Activiti7 回退与会签
1. 回退(驳回)
回退的思路就是动态更改节点的流向。先遇水搭桥,最后再过河拆桥。
具体操作如下:
- 取得当前节点的信息
- 取得当前节点的上一个节点的信息
- 保存当前节点的流向
- 新建流向,由当前节点指向上一个节点
- 将当前节点的流向设置为上面新建的流向
- 当前节点完成任务
- 将当前节点的流向还原
- 取得之前上个节点的执行人
- 设置上个节点的assignee为之前的执行人
代码实现起来可能是这样的:
@Test
public void huitui() throws Exception {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId("55001").singleResult();
backProcess(task);
}
/**
* 驳回 / 回退
* 按照这种方法,可以回退至任意节点
* @param task
* @throws Exception
*/
public void backProcess(Task task) throws Exception {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
HistoryService historyService = processEngine.getHistoryService();
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
String processInstanceId = task.getProcessInstanceId();
// 获取所有历史任务(按创建时间降序)
List<HistoricTaskInstance> hisTaskList = historyService.createHistoricTaskInstanceQuery()
.processInstanceId(processInstanceId)
.orderByTaskCreateTime()
.desc()
.list();
List<HistoricActivityInstance> hisActivityList = historyService.createHistoricActivityInstanceQuery()
.processInstanceId(processInstanceId).list();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(hisTaskList) || hisTaskList.size() < 2) {
return;
}
// 当前任务
HistoricTaskInstance currentTask = hisTaskList.get(0);
// 前一个任务
HistoricTaskInstance lastTask = hisTaskList.get(1);
// 当前活动
HistoricActivityInstance currentActivity = hisActivityList.stream().filter(e -> currentTask.getId().equals(e.getTaskId())).collect(Collectors.toList()).get(0);
// 前一个活动
HistoricActivityInstance lastActivity = hisActivityList.stream().filter(e -> lastTask.getId().equals(e.getTaskId())).collect(Collectors.toList()).get(0);
