Codeforces Round 973 (Div. 2)
比赛链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/2013/problem
A. Zhan's Blender

一次最多可以榨汁\(min(x,y)\)水果,答案得解
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<random>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll x, ll y)
{
if (y == 0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
ll ksm(ll x, ll y)
{
ll ans = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)
ans *= x;
x *= x;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
ll n,x,y;
cin >> n >> x >> y;
ll j = min(x, y);
ll u = n / j;
if (n % j > 0)
{
u++;
}
cout << u << endl;
}
}
B. Battle for Survive

分析可得,令\(a(n-1)-a(n-2)-...\),最后用\(an\)再减反转下值可以保留最大
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<random>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll x, ll y)
{
if (y == 0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
ll ksm(ll x, ll y)
{
ll ans = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)
ans *= x;
x *= x;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
ll a[200005];
int main()
{
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
ll n;
cin >> n;
ll sum = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
if (i <= n - 2)
sum += a[i];
}
ll ans = a[n] - a[n - 1] + sum;
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
C. Password Cracking
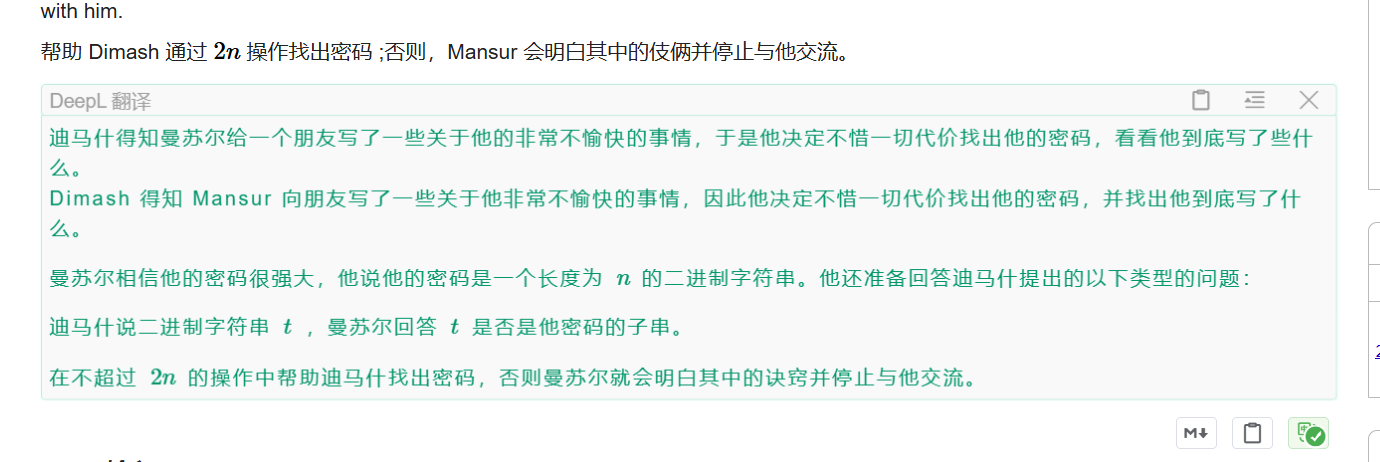
直接假设目前子串为符合子串,如果不可加且长度不够则往前加,最后答案得出
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<random>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll query(string f)
{
cout << "?" << " " << f << endl;
cout.flush();
ll x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
int main()
{
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
ll g = 0;
ll n;
cin >> n;
string e = "1";
if (n == 1)
{
if (query(e) == 1)
cout << "!" << " " << 1 << endl;
else
cout << "!" << " " << 0 << endl;
continue;
}
if (query(e) == 0)//一次
e = "0";
for (ll i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
string k1,k2;
k1 = e + '0';k2 = e + '1';
if (query(k1))
e = k1;
else if (query(k2))
e = k2;
else
break;
}
while (e.size() != n)
{
string k1 = '0'+e, k2 = '1'+e;
if (query(k1))
e = k1;
else
e = k2;
}
cout << "!" << " " << e << endl;
}
}
E. Prefix GCD

首先显然最小的数放在前面是最佳的,其作为了整体约束。
随后发现不可能每个样例一两下就到最小gcd,思考\(2*3,3*7,2*7\)情况,得三次才有最小gcd,或者类似于2的次方,但是有其他数参杂,最多也就60多次吧(远远达不到这么多)近似于这样,
最多暴力枚举前面可能20多个数即可达到最小gcd,质因数分解找最小合成数(最大约束),随后用map再优化下,答案得解
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<cctype>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<random>
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
using namespace std;
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
//const ll p=rnd()%mod;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=1e9+7;
const ll N=2e5+5;
ll ksm(ll x,ll y)
{
ll ans=1;
while(y)
{
if(y&1)
ans=(ans%mod*x%mod)%mod;
x=x%mod*(x%mod)%mod;
y>>=1;
}
return ans%mod%mod;
}
ll gcd(ll x,ll y)
{
if(y==0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y,x%y);
}
void fio()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
bool vi[250000];
ll gs=0;
ll zs[1500000];
map<ll,ll>q,f;
void ola(ll x)
{
for(ll i=2;i<=x;i++)
{
if(!vi[i])gs++,zs[gs]=i,q[i]++;
for(ll j=1;zs[j]<=x/i;j++)
{
vi[zs[j]*i]=1;
if(i%zs[j]==0)break;
}
}
}
ll a[250000];
vector<ll>g[250000];
int main()
{
fio();
ola(100000);
ll t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
ll n;
cin>>n;
ll cnt=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
vi[i]=0;
cnt=gcd(cnt,a[i]);
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
ll k=a[1];
ll cf=1;
vi[1]=1;
ll ans1=0;
ans1+=a[1];
while(k!=cnt)
{
ll m=k;
f.clear();
ll l=1;
while(m!=1)
{
if(q[m])
{
f[m]++;break;
}
if(m%zs[l]==0)
{
f[zs[l]]++;
m/=zs[l];
}
else l++;
}
ll ans=9999999999999;
ll wz;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(vi[i])continue;
ll u=a[i];
ll cnt1=1;
ll l=1;
ll op=0;
while(u!=1)
{
if(u%zs[l]==0)
{
if(op<f[zs[l]])
{
op++;
cnt1*=zs[l];
}
u/=zs[l];
}
else l++,op=0;
}
if(ans>cnt1)
{
ans=cnt1;
wz=i;
}
}
vi[wz]=1;
k=gcd(k,ans);
ans1+=k;
cf++;
}
cout<<ans1+(n-cf)*cnt<<endl;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号