uniapp - props、 ref、$emit、$parent、$child、$on、$set
举个例子来解释一下何为父组件,何为子组件?
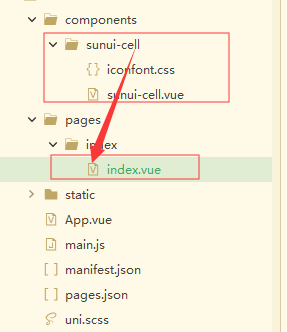
index.vue导入sunui-cell组件的时候,我们就称index.vue为父组件依次类推,在vue中只要能获取到组件的实例,那么就可以调用组件的属性或是方法进行操作
一、props(一般用来单向传值)
1. 何为单向传值?
即父组件传值给子组件(首次)但不能动态(再次)改变子组件现有的值,但我非要改呢? 通过watch监听或者通过$ref标识获取实例后修改以及使用v-modal,使用v-modal会存在不同步情况->使用.sync
2.props静态传值
子组件通过props选项来声明一个自定义的属性,然后父组件就可以在嵌套标签的时候,通过这个属性往子组件传递数据 - 引用脚本之家

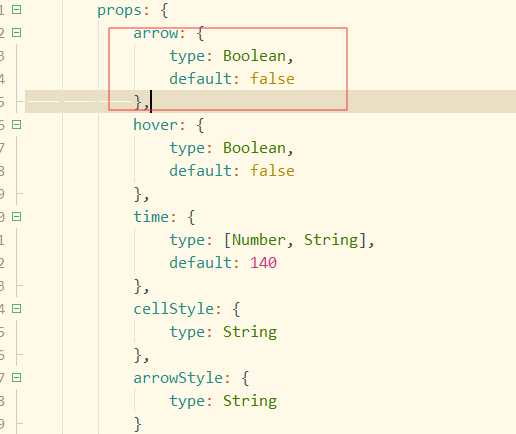
3. props动态传值
通过v-bind绑定props的自定义的属性,传递去过的就不是静态的字符串了,它可以是一个表达式、布尔值、对象等等任何类型的值 - 引用脚本之家