BpmnModel bpmnModel = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(task.getProcessDefinitionId());
// 获取前一个活动节点
FlowNode lastFlowNode = (FlowNode) bpmnModel.getMainProcess().getFlowElement(lastActivity.getActivityId());
// 获取当前活动节点
FlowNode currentFlowNode = (FlowNode) bpmnModel.getMainProcess().getFlowElement(currentActivity.getActivityId());
// 临时保存当前活动的原始方向
List<SequenceFlow> originalSequenceFlowList = new ArrayList<>();
originalSequenceFlowList.addAll(currentFlowNode.getOutgoingFlows());
// 清理活动方向
currentFlowNode.getOutgoingFlows().clear();
// 建立新方向
SequenceFlow newSequenceFlow = new SequenceFlow();
newSequenceFlow.setId("newSequenceFlowId");
newSequenceFlow.setSourceFlowElement(currentFlowNode);
newSequenceFlow.setTargetFlowElement(lastFlowNode);
List<SequenceFlow> newSequenceFlowList = new ArrayList<>();
newSequenceFlowList.add(newSequenceFlow);
// 当前节点指向新的方向
currentFlowNode.setOutgoingFlows(newSequenceFlowList);
// 完成当前任务
taskService.complete(task.getId());
// 重新查询当前任务
Task nextTask = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(processInstanceId).singleResult();
if (null != nextTask) {
taskService.setAssignee(nextTask.getId(), lastTask.getAssignee());
}
// 恢复原始方向
currentFlowNode.setOutgoingFlows(originalSequenceFlowList);
}以请假为例
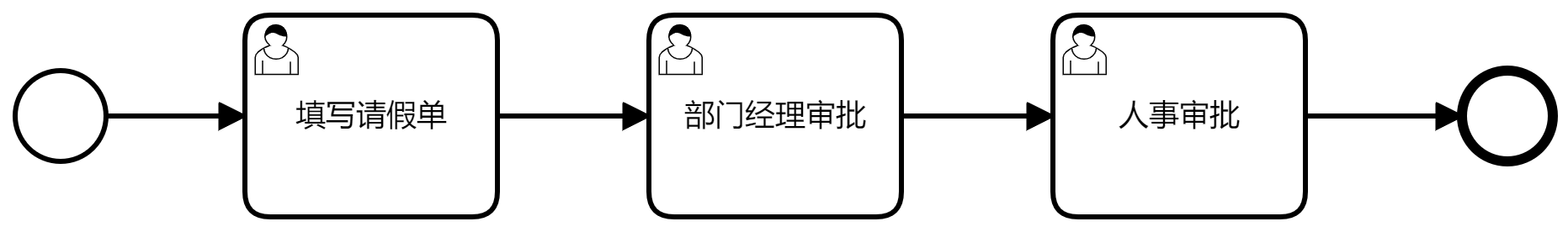
<process id="holiday" name="holiday" isExecutable="true">
<startEvent id="startevent1" name="Start"></startEvent>
<userTask id="usertask1" name="填写请假单" activiti:assignee="${assignee1}"></userTask>
