10)) 11 print(round(2.5)) 12 print(type(r)) 13 a = "1234" 14 print(int(a)) 15 b = 99 16 print(str(b)) 17 print(hex(b)) 18 print(list([1,2,3,4])) 19 20 # 字符串函数 21 # str.capitalize() 首字母大写 22 # str.replace() 字符替换 23 # str.split() 分割 24 help(str.capitalize) 25 help(str.replace) 26 help(str.split) 27 s = "hello" 28 print(s.capitalize()) 29 y = "123123123123" 30 print(y.replace("12", "AB")) 31 print(y.replace("12", "AB", 1)) 32 print(y.replace("12", "AB", 2)) 33 ip = "192.168.12.93" 34 print(ip.split(".")) 35 print(ip.split(".", 1)) 36 print(ip.split(".", 2)) 37 38 # 序列处理函数 39 help(filter) 40 help(zip) 41 help(map) 42 from functools import reduce 43 help(reduce) 44 def f1(x): 45 if(x > 0): 46 return True 47 return False 48 r = [1,2,-1,-2,0,3] 49 ss = filter(f1, r) 50 print(ss) 51 print(list(filter(lambda x:x%2==0, range(10)))) 52 53 result = filter(lambda x:x*2, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) 54 print(result) 55 print(list(result)) 56 print(list(filter(lambda x: x%2 == 0, range(8)))) 57 58 # 这里的map函数和reduce函数就相当于MapReduce中的Map阶段和Reduce阶段 59 # Map阶段计算,Reduce阶段合并结果 60 foo = [2, 18, 9, 22, 17, 24, 8, 12, 27] 61 print(list(filter(lambda x:x % 3 == 0, foo))) 62 print(map(lambda x:x*2+10, foo)) 63 print(list(map(lambda x:x*2+10, foo))) 64 print(reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])) 65 print(reduce(lambda x, y: x*y, range(1, 6))) 66 print(reduce(lambda x,y:x+y, foo)) 67 68 t1 = ["zhangsan", "lisi", "wangwu", "zhaoliu"] 69 t2 = ["北京", "上海", "广州", "深圳"] 70 t3 = [20, 21, 22, 23] 71 res = zip(t1, t2, t3) 72 print(list(res)) 73 74 ''' 75 包 76 Python的模块可以按目录组织为包 77 创建一个包的步骤是: 78 1、建立一个名字为包名字的文件夹 79 2、在该文件夹下创建一个__init__.py文件 80 3、根据需要在该文件夹下存放脚本文件、已编译扩展及子包 81 4、import pack.m1, pack.m2, pack.m3 82 83 模块 84 模块是Pyhon组织代码的基本方式 85 Pyhon的脚本都是用扩展名为py的文本文件保存的,一个脚本可以单独运行, 86 也可以导入另一个脚本中运行。当脚本被导入运行时,我们将其称为模块(module) 87 88 模块名与脚本的文件名相同(例如,我们编写了一个名为items.py的脚本,则可以在另一个脚本中用import items语句来导入它) 89 90 '''
正则表达式
1 # 正则表达式 2 # 参考菜鸟教程 http://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-reg-expressions.html 3 import re 4 print(re.match('www', 'www.baidu.com')) 5 print(re.match('www', 'www.baidu.com').span(0)) 6 print(re.match('com', 'www.baidu.com')) 7 8 line = "Cats are smarter than dogs" 9 matchObj = re.match(r'(.*) are (.*?) .*', line, re.M|re.I) 10 if matchObj: 11 print(matchObj.group()) 12 print(matchObj.group(1)) 13 print(matchObj.group(2)) 14 else: 15 print("No match!!!") 16 17 print(re.search('www', 'www.baidu.com').span()) 18 print(re.search('com', 'www.baidu.com').span()) 19 20 # re.match与re.search的区别 21 # re.match只匹配字符串的开始,如果字符串开始不符合正则表达式,则匹配失败,函数返回None; 22 # 而re.search匹配整个字符串,直到找到一个匹配。 23 24 line = "Cats are smarter than dogs" 25 26 # 简单地来说,re.match看的是字符串是不是以指定的正则表达式开头的 27 matchObj = re.match(r'dogs', line, re.M|re.I) 28 if matchObj: 29 print("match --> matchObj.group(): ", matchObj.group()) 30 else: 31 print("No match!!!") 32 33 matchObj = re.search(r'dogs', line, re.M|re.I) 34 if matchObj: 35 print("search --> matchObj.group(): ", matchObj.group()) 36 else: 37 print("No match!!!") 38 39 # 检索和替换 40 # re.sub用于替换字符串中的匹配项 41 # 42 # 语法:re.sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0) 43 # 参数: 44 # pattern : 正则中的模式字符串。 