39.Combination Sum
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum/description/
题目大意:给出一串数字(没有重复数字)和一个数字,找出所有组合数的和与这个数字相等的组合数,其中组合数的每一个数字可以重复选,例子如下:
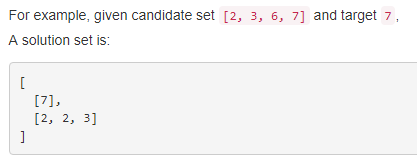
法一:利用78题的法一,只是这里对target有所限制,还要注意可以重复取数字。代码如下(耗时23ms):

1 public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { 2 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); 3 List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 4 dfs(res, tmp, candidates, target, 0); 5 return res; 6 } 7 public static void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> tmp, int[] candidates, int target, int start) { 8 if(target == 0) {//递归结束条件 9 res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(tmp)); 10 return; 11 } 12 else if(target > 0){//这里一定要判断target>0,因为如果不判断就会导致target<0时还在往下递归 13 for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) { 14 tmp.add(candidates[i]); 15 dfs(res, tmp, candidates, target - candidates[i], i);//这里不是i+1而是i,因为可以重复选 16 tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1); 17 } 18 } 19 }
剪枝,先排序,然后在递归的时候,一旦总和<=0则跳出后面的循环。代码如下(耗时18ms):

1 public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { 2 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); 3 List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 4 Arrays.sort(candidates);//先进行排序 5 dfs(res, tmp, candidates, target, 0); 6 return res; 7 } 8 public static boolean dfs(List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> tmp, int[] candidates, int target, int start) { 9 if(target < 0) { 10 return false; 11 } 12 if(target == 0) {//递归结束条件 13 res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(tmp)); 14 return false; 15 } 16 else {//这里一定要判断target>0,因为如果不判断就会导致target<0时还在往下递归 17 for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) { 18 tmp.add(candidates[i]); 19 boolean flag = dfs(res, tmp, candidates, target - candidates[i], i);//这里不是i+1而是i,因为可以重复选 20 tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1); 21 //剪枝,因为数组是排好序的,所以一旦总和<=0,那么其后的数字一定会导致当前结果<0,所以可以直接从此跳过后面的循环 22 if(flag == false) { 23 break; 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 return true; 28 }
另一个方法剪枝,不用等到总和<=0才剪枝,而是在dfs之前就判断是否能选该数,否则就跳出循环。代码如下(耗时15ms):

1 public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { 2 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); 3 List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 4 Arrays.sort(candidates); 5 dfs(res, tmp, candidates, target, 0); 6 return res; 7 } 8 public static void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> tmp, int[] candidates, int target, int start) { 9 if(target == 0) {//递归结束条件 10 res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(tmp)); 11 return; 12 } 13 else if(target > 0){//这里一定要判断target>0,因为如果不判断就会导致target<0时还在往下递归 14 for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) { 15 //快速剪枝 16 if(target < candidates[i]) { 17 break; 18 } 19 tmp.add(candidates[i]); 20 dfs(res, tmp, candidates, target - candidates[i], i);//这里不是i+1而是i,因为可以重复选 21 tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1); 22 } 23 } 24 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号