<sequenceFlow id="flow1" sourceRef="startevent1" targetRef="usertask1"></sequenceFlow>
<userTask id="usertask2" name="部门经理审批" activiti:assignee="${assignee2}"></userTask>
<sequenceFlow id="flow2" sourceRef="usertask1" targetRef="usertask2"></sequenceFlow>
<userTask id="usertask3" name="人事审批" activiti:candidateUsers="tom,jerry"></userTask>
<sequenceFlow id="flow3" sourceRef="usertask2" targetRef="usertask3"></sequenceFlow>
<endEvent id="endevent1" name="End"></endEvent>
<sequenceFlow id="flow4" sourceRef="usertask3" targetRef="endevent1"></sequenceFlow>
</process>假设现在已经到“人事审批”这个节点了,当前活动是usertask3
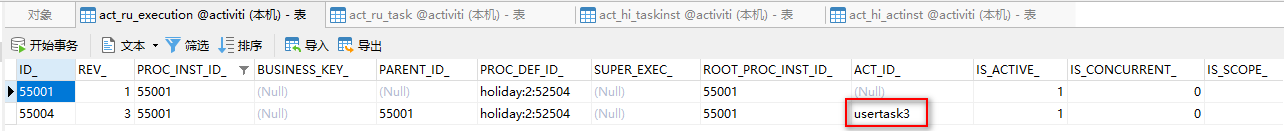

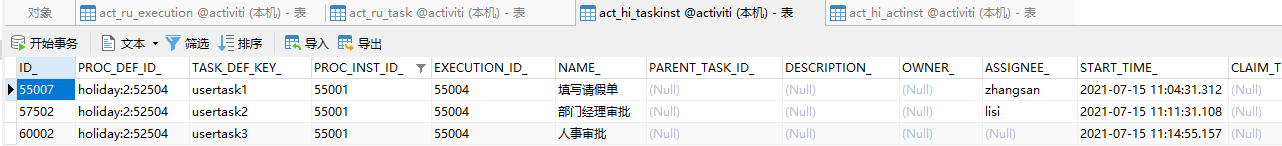

接下来,我们运行上面的代码,回退到上一个节点“部门经理审批”,于是


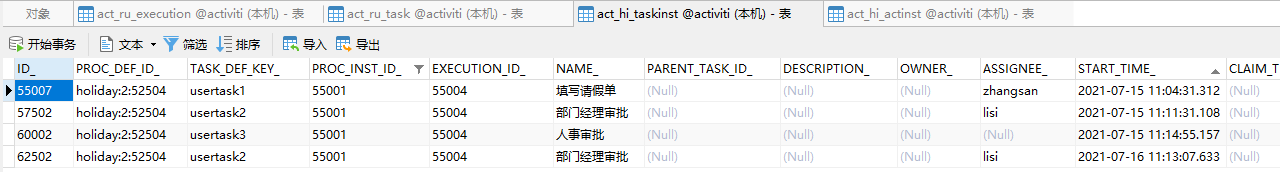
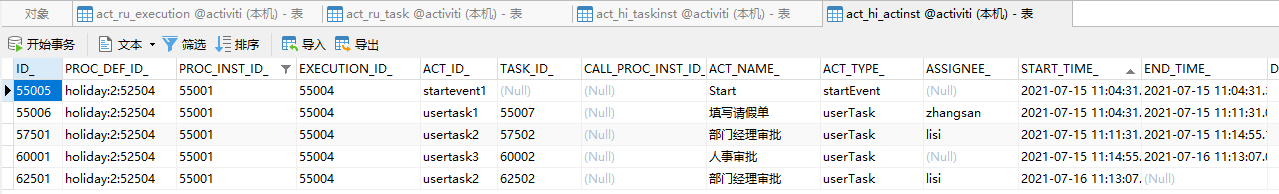
流程重新从“部门经理审批”节点开始往下走,当流程走完以后

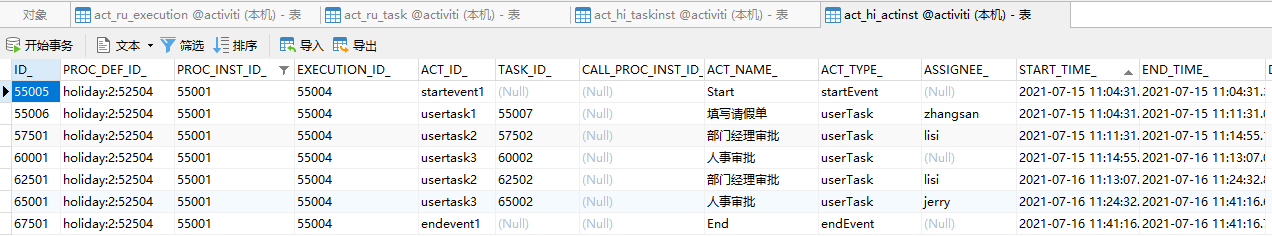
证明,思路正确,写法没啥问题。但是,上面的代码可以简化一下,如下:
/**
* 跳到最开始的任务节点(直接打回)
* @param task 当前任务
*/
public void jumpToStart(Task task) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
HistoryService historyService = processEngine.getHistoryService();
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
String processInstanceId = task.getProcessInstanceId();
// 获取所有历史任务(按创建时间升序)
List<HistoricTaskInstance> hisTaskList = historyService.createHistoricTaskInstanceQuery()
.processInstanceId(processInstanceId)
.orderByTaskCreateTime()
.asc()
.list();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(hisTaskList) || hisTaskList.size() < 2) {
return;