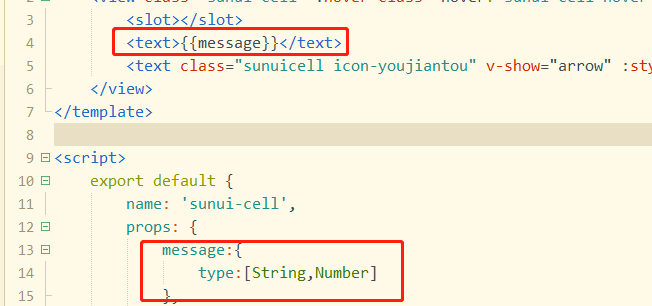
4. props最适合传递数据,它并不能调用子组件里的属性和方法
二、$ref
1.不大适合传递数据
主要用来调用子组件里的属性和方法
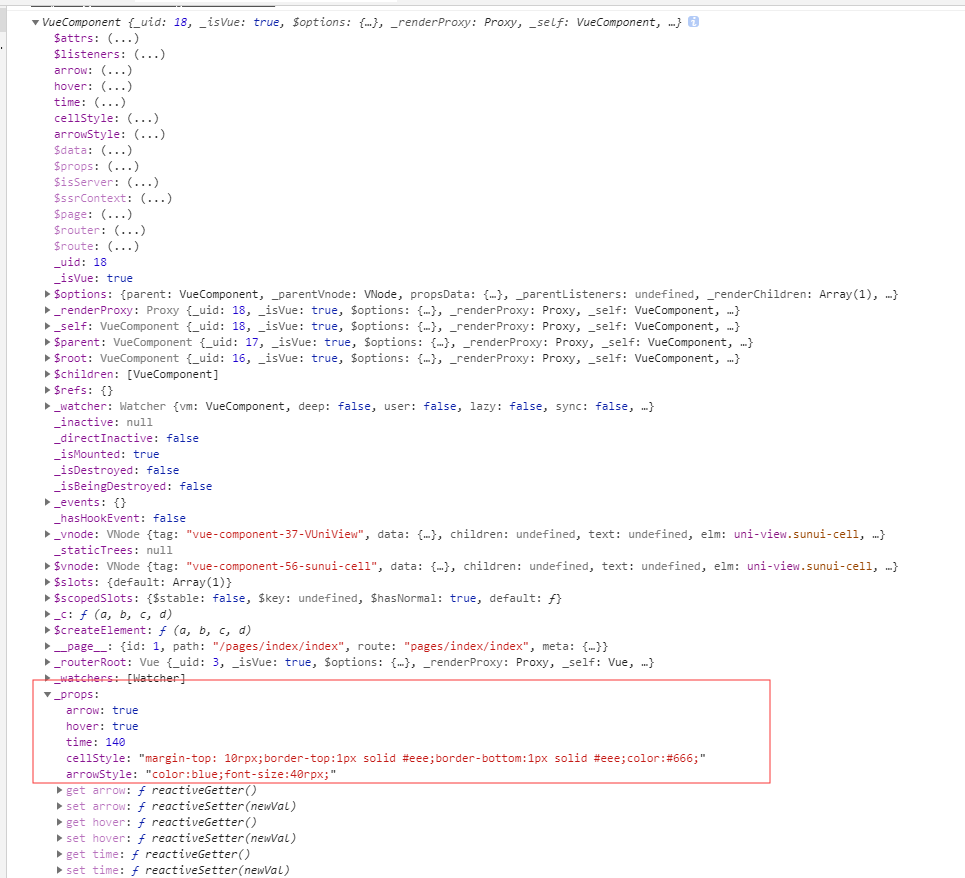
2. 通常是初始化页面(也就是视图层渲染完以后)才能调用
如果是初始化的话建议在mounted生命周期或者使用this.$nextTick()将回调延迟到下次 DOM 更新循环之后执行(但我们首先得标识ref,相同组件ref的值如果重复会被后面的组件覆盖),如果不是初始化的话必须要等待它加载完以后才能够调用(this.nextTick)

