SpringBoot2 整合OAuth2组件,模拟第三方授权访问
一、模式描述
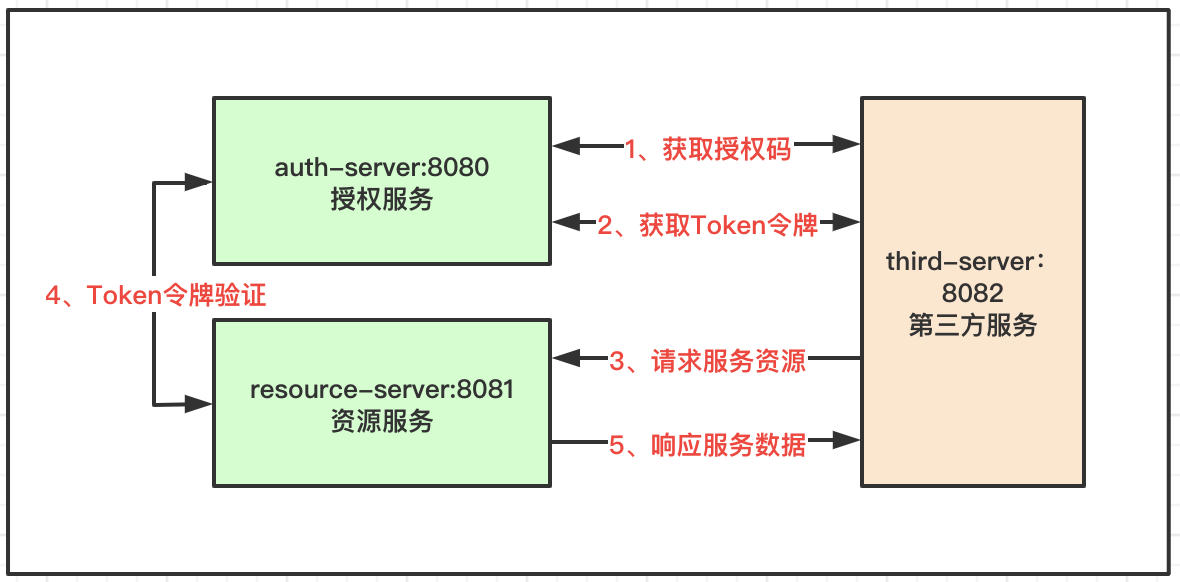
授权服务
验证第三方服务的身份,验证邮箱用户的身份,记录和管理认证Token,为资源服务器提供Token校验。场景:第三方网站借助用户的邮箱登录,并访问邮箱账户的基础信息,头像、名称等。
资源服务
第三方服务通过邮箱账户登录后需要获取的一些信息,即理解为资源,存储邮箱账户的数据资源。
第三方服务
即借助邮箱用户的账户,快速登录第三个服务,免去繁杂的注册流程,有助于快速积累新用户。
交互流程
第三方服务给用户开放快速邮箱登录功能,引导用户调到邮箱认证服务,通过认证后返回身份令牌到第三方服务,第三方服务携带令牌访问邮箱的资源服务,获取一些基本的邮箱用户信息。
二、项目配置管理
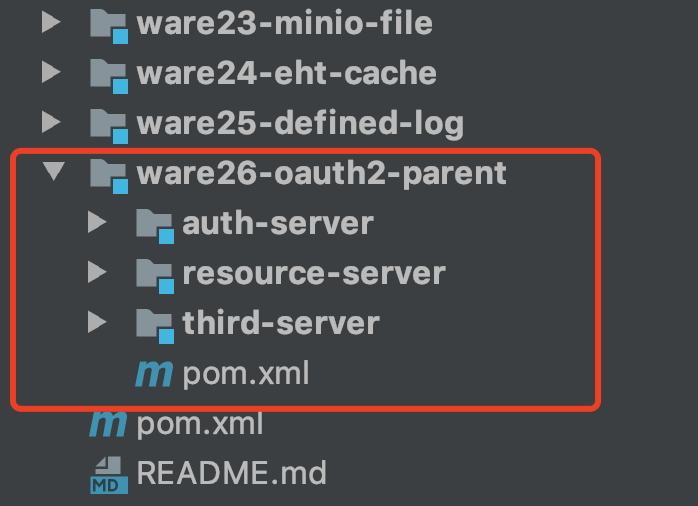
1、案例结构
核心依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
这里有两个核心组件依赖:OAuth2组件和Security组件。
模块划分
- auth-server:授权服务
- resource-server:资源服务器
- third-server:第三个服务
2、配置描述
【授权服务】
OAuth2配置
这里的配置管理的是第三方的授权流程和发放给第三方的身份证明ClientID和密码,实际的场景就是第三方借助邮箱账号登录,首先就是向邮箱管理方提供材料,获取访问邮箱服务的身份证明,然后才能对接开放服务,这种模式在第三方对接业务中很常见。
/**
* 模拟第三方授权配置
*/
@EnableAuthorizationServer
@Configuration
public class AuthConfig extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Resource
ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
/**
* 资源服务器校验Token
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) {
security.checkTokenAccess("permitAll()").allowFormAuthenticationForClients();
}
/**
* 第三方客户端请求配置,和资源服务访问的配置,不设置默认都可以访问,提供默认回调地址
*/
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()
.withClient("third01")
.secret(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("third01"))
.resourceIds("resource-01")
.authorizedGrantTypes("authorization_code","refresh_token")
.scopes("all")
.redirectUris("http://localhost:8082/notify.html");
}
/**
* 配置访问端点
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) {
endpoints.authorizationCodeServices(authorizationCodeServices()).tokenServices(tokenServices());
}
/**
* 内存管理
*/
@Bean