}
// 第一个任务
HistoricTaskInstance startTask = hisTaskList.get(0);
// 当前任务
HistoricTaskInstance currentTask = hisTaskList.get(hisTaskList.size() - 1);
BpmnModel bpmnModel = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(task.getProcessDefinitionId());
// 获取第一个活动节点
FlowNode startFlowNode = (FlowNode) bpmnModel.getMainProcess().getFlowElement(startTask.getTaskDefinitionKey());
// 获取当前活动节点
FlowNode currentFlowNode = (FlowNode) bpmnModel.getMainProcess().getFlowElement(currentTask.getTaskDefinitionKey());
// 临时保存当前活动的原始方向
List<SequenceFlow> originalSequenceFlowList = new ArrayList<>();
originalSequenceFlowList.addAll(currentFlowNode.getOutgoingFlows());
// 清理活动方向
currentFlowNode.getOutgoingFlows().clear();
// 建立新方向
SequenceFlow newSequenceFlow = new SequenceFlow();
newSequenceFlow.setId("newSequenceFlowId");
newSequenceFlow.setSourceFlowElement(currentFlowNode);
newSequenceFlow.setTargetFlowElement(startFlowNode);
List<SequenceFlow> newSequenceFlowList = new ArrayList<>();
newSequenceFlowList.add(newSequenceFlow);
// 当前节点指向新的方向
currentFlowNode.setOutgoingFlows(newSequenceFlowList);
// 完成当前任务
taskService.complete(task.getId());
// 重新查询当前任务
Task nextTask = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(processInstanceId).singleResult();
if (null != nextTask) {
taskService.setAssignee(nextTask.getId(), startTask.getAssignee());
}
// 恢复原始方向
currentFlowNode.setOutgoingFlows(originalSequenceFlowList);
}
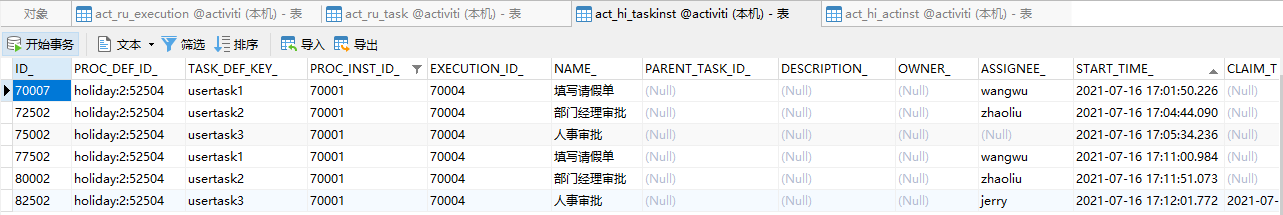
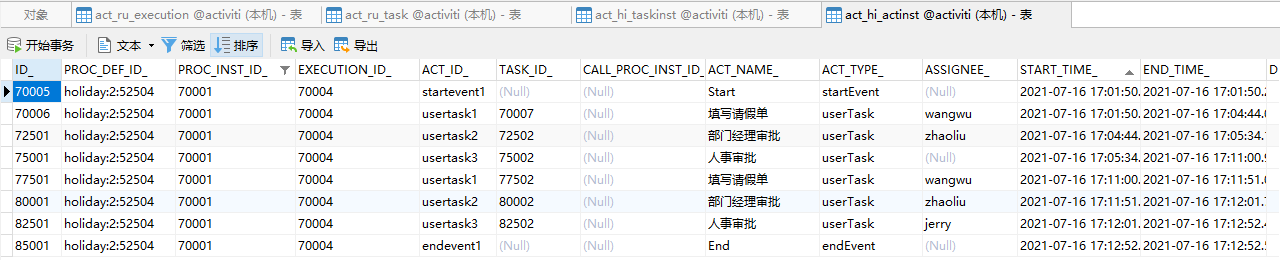
2. 会签