三、$emit
1. $emit 绑定一个自定义事件event,当这个这个语句被执行到的时候,就会将参数arg传递给父组件,父组件通过@event监听并接收参数

四、$on(非父组件之间传值)
1.父组件需要导入A和B组件
<template>
<view class="content">
<view style="padding: 12px 15px;">
点击hover效果
</view>
<onA></onA>
<onB></onB>
</view>
</template>
<script>
import onA from '@/components/onA.vue';
import onB from '@/components/onB.vue';
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello'
}
},
components: {
onA,
onB
},
onLoad() {
},
mounted() {
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
</style>
2. onA组件
<template>
<view>
<button type="primary" @click="onSend">传值给onB组件</button>
</view>
</template>
<script>
import bridge from '@/utils/bridge.js';
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello,onB'
};
},
methods: {
onSend() {
bridge.$emit('receiveA', this.msg);
}
},
mounted() {
bridge.$on('receiveB', (val) => {
console.log('我是onA组件,接收来自onB的值:', val);
});
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
3.onB组件
<template>
<view>
<button type="primary" @click="onSend">传值给onA组件</button>
</view>
</template>
<script>
import bridge from '@/utils/bridge.js';
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello,onA'
};
},
methods: {
onSend() {
bridge.$emit('receiveB', this.msg);
}
},
mounted() {
bridge.$on('receiveA', (val) => {
console.log('我是onB组件,接收来自onA的值:', val);
});
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
4.bridge.js
import Vue from 'vue'
export default new Vue()
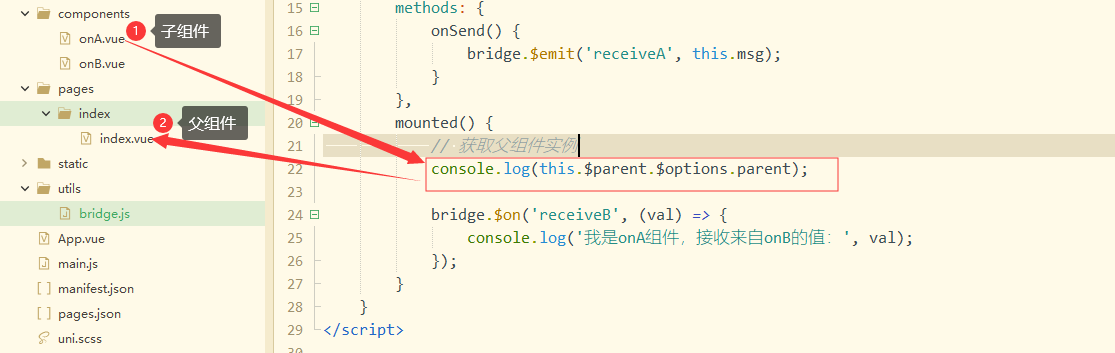
五、$parent(用于子组件获取父组件实例) - 当前组件树的根 Vue 实例。如果当前实例没有父实例,此实例将会是其自己
六、$child - 当前实例的直接子组件。需要注意 $children 并不保证顺序,也不是响应式的。如果你发现自己正在尝试使用 $children 来进行数据绑定,考虑使用一个数组配合 v-for 来生成子组件,并且使用 Array 作为真正的来源
<template>
<view class="content">
<view style="padding: 12px 15px;">
点击hover效果
</view>
<onA></onA>
<onB></onB>
</view>
</template>
<script>
import onA from '@/components/onA.vue';
import onB from '@/components/onB.vue';
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello'
}
},
components: {
onA,
onB
},
onLoad() {
},
mounted() {
console.log(this.$root.$children[0].$children[0]._data);
console.log(this.$root.$children[0].$children[1]._data.msg);
console.log(this.$root.$children[0].$children[2]._data.msg);
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
</style>
七、$set - 在开发过程中,我们时常会遇到这样一种情况:当vue的data里边声明或者已经赋值过的对象或者数组(数组里边的值是对象)时,向对象中添加新的属性,如果更新此属性的值,是不会更新视图的
1.运行这个示例时,我们发现对象新增的属性(e)是不会更新的
<template>
<view>
<view @click="addd(obj)">点击增加1:{{obj.d}}</view>
<view @click="adde(obj)">点击增加2:{{obj.e}}</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
obj: {}
}
},
mounted() {
// 原有的
this.obj = {
d: 0
};
// 新增的对象.e
this.obj.e = 0;
console.log('after--', this.obj);
},
methods: {
addd(item) {
item.d = item.d + 1;
console.log('item--1', item);
},
adde(item) {
item.e = item.e + 1;
// this.$forceUpdate();
console.log('item--2', item);
}
}
}
</script>
2. 我们有两种解决方案,一种是利用this.$set或者this.$foreUpdate();让它渲染到视图层 - 代码引用简书:https://www.jianshu.com/p/71b1807b1815

<template>
<view>
<view @click="addd(obj)">点击增加1:{{obj.d}}</view>
<view @click="adde(obj)">点击增加2:{{obj.e}}</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
obj: {}
}
},
mounted() {
// 原有的
this.obj = {
d: 0
};
// 新增的对象.e
// this.obj.e = 0;
this.$set(this.obj, 'e', 0);
console.log('after--', this.obj);
},
methods: {
addd(item) {
item.d = item.d + 1;
console.log('item--1', item);
},
adde(item) {
item.e = item.e + 1;
// this.$forceUpdate();
console.log('item--2', item);
}
}
}
</script>
理清一下已经使用过的vue实例,可能会再次更新(-.-)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号