45 # repl : 替换的字符串,也可为一个函数。 46 # string : 要被查找替换的原始字符串。 47 # count : 模式匹配后替换的最大次数,默认 0 表示替换所有的匹配。 48 49 phone = "2004-959-559 # 这是一个电话号码" 50 num = re.sub(r'#.*$', "", phone) 51 print("电话号码:", num) 52 53 num = re.sub(r'\D', "", phone) 54 print("电话号码:", num) 55 56 # compile函数 57 # compile 函数用于编译正则表达式,生成一个正则表达式( Pattern )对象,供 match() 和 search() 这两个函数使用。 58 # 语法:re.compile(pattern[, flags]) 59 60 pattern = re.compile(r'\d+') 61 m = pattern.match('one1two2three3four4') 62 print(m) 63 m = pattern.match('one1two2three3four4', 3, 10) 64 print(m) 65 print(m.group()) 66 print(m.start()) 67 print(m.end()) 68 print(m.span()) 69 # group([group1, …]) 方法用于获得一个或多个分组匹配的字符串,当要获得整个匹配的子串时,可直接使用 group() 或 group(0); 70 # start([group]) 方法用于获取分组匹配的子串在整个字符串中的起始位置(子串第一个字符的索引),参数默认值为 0; 71 # end([group]) 方法用于获取分组匹配的子串在整个字符串中的结束位置(子串最后一个字符的索引+1),参数默认值为 0; 72 # span([group]) 方法返回 (start(group), end(group))。 73 74 # findall 75 # 在字符串中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并返回一个列表,如果没有找到匹配的,则返回空列表。 76 # 77 # 注意: match 和 search 是匹配一次 findall 匹配所有。 78 79 # 语法:findall(string[, pos[, endpos]]) 80 # 参数: 81 # string 待匹配的字符串 82 # pos 可选参数,指定字符串的起始位置,默认为0 83 # endpos 可选参数,指定字符串的结束位置,默认为字符串的长度 84 85 pattern = re.compile(r'\d+') 86 result1 = pattern.findall('runoob 123 google 456') 87 result2 = pattern.findall('run88oob123google456', 0, 10) 88 print(result1) 89 print(result2) 90 91 # re.finditer 92 # 和 findall 类似,在字符串中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并把它们作为一个迭代器返回。 93 94 it = re.finditer(r"\d+", "12a23bce34fj666") 95 for match in it: 96 print(match.group()) 97 98 # re.split 99 # split 方法按照能够匹配的子串将字符串分割后返回列表 100 # 语法:re.split(pattern, string[, maxsplit=0, flags=0]) 101 102 print(re.split('\W+', 'abc, runoob, wahaha, 1342')) 103 print(re.split('(\W+)', 'abc, runoob, wahaha, 1342')) 104 print(re.split('\W+', 'abc, runoob, wahaha, 1342', 1)) 105 print(re.split('a+', 'hello world'))# 对于一个找不到匹配的字符串而言,split 不会对其作出分割
文件操作
1 # 文件读写 2 f = open("D:/python/a.txt","r") 3 print(f.readline()) 4 txt = f.read() 5 print(txt) 6 f.close() 7 ## f.read() 8 9 f = open("D:/python/a.txt","r") 10 for line in f: 11 print(line) 12 f.close() 13 14 f = open("D:/python/b.txt","w+") 15 f.write("I am Mr.Cheng") 16 f.write("Very Good!") 17 print(f.read()) 18 f.flush() 19 f.seek(0) 20 print(f.read()) 21 f.close() 22 23 f = open("D:/python/b.txt","a+") 24 f.write("\nhot") 25 f.seek(0) 26 print(f.read()) 27 f.close()
异常处理
1 # finally 2 try: 3 ff = open("D:/python/b.txt","a+") 4 except Exception: 5 print(1) 6 finally: 7 ff.close() 8 print(2) 9 10 11 try: 12 f = open("abc.txt") 13 f.close() 14 except (OSError, RuntimeError, TypeError, NameError): 15 pass 16 17 try: 18 f = open("abc.txt") 19 f.close() 20 except OSError as err: 21 print("OSError") 22 except ValueError: 23 print("ValueError") 24 except NameError: 25 print("NameError") 26 except: 27 print("Unexpected Error") 28 29 # raise 抛出异常 30 try: 31 x = int(input("Please enter a number: ")) 32 if(x == 123): 33 raise NameError("You are kidding!") 34 except NameError: 35 print("name error") 36 except ValueError: 37 print("value error") 38 except TypeError: 39 print("type error") 40 finally: 41 print("Goodbye")
类和对象