多个人同时处理一个任务,这种任务我们称之为会签任务 。Activiti实现会签是基于多实例任务,将节点设置成多实例,主要通过在UserTask节点的属性上配置。
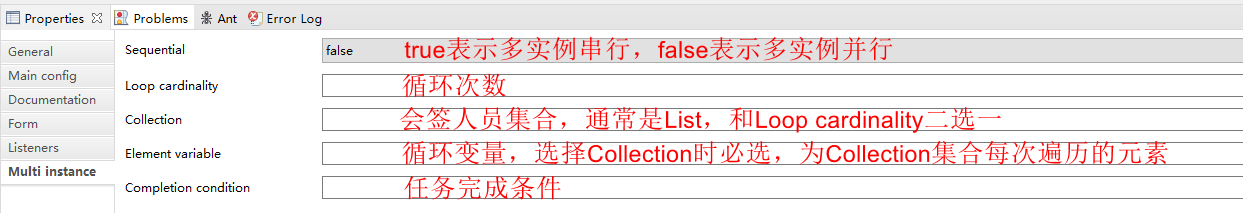
会签的种类:
- 按数量通过: 达到一定数量的通过表决后,会签通过。
- 按比例通过: 达到一定比例的通过表决后,会签通过。
- 一票否决: 只要有一个表决时否定的,会签通过。
- 一票通过: 只要有一个表决通过的,会签通过。
每个实例有以下变量:
- nrOfInstances: 实例总数
-
nrOfActiveInstances: 当前激活的(未完成的)实例总数。 如果串行执行,则改值永远是1
- nrOfCompletedInstances: 已完成的实例总数
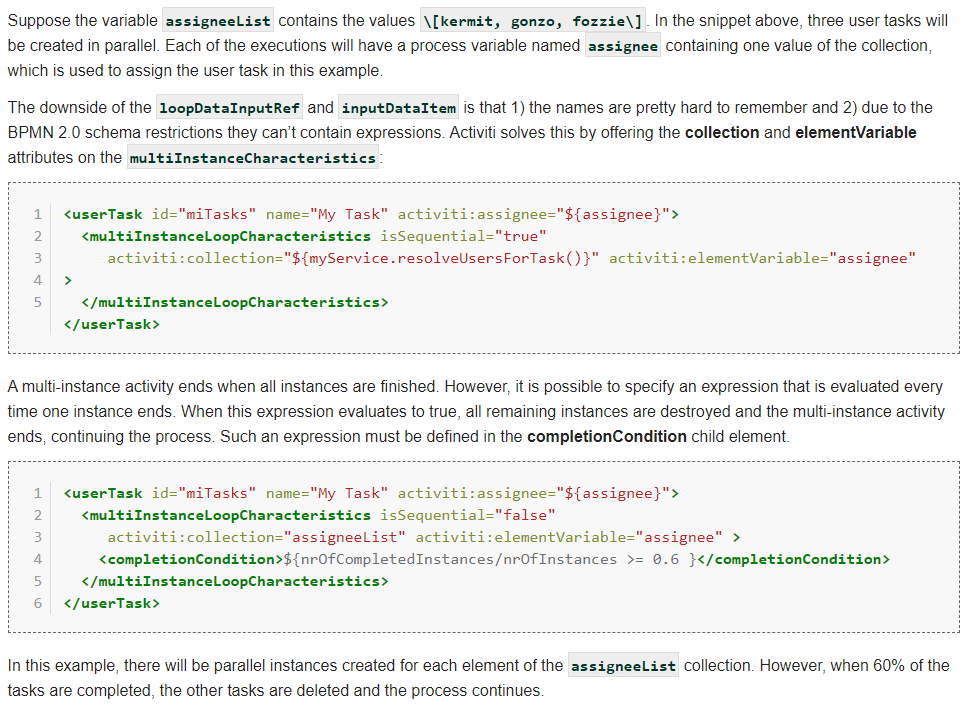
条件${nrOfInstances == nrOfCompletedInstances}表示所有人员审批完成后会签结束。
条件${ nrOfCompletedInstances == 1}表示一个人完成审批,该会签就结束。
其他条件依次类推,同时这里也可以写自己添加的流程变量。
相关文档如下:
下面举个例子:


<process id="countersign" name="countersign" isExecutable="true">
<startEvent id="startevent1" name="Start"></startEvent>
<userTask id="usertask1" name="申请" activiti:assignee="zhangsan"></userTask>
<sequenceFlow id="flow1" sourceRef="startevent1" targetRef="usertask1"></sequenceFlow>
<userTask id="usertask2" name="会签审批" activiti:assignee="${approver}">
<multiInstanceLoopCharacteristics isSequential="false"
activiti:collection="${approverList}" activiti:elementVariable="approver">
<completionCondition>${nrOfCompletedInstances == nrOfInstances}</completionCondition>
</multiInstanceLoopCharacteristics>
</userTask>
<sequenceFlow id="flow2" sourceRef="usertask1" targetRef="usertask2"></sequenceFlow>
<userTask id="usertask3" name="备案" activiti:assignee="tianqi"></userTask>
<sequenceFlow id="flow3" sourceRef="usertask2" targetRef="usertask3"></sequenceFlow>
<endEvent id="endevent1" name="End"></endEvent>
<sequenceFlow id="flow4" sourceRef="usertask3" targetRef="endevent1"></sequenceFlow>
</process>编写代码:
// 部署流程定义
