实验1 现代C++编程初体验
一、实验目的
体验现代C++标准库、算法库用法
灵活组合使用现代C++基础语言特性(数据表示、分支、循环、函数)和标准库,编程解决简单、
基础问题
编程代码过程中,注意编码素养。关注代码表达,提升代码的可读性、易于维护性
二、实验准备
系统浏览教材以下章节,对现代c++基础语言特性和用法构建全局认知
第2章 C++语言简单程序设计
第3章 函数
第9章 9.1.1节 函数模板
通过以下网站,了解现代C++标准库中各类标准库组件、算法工具等的用法(如string, vector、算
法库等)
https://www.runoob.com/cplusplus/cpp-tutorial.html

三、实验内容
1. 实验任务1
验证性实验。
在C++编码环境中,输入以下代码,结合运行结果和注释,体验使用C++标准库进行编程的便捷,同时,
从面向对象编程范式的角度,体会面向对象设计中封装、暴露接口(interface)、基于接口编程的意义。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c);
void test1();
void test2();
void test3();
int main() {
cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
cout << "\n测试3: \n";
test3();
}
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c) {
for(auto &i: c)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
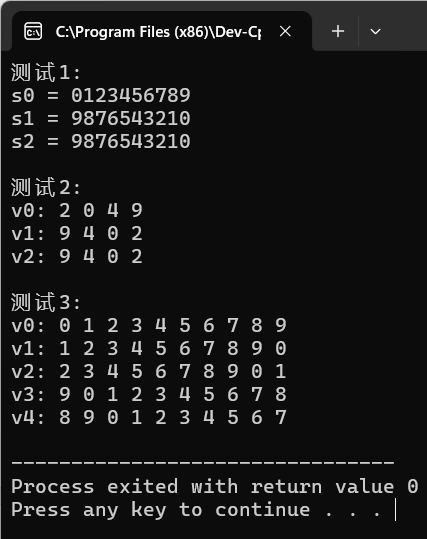
void test1() {
string s0{"0123456789"};
cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl;
string s1{s0};
reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end());
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
string s2{s0};
reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin());
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
}
void test2() {
vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9};
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end());
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin());
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
}
void test3() {
vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end());
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end());
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
vector<int> v3{v0};
rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end()-1, v3.end());
cout << "v3: ";
output(v3);
vector<int> v4{v0};
rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end()-2, v4.end());
cout << "v4: ";
output(v4);
}
2. 实验任务2
验证性实验。
在C++编码环境中,输入以下代码,结合运行结果和注释,体验使用C++标准库高效编程解决基础问题
(对指定区间进行排序、赋值;求最大值、最小值、均值)
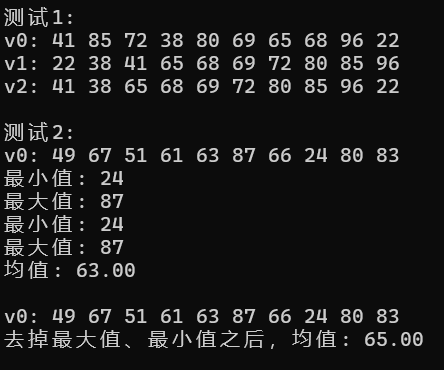
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <numeric> 6 #include <iomanip> 7 using namespace std; 8 template<typename T> 9 void output(const T &c); 10 // 普通函数声明 11 int rand_int_100(); 12 void test1(); 13 void test2(); 14 int main() { 15 cout << "测试1: \n"; 16 test1(); 17 cout << "\n测试2: \n"; 18 test2(); 19 } 20 template <typename T> 21 void output(const T &c) { 22 for(auto &i: c) 23 cout << i << " "; 24 cout << endl; 25 } 26 // 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数 27 int rand_int_100() { 28 return rand() % 101; 29 } 30 // 测试1 31 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、排序 32 void test1() { 33 vector<int> v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10 