1 # 类和对象 2 class MyClass: 3 i = 123 4 5 def m(self): 6 return 'hello' 7 8 x = MyClass() 9 10 print(x.i) 11 print(x.m()) 12 13 14 # __init__()是构造方法 15 class Person: 16 17 name = "" 18 age = 0 19 20 def __init__(self): 21 print("无参构造方法被调用") 22 23 def __init__(self, name, age): 24 print("带参数的构造法被调用") 25 self.name = name 26 self.age = age 27 28 def toString(self): 29 print("Person [name={0}, age={1}]".format(self.name, self.age)) 30 31 32 person = Person("zhangsan", 25) 33 person.toString() 34 35 print(id(person)) 36 37 # self 代表类的实例,self 在定义类的方法时是必须有的,虽然在调用时不必传入相应的参数 38 # self相当于Java中的this 39 # 类的方法必须有一个额外的第一个参数,按照惯例它的名称是 self 40 41 class Employee: 42 43 empCount = 0 44 45 46 def __init__(self, name, salary): 47 self.name = name 48 self.salary = salary 49 Employee.empCount += 1 50 51 def displayCount(self): 52 print("Total Employee %d" % Employee.empCount) 53 54 def toString(self): 55 print("wahaha") 56 57 employee1 = Employee("zhangsan", 27) 58 employee2 = Employee("lisi", 28) 59 employee3 = Employee("wangwu", 29) 60 print(Employee.empCount) 61 print(employee1.displayCount()) 62 print(employee2.name) 63 print(employee3.salary) 64 print(Employee.__name__) 65 print(Employee.__module__) 66 67 # 继承 68 class Leader(Employee): 69 def __init__(self): 70 print("调用子类的构造方法") 71 72 73 leader = Leader() 74 leader.toString() 75 76 class Father: 77 def sing(self): 78 print("我会唱歌") 79 def write(self): 80 print("我擅长写粉笔字") 81 82 class Mother: 83 def dance(self): 84 print("我会跳舞") 85 86 class Son(Father, Mother): 87 def draw(self): 88 print("我会画画") 89 def write(self): 90 print("我擅长写毛笔字") 91 92 son = Son() 93 son.sing() 94 son.dance() 95 son.draw() 96 son.write() 97 98 # 两个下划线开头,声明该属性为私有,不能在类的外部被使用或直接访问。在类内部的方法中使用时 self.__private_attrs 99 # 两个下划线开头,声明该方法为私有方法,不能在类的外部调用。在类的内部调用 self.__private_methods 100 class Daughter: 101 102 name = "" # public属性 103 _height = 0 # protected属性 104 __age = 0 # private属性 105 106 def __init__(self, name, height, age): 107 self.name = name 108 self._height = height 109 self.__age = age 110 111 def getName(self): # public 112 return self.name 113 114 def __getAge(self): # private 115 return self.__age 116 117 def getAge(self): 118 return self.__age 119 120 daughter = Daughter("Alice", 170, 24) 121 print(daughter.name) 122 print(daughter._height) 123 #print(daughter.__age) 124 #print(daughter.__getAge()) 125 print(daughter.getAge())
MySQL操作
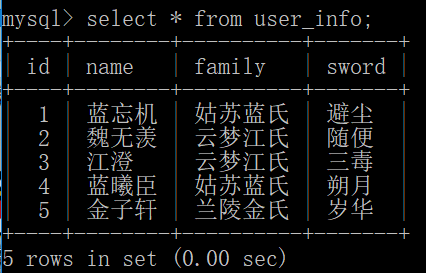
1 import pymysql 2 ''' 3 # 建立连接 4 conn = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "123456", "mytest") 5 # 获取游标 6 cursor = conn.cursor() 7 # SQL语句 8 #sql = "insert into user_info(name, family, sword) values('蓝忘机', '姑苏蓝氏', '避尘')" 9 sql = "insert into user_info(name, family, sword) values('%s', '%s', '%s')" % ('魏无羡', '云梦江氏', '随便') 10 try: 11 # 执行SQL 12 cursor.execute(sql) 13 # 提交 14 conn.commit() 15 except: 16 # 回滚 17 conn.rollback() 18 finally: 19 # 关闭连接 20 conn.close() 21 22 # 批量插入 23 conn = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "123456", "mytest") 24 cursor = conn.cursor() 25 sqlTemplate = "insert into user_info(name, family, sword) values('%s', '%s', '%s')" 26 dataList = [('江澄', '云梦江氏', '三毒'), ('蓝曦臣', '姑苏蓝氏', '朔月'), ('金子轩', '兰陵金氏', '岁华')] 27 try: 28 # 方式一:使用execute 29 for data in dataList: 30 sql = sqlTemplate % data 31 cursor.execute(sql) 32 33 # 方式二:使用executemany 34 insertTemplate = "insert into user_info(name, family, sword) values(%s, %s, %s)" 35 dataArray = [('江澄', '云梦江氏', '三毒'), ('蓝曦臣', '姑苏蓝氏', '朔月'), ('金子轩', '兰陵金氏', '岁华')] 36 cursor.executemany(insertTemplate, dataArray) 37 38 conn.commit() 39 except Exception as ex: 40 print(ex) 41 conn.rollback() 42 finally: 43 conn.close() 44 ''' 45 # 查询 46 # Python查询Mysql使用 fetchone() 方法获取单条数据, 使用fetchall() 方法获取多条数据。 