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
Deployment deployment = repositoryService.createDeployment()
.addClasspathResource("diagram/countersign.bpmn")
.name("会签示例")
.key("countersign")
.deploy();
// 启动流程实例
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
variables.put("approverList", Arrays.asList("lisi","wangwu","zhaoliu"));
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("countersign", variables);
// 完成任务
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId("107501").taskAssignee("zhaoliu").singleResult();
if (null != task) {
taskService.complete(task.getId());
}流程启动后,首先是zhangsan审批
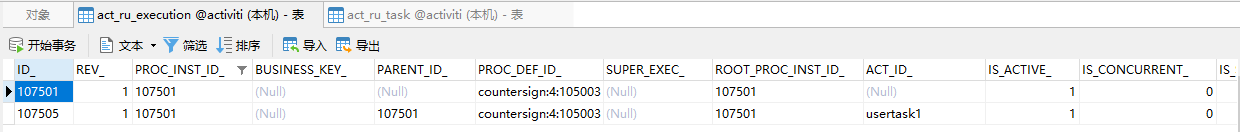

当zhangsan完成自己的任务后,进入会签环节,于是我们看到当前有3个激活的任务
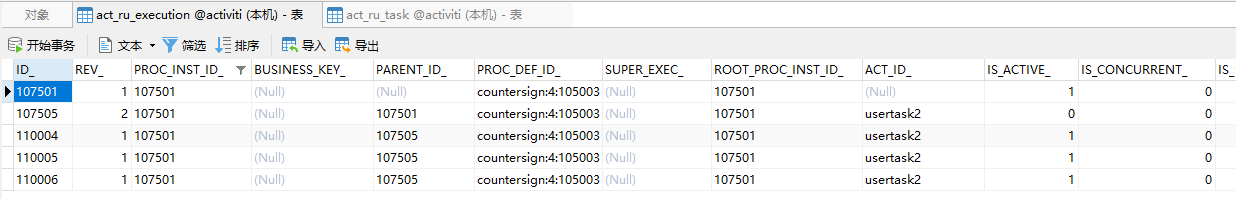

当lisi完成任务以后,当前任务剩下2个
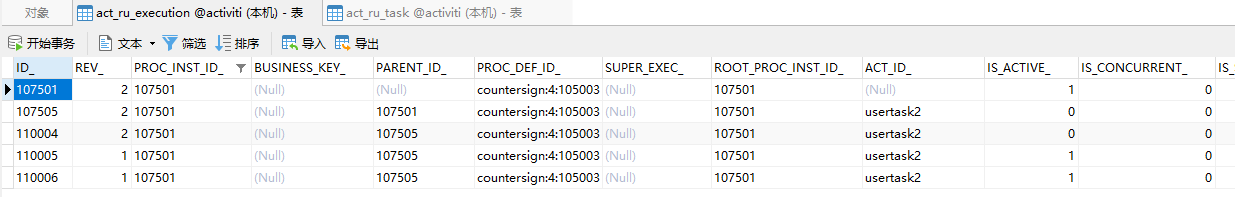
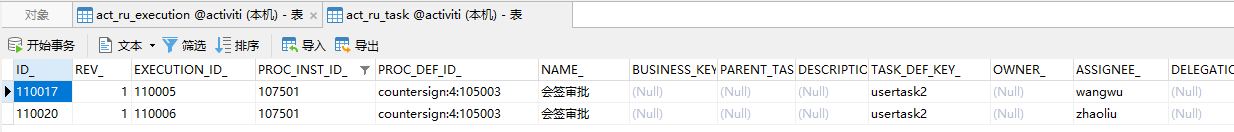
当wangwu和zhaoliu都完成任务了以后,会签任务完成,进入下一个环节
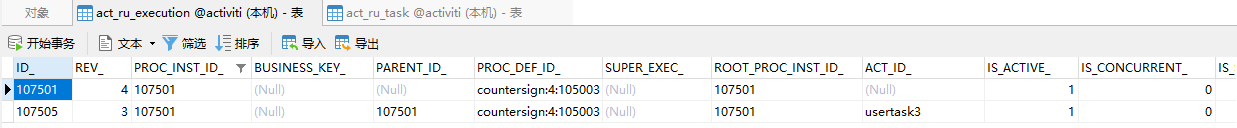

刚才的例子中没有考虑到审批不通过的情况,接下来我们完善一下,考虑下面的流程
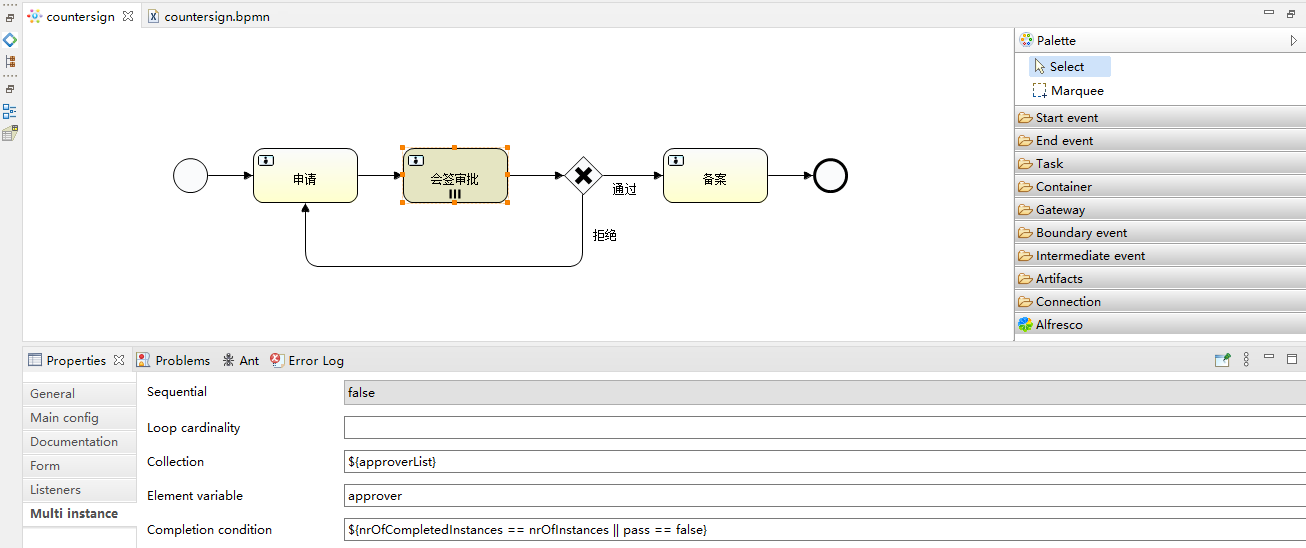

<process id="countersign" name="countersign" isExecutable="true">
<startEvent id="startevent1" name="Start"></startEvent>
<userTask id="usertask1" name="申请" activiti:assignee="zhangsan"></userTask>
<sequenceFlow id="flow1" sourceRef="startevent1" targetRef="usertask1"></sequenceFlow>
<userTask id="usertask2" name="会签审批" activiti:assignee="${approver}">
<multiInstanceLoopCharacteristics isSequential="false" activiti:collection="${approverList}" activiti:elementVariable="approver">
<completionCondition>${nrOfCompletedInstances / nrOfInstances == 1 || pass == false}</completionCondition>