34 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); // 产生[0, 100]之间的随机整数赋值给指定迭代器区间[v0.begin(), v0.end())内的每个数据项 35 cout << "v0: "; 36 output(v0); 37 vector<int> v1{v0}; 38 sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())内数据项进行升序排序 39 cout << "v1: "; 40 output(v1); 41 vector<int> v2{v0}; 42 sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin()+1,v1.end()-1)内数据项进行升序排序 43 cout << "v2: "; 44 output(v2); 45 } 46 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值 47 void test2() { 48 vector<int> v0(10); 49 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); 50 cout << "v0: "; 51 output(v0); 52 auto iter1 = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 53 cout << "最小值: " << *iter1 << endl; 54 auto iter2 = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 55 cout << "最大值: " << *iter2 << endl; 56 auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 57 cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl; 58 cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl; 59 double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0)/v0.size(); 60 cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl; 61 cout << endl; 62 vector<int> v1{v0}; 63 cout << "v0: "; 64 output(v0); 65 sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); 66 double avg2 = accumulate(v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1, 0)/(v1.size()-2); 67 cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl; 68 }
3. 实验任务3
编写程序,实现判断回文串。具体要求如下:
编写函数 bool is_palindrome(std::string s) 用于判断字符串s是否是回文串,是返回 true ,
否则,返回 false 。
在main函数中,输入字符串,调用 is_palindrome , 输出结果,要求支持多组输入
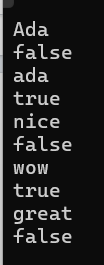
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 bool is_palindrome(std::string s) 6 { 7 8 9 int left = 0; 10 int right = s.size() - 1; 11 while (left < right) { 12 if (s[left]!= s[right]) { 13 return false; 14 } 15 left++; 16 right--; 17 } 18 return true; 19 } 20 21 int main() { 22 using namespace std; 23 string s; 24 25 while(cin >> s) // 多组输入,直到按下Ctrl+Z后结束测试 26 cout << boolalpha << is_palindrome(s) << endl; 27 }
4. 实验任务4
编写程序实现进制转换。具体要求如下:
编写函数 std::string dec_to_n(x, n) 实现把一个十进制数x转换成n进制,结果以字符串形式
返回。如果第2个参数没有指定,默认转换成二进制。
在main函数中,输入十进制整数,调用函数 dec2n 得到转换成指定进制的字符串,输出。要求支持
多组输入。
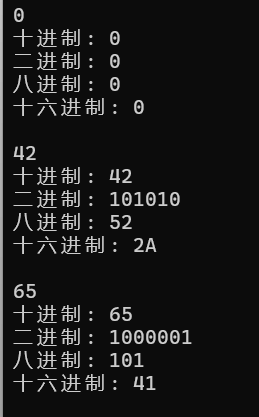