47 # fetchone(): 该方法获取下一个查询结果集。结果集是一个对象 48 # fetchall(): 接收全部的返回结果行. 49 conn = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "123456", "mytest") 50 cursor = conn.cursor() # 隐式开启事务 51 sql = "select * from user_info" 52 try: 53 cursor.execute(sql) # 返回受影响的行数 54 records = cursor.fetchall() 55 for row in records: 56 print(row) 57 for row in records: # 数组的元素是元组 58 print("name=%s, family=%-3s, sword=%4s" % (row[0], row[1], row[2])) 59 except: 60 print("Error: unable to fetch data") 61 finally: 62 conn.close()
Socket编程
1 import socket 2 import sys 3 4 # 创建socket对象 5 serverSocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) 6 7 # 绑定端口 8 # #host = socket.gethostname() 9 10 host = "localhost" 11 port = 9999 12 serverSocket.bind((host, port)) 13 14 # 设置最大连接数 15 serverSocket.listen(5) 16 17 # 监听客户端连接 18 while True: 19 print(1234) 20 clientSocket, addr = serverSocket.accept() 21 print("客户端连接: %s" % str(addr)) 22 msg = "Hello World" 23 clientSocket.send(msg.encode("utf-8")) 24 clientSocket.close()
1 import socket 2 import sys 3 4 clientSocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) 5 print(4455) 6 clientSocket.connect(("localhost", 9999)) 7 8 msg = clientSocket.recv(1024) 9 10 print(msg.decode("utf-8"))
线程
1 import threading 2 import time 3 4 ''' 5 相当于 6 class MyThread extends Thread { 7 public Integer threadId; 8 public String threadName; 9 10 public MyThread(Integer threadId, String threadName) { 11 this.threadId = threadId; 12 this.threadName = threadName; 13 } 14 15 @Override 16 public void run() { 17 System.out.print(this.threadName + " : " + new Date()); 18 } 19 } 20 21 Thread thread1 = new MyThread(); 22 Thread thread2 = new MyThread(); 23 thread1.start(); 24 thread2.start(); 25 ''' 26 27 28 class MyThread(threading.Thread): 29 30 def __init__(self, threadId, threadName): 31 threading.Thread.__init__(self) 32 33 self.threadId = threadId 34 self.threadName = threadName 35 36 def run(self): 37 print("启动线程:" + self.name) 38 self.do_something() 39 40 def do_something(self): 41 print("%s: %s" % (self.threadName, time.ctime(time.time()))) 42 43 44 thread1 = MyThread(1, "Thread-1") 45 thread2 = MyThread(2, "Thread-2") 46 47 thread1.start() 48 thread2.start() 49 50 print("****************************************") 51 52 # 相当于synchronized代码块 53 threadLock = threading.Lock() 54 55 class Ticket: 56 __total = 100 57 58 def decr(self): 59 threadLock.acquire() 60 time.sleep(1) 61 if self.__total > 0: 62 self.__total = self.__total - 1 63 print("成功售出一张票,剩余%s张" % self.__total) 64 else: 65 print("今日已售罄") 66 threadLock.release() 67 68 69 class Customer(threading.Thread): 70 def __init__(self, ticket): 71 threading.Thread.__init__(self) 72 self.ticket = ticket 73 74 def run(self): 75 self.ticket.decr() 76 77 78 ticketObj = Ticket() 79 for i in range(150): 80 consumer = Customer(ticketObj) 81 consumer.start()