</multiInstanceLoopCharacteristics>
</userTask>
<sequenceFlow id="flow2" sourceRef="usertask1" targetRef="usertask2"></sequenceFlow>
<userTask id="usertask3" name="备案" activiti:assignee="tianqi"></userTask>
<exclusiveGateway id="exclusivegateway1" name="Exclusive Gateway"></exclusiveGateway>
<sequenceFlow id="flow5" sourceRef="usertask2" targetRef="exclusivegateway1"></sequenceFlow>
<sequenceFlow id="flow6" name="通过" sourceRef="exclusivegateway1" targetRef="usertask3">
<conditionExpression xsi:type="tFormalExpression"><![CDATA[${pass == true}]]></conditionExpression>
</sequenceFlow>
<sequenceFlow id="flow7" name="拒绝" sourceRef="exclusivegateway1" targetRef="usertask1">
<conditionExpression xsi:type="tFormalExpression"><![CDATA[${pass == false}]]></conditionExpression>
</sequenceFlow>
<endEvent id="endevent1" name="End"></endEvent>
<sequenceFlow id="flow8" sourceRef="usertask3" targetRef="endevent1"></sequenceFlow>
</process>在会签审批完成任务时就要加上流程变量pass了
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId("152501").taskAssignee("lisi").singleResult();
if (null != task) {
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
variables.put("pass", true);
// variables.put("pass", false);
taskService.complete(task.getId(), variables);
runtimeService.getVariable(task.getExecutionId(), "nrOfCompletedInstances");
}zhaoliu审批的时候pass传的false,于是流程又走到zhangsan那里,流程重新又走了一遍才全部完成
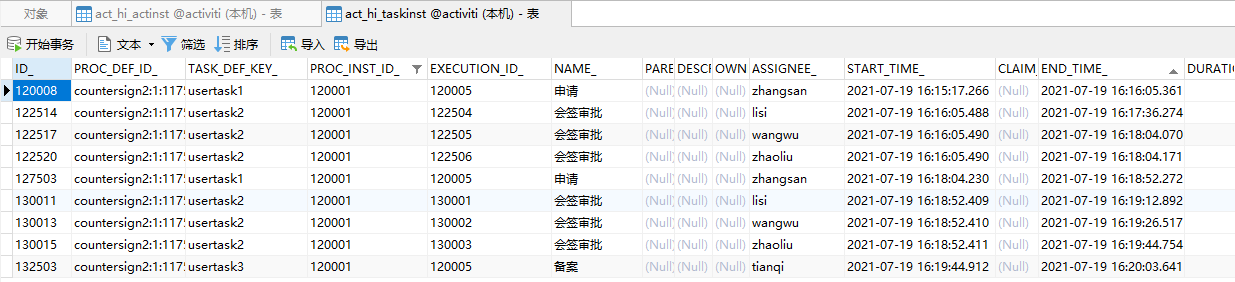

关于回退和会签就先讲到这里
3. 参考
https://www.activiti.org/userguide/index.html#bpmnMultiInstance