AuthorizationCodeServices authorizationCodeServices() {
return new InMemoryAuthorizationCodeServices();
}
/**
* Token管理规则
*/
@Bean
AuthorizationServerTokenServices tokenServices() {
DefaultTokenServices services = new DefaultTokenServices();
services.setClientDetailsService(clientDetailsService);
services.setSupportRefreshToken(true);
services.setTokenStore(tokenStore());
services.setAccessTokenValiditySeconds(3600);
services.setRefreshTokenValiditySeconds(3600*7);
return services;
}
@Bean
TokenStore tokenStore() {
return new InMemoryTokenStore();
}
}
通常需要数据库存储第三方信息,可以到第OAuth2开源项目中,获取表结构放到本地数据库中,然后这里换成数据源加载模式即可,简单的流程管理都在源码里写了SQL语句,数据源引入即可。
Security配置
/**
* 模拟本地用户配置
*/
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* 密码加密方式
*/
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* 内存中虚拟用户和角色
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("user")
.password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"))
.roles("user");
}
/**
* 表单登录
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable().formLogin();
}
}
基于这里的配置管理邮箱用户的认证流程,例如使用邮箱账号密码登录验证,判断授权是否成立,这里管理的是服务本地的邮箱账号,基于数据源存储数据在下面案例中都有。
关于Spring框架中安全认证的相关的几个组件,在使用OAuth2之前可以先了解一下。
【资源服务】
主要功能有三块,配置第三方携带的Token身份令牌校验机制,即访问授权服务校验接口,这里是OAuth2自定义好的接口;配置resourceId资源服务的编号,用来控制第三个服务能访问的资源服务范围,属于大的权限点控制;模拟校验用户的Role角色,较精细的控制权限。
/**
* 资源服务管理配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* Token令牌校验
*/
@Bean
RemoteTokenServices tokenServices() {
RemoteTokenServices services = new RemoteTokenServices();
services.setCheckTokenEndpointUrl("http://localhost:8080/oauth/check_token");
services.setClientId("third01");
services.setClientSecret("third01");
return services;