HTTP请求
1 import urllib.request 2 import urllib.parse 3 import requests 4 5 resp = urllib.request.urlopen("http://www.baidu.com/") 6 html = resp.read().decode("utf-8") 7 print(html) 8 9 # GET 10 resp = urllib.request.urlopen("http://localhost:8080/sayHello?name=zhangsan") 11 print(resp.status) 12 print(resp.read().decode("UTF-8")) 13 14 # POST 15 data = urllib.parse.urlencode({"username": "lisi", "password":"123456"}) 16 data = data.encode("UTF-8") 17 resp = urllib.request.urlopen("http://localhost:8080/login", data) 18 print(resp.read().decode("UTF-8")) 19 20 # 带Header 21 header = { 22 "POSID": "1010101" 23 } 24 req = urllib.request.Request("http://localhost:8080/login", data, header) 25 resp = urllib.request.urlopen(req) 26 print(resp.read().decode("UTF-8")) 27 28 # requests 29 # GET 30 response = requests.get("http://localhost:8080/sayHello", "name=zhangsan") 31 print(response.status_code) 32 print(response.headers) 33 print(response.headers["Content-Type"]) 34 print(response.encoding) 35 print(response.text) 36 37 # POST 38 # 类似jQuery 39 # response = requests.post("http://localhost:8080/login", {"username":"lisi","password":"123456"}) 40 response = requests.post("http://localhost:8080/login", "username=lisi&password=123456") 41 if response.status_code == 200: 42 print(response.text) 43 print(response.json()) 44 45 # 带headers 46 url = "http://localhost:8080/login" 47 data = "username=lisi&password=123456" 48 headers = {"id":"123", "name": "abc"} 49 response = requests.post(url, data, headers=headers, timeout=3) 50 if response.status_code == 200: 51 print(response.text) 52 print(response.json())
JSON
1 import json 2 3 # Python中的json库提供的主要功能是在字典和JSON之间做转换 4 # json.dumps(): 转成JSON 5 # json.loads(): JSON字符串转字典 6 7 data_list = [1, 2, 'a', 'b', True, [4, 5, 6]] 8 json_str = json.dumps(data_list) 9 print(json_str) 10 11 data2 = {'name': 'zhangsan', 'age': 25} 12 json_str2 = json.dumps(data2) 13 print("原对象:", data2) 14 print("JSON对象:", json_str2) 15 16 data3 = '{"a":"b"}' 17 json_str3 = json.loads(data3) 18 print("原对象:", data3) 19 print("字典对象:", json_str3) 20 print()
日期时间
1 import time 2 from datetime import date 3 from datetime import datetime 4 from datetime import timedelta 5 import calendar 6 7 # time 8 print("当前时间戳:", time.time()) 9 print("本地时间:", time.localtime(time.time())) 10 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())) 11 # 日历 12 cal = calendar.month(2018, 8) 13 print(cal) 14 15 # date 16 print(date.today()) 17 18 startDate = date(2018, 6, 1) 19 endDate = date(2018, 8, 5) 20 print(startDate) 21 print(endDate) 22 diff = endDate - startDate 23 print(diff.days) 24 # print(diff.seconds) 25 26 # datetime 27 print(datetime.now()) 28 dt = datetime(2018, 8, 5, 19, 22, 18) 29 print(dt) 30 31 # 加3天 32 print(dt + timedelta(3)) 33 # 减5天 34 print(dt + timedelta(-5)) 35 # 加1小时 36 print(dt + timedelta(hours=1)) 37 # 减2小时 38 print(dt + timedelta(hours=-2)) 39 # 加25分钟 40 print(dt + timedelta(minutes=25)) 41 # 减10分钟 42 print(dt + timedelta(minutes=-10))
感想
解决问题的思路才是关键,编程语言只是语法不同而已。
习惯性以分号结尾;哈哈哈!!!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号