SSL编程(2).NET最简单的客户端
在Windows平台上,实现SSL的.NET类是System.Net.Security.SslStream类。这个类既可以用于建立SSL服务,也可以用来作为SSL客户端连接远端的SSL服务。
最简单的SSL客户端是连接一个无需客户端验证的服务器,客户端不必出示数字证书。对公众提供服务的门户网站的https入口一般都是如此,检验服 务器证书的有效性是客户端自己的事情。浏览器自己是一个典型的SSL客户端,由于客户端要负责验证服务器证书,所以使用可信的浏览器对于安全上网十分重 要。SSL服务器端网上很好找,随便选一个https网站作为对端,我们的客户端演示程序就能够建立一个实际的SSL安全连接了。
这里,我们的客户端程序连接一个拥有公网数字证书的https网站,如https: //www.alipay.com。默认的系统安全配置会检验服务器给出的证书,决定安全协商的结果。如果远端数字证书有 效,SslStream.AuthenticateAsClient函数调用会成功,不抛出任何异常。这个函数的名称不是很准确,看起来像是只做了鉴别工 作,实际上这个函数如果正常完成,意味着整个SSL握手工作的完成,包括鉴别和密钥交换。应用程序随后就可以用这个SslStream对象的读写函数与远 端服务器安全通信,如请求一个网页等等,服务器发送账单,用户提交用户信用卡号等敏感信息都应该在这样的安全连接中进行。
这里我们先建立一个普通的TCP连接,然后在基于这个TCP连接的通信通道,建立SSL安全连接。这里我们不讨论普通TCP连接的建立和使用问题。
我们的例子代码的功能是,作为ssl客户端,连接一个知名的网站的https服务的端口。这个端口一般是443。ssl握手鉴别成功之后,我们在 ssl通道上给服务器发送一个http页面请求,然后接收服务器应答的html页面数据,把页面源码直接以字符形式打印在控制台上。感兴趣的读者可以进一 步把它保存成html文件,用浏览器打开查看返回的网页。
代码的简要流程如下:
1 建立普通tcp连接。
2 构造sslstream对象
3 在try块中,调用authenticateasclient开始ssl握手过程,试图与也服务器建立ssl连接。
4 安全地 收发加密的数据,或者 在catch块中处理ssl握手异常。
代码全文如下:
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Security;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Security.Authentication;
using System.Text;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.IO;
namespace Examples.System.Net
{
public class SslTcpClient
{
private static Hashtable certificateErrors = new Hashtable();
// 验证服务器证书的回调函数。
public static bool ValidateServerCertificate(
object sender,
X509Certificate certificate,
X509Chain chain,
SslPolicyErrors sslPolicyErrors)
{
if (sslPolicyErrors == SslPolicyErrors.None)
return true;
Console.WriteLine("Certificate error: {0}", sslPolicyErrors);
// 不能通过的服务器证书验证的,返回false,阻止建立连接。
return false;
}
public static void RunClient(string machineName, string serverName)
{
// 1 建立普通tcp连接。
TcpClient client = new TcpClient(machineName, 443);
Console.WriteLine("Client connected.");
// 2 构造SslStream类的对象.
SslStream sslStream = new SslStream(
client.GetStream(),
false,
new RemoteCertificateValidationCallback(ValidateServerCertificate),
null
);
// The server name must match the name on the server certificate.
try
{
// 3 发起ssl握手,试图建立ssl连接.
sslStream.AuthenticateAsClient(serverName, null, SslProtocols.Tls, false);
}
catch (AuthenticationException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception: {0}", e.Message);
if (e.InnerException != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Inner exception: {0}", e.InnerException.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine("Authentication failed - closing the connection.");
client.Close();
return;
}
// Encode a test message into a byte array.
// Signal the end of the message using the "<EOF>".
byte[] messsage = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("GET " + machineName + "/ HTTP/1.0\r\n");
// 发送ssl加密数据。.
sslStream.Write(messsage);
sslStream.Flush();
// Read message from the server.
string serverMessage = ReadMessage(sslStream);
Console.WriteLine("Server says: {0}", serverMessage);
// Close the client connection.
client.Close();
Console.WriteLine("Client closed.");
}
static string ReadMessage(SslStream sslStream)
{
// Read the message sent by the server.
// The end of the message is signaled using the
// "<EOF>" marker.
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
StringBuilder messageData = new StringBuilder();
int bytes = -1;
do
{
//接收来自服务器的Ssl加密保护的数据。
bytes = sslStream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
// Use Decoder class to convert from bytes to UTF8
// in case a character spans two buffers.
Decoder decoder = Encoding.UTF8.GetDecoder();
char[] chars = new char[decoder.GetCharCount(buffer, 0, bytes)];
decoder.GetChars(buffer, 0, bytes, chars, 0);
messageData.Append(chars);
} while (bytes != 0);
return messageData.ToString();
}
private static void DisplayUsage()
{
Console.WriteLine("To start the client specify:");
Console.WriteLine("clientSync machineName [serverName]");
Environment.Exit(1);
}
public static int Main(string[] args)
{
string serverCertificateName = "www.taobao.com";
string machineName = "www.taobao.com";
SslTcpClient.RunClient(machineName, serverCertificateName);
return 0;
}
}
}
在调试器中,看到的sslStream对象的状态如下:
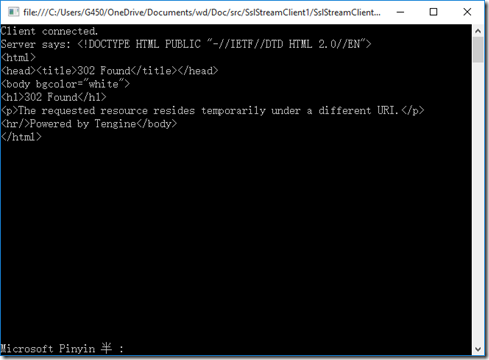
代码运行的结果如下:
我们看到了服务器通过SSL安全通道返回的HTML网页数据。