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2) 6 { 7 std::string result; 8 while (x >0) { 9 int remainder = x % n; 10 if (remainder < 10) { 11 result += remainder + '0'; 12 } else { 13 result += remainder - 10 + 'A'; 14 } 15 x /= n; 16 } 17 std::reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); 18 return result; 19 } 20 21 int main() 22 { 23 using namespace std; 24 25 int x; 26 while(cin >> x) 27 { 28 if(x==0) 29 { 30 cout << "十进制: " << 0 << endl; 31 cout << "二进制: " << 0 << endl; 32 cout << "八进制: " << 0 << endl; 33 cout << "十六进制: " << 0 << endl << endl; 34 } 35 else 36 { 37 38 cout << "十进制: " << x << endl; 39 cout << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << endl; 40 cout << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << endl; 41 cout << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << endl << endl; 42 } 43 } 44 }
5. 实验任务5
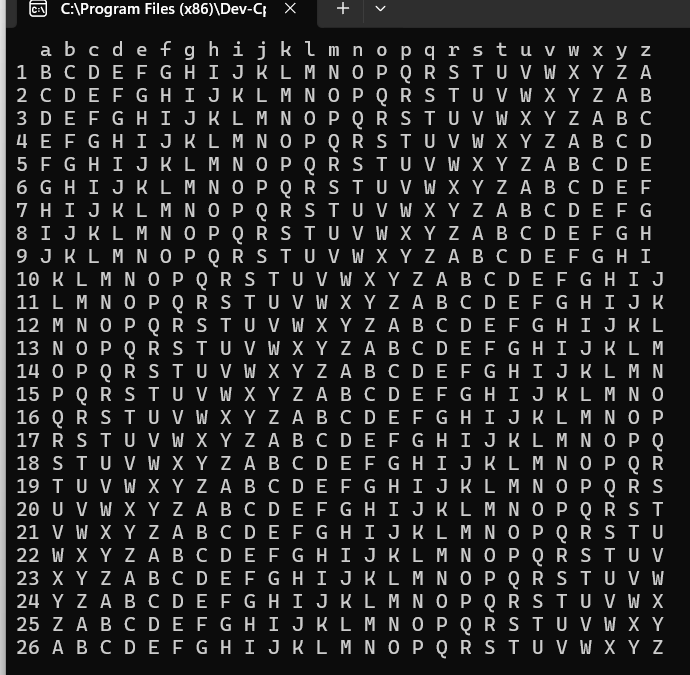
编写一个程序,在屏幕上打印字母密文对照表。
程序正确编写后,预期输出如下:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main(){ 5 vector<char> member; 6 char ch; 7 cout<<" "; 8 for(int i=0;i<26;i++){ 9 ch='a'+i; 10 cout<<ch<<' '; 11 member.push_back(ch-32); 12 } 13 cout<<endl; 14 for(int i=1;i<=26;i++){ 15 cout<<i<<' '; 16 for(int j=i;j<26;j++) 17 cout<<member[j]<<' '; 18 for(int k=0;k<i;k++) 19 cout<<member[k]<<' '; 20 cout<<endl; 21 } 22 }
6. 实验任务6
编写一个程序,实现自动生成算术运算题目并自动评测。具体要求如下:
程序运行后,自动生成10道10以内的算术运算题目。
运算式(包括=)在程序运行时自动生成。运算式=右侧的答案由用户输入
算术运算包括:加、减、乘、除。生成题目时,运算随机。
两个操作数限制在[1, 10]区间内的整数。
当生成的随机运算是减法时,要求第一个操作数>第二个操作数
当生成的随机u那算时除法时,要求第一个操作数能整除第二个操作数整除
用户完成10道测试后,屏幕给出正确率,要求以百分号形式输出,保留小数点后两位。
多次运行程序时,每次生成的题目与上次不同。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <ctime> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <iomanip> 5 6 7 void generateQuestion(int &num1, int &num2, char &op) { 8 num1 = rand() % 10 + 1; 9 num2 = rand() % 10 + 1; 10 int operation = rand() % 4; 11 switch (operation) { 12 case 0: 13 op = '+'; 14 break; 15 case 1: 16 op = '-'; 17 if (num1 <= num2) { 18 std::swap(num1, num2); 19 } 20 break; 21 case 2: 22 op = '*'; 23 break; 24 case 3: 25 op = '/'; 26 while (num1 % num2!= 0) { 27 num1 = rand() % 10 + 1; 28 num2 = rand() % 10 + 1; 29 } 30 break; 31 } 32 } 33 34 35 int calculateAnswer(int num1, int num2, char op) { 36 switch (op) { 37 case '+': 38 return num1 + num2; 39 case '-': 40 return num1 - num2; 41 case '*': 42 return num1 * num2; 43 case '/': 44 return num1 / num2; 45 } 46 return 0; 47 } 48 49 int main() { 50 srand(static_cast<unsigned int>(time(nullptr))); 51 int correctCount = 0; 52 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 53 int num1, num2; 54 char op; 55 generateQuestion(num1, num2, op); 56 std::cout << num1 << " " << op << " " << num2 << " = "; 57 int userAnswer; 58 std::cin >> userAnswer; 59 int correctAnswer = calculateAnswer(num1, num2, op); 60 if (userAnswer == correctAnswer) { 61 correctCount++; 62 } 63 } 64 double accuracy = static_cast<double>(correctCount) / 10.0 * 100.0; 65 std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << accuracy << "%" << std::endl; 66 return 0; 67 }