}
/**
* 服务资源ID配置
*/
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception {
resources.resourceId("resource-01").tokenServices(tokenServices());
}
/**
* 模拟用户权限规则
*/
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("user")
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
【第三方服务】
主要提供两个流程的模拟:请求授权服务获取身份令牌;携带身份令牌请求资源服务获取数据。这里则是授权码回调接口的处理方式。
@Controller
public class NotifyController {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NotifyController.class);
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/notify.html")
public String notify(String code, Model model) {
if (code != null) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> map = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
map.add("code", code);
map.add("client_id", "third01");
map.add("client_secret", "third01");
map.add("redirect_uri", "http://localhost:8082/notify.html");
map.add("grant_type", "authorization_code");
Map<String,String> resp = restTemplate.postForObject("http://localhost:8080/oauth/token", map, Map.class);
String accessToken = resp.get("access_token");
LOG.info("身份令牌:{}",accessToken);
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Authorization", "Bearer " + accessToken);
HttpEntity<Object> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(headers);
ResponseEntity<String> entity = restTemplate.exchange("http://localhost:8081/user/resource", HttpMethod.GET, httpEntity, String.class);
model.addAttribute("notifyMsg", entity.getBody());
}
return "notify";
}
}
三、测试流程
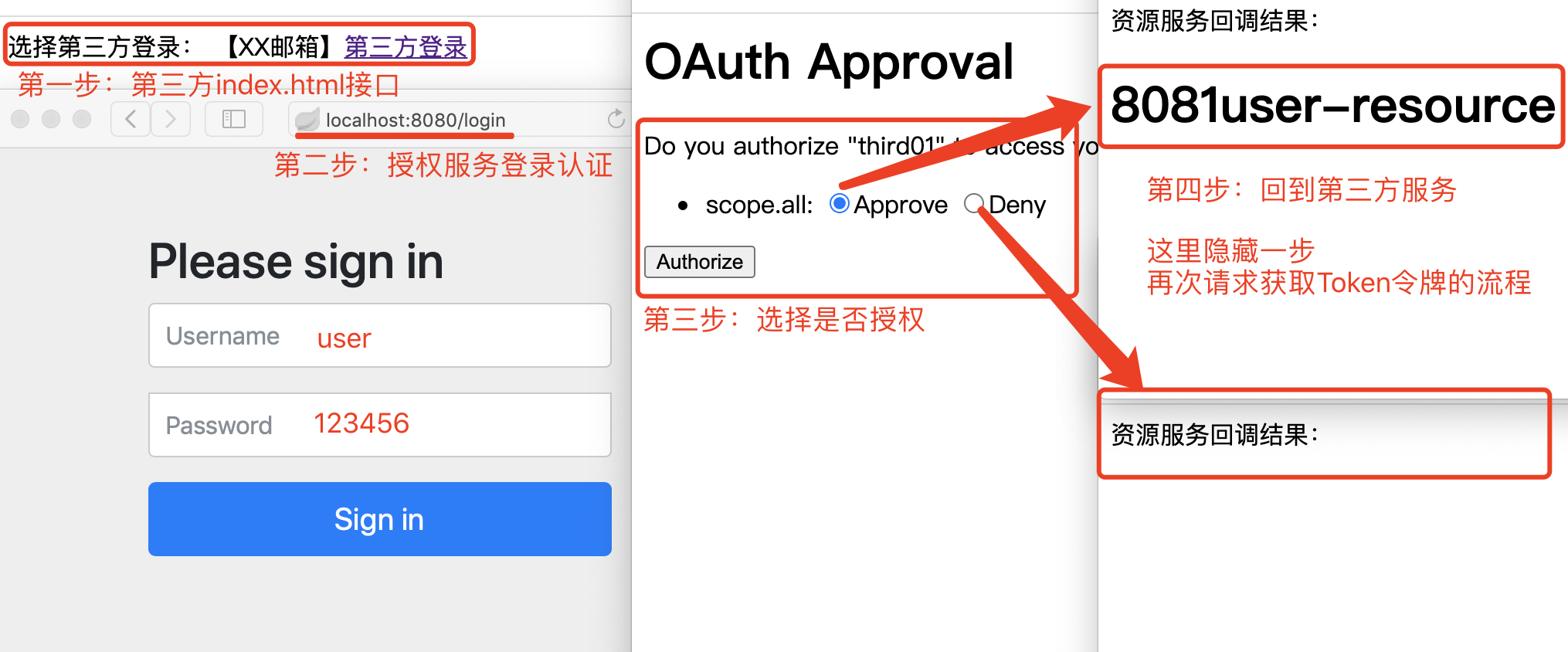
通过上述测试流程,对比常见的第三方登录机制,理解OAuth2的授权码模式。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix