SpringBoot2.0 基础案例(03):配置系统全局异常映射处理
一、异常分类
这里的异常分类从系统处理异常的角度看,主要分类两类:业务异常和系统异常。
1、业务异常
业务异常主要是一些可预见性异常,处理业务异常,用来提示用户的操作,提高系统的可操作性。
常见的业务异常提示:
1)请输入xxx
2)xxx不能为空
3)xxx重复,请更换
2、系统异常
系统异常主要是一些不可预见性异常,处理系统异常,可以让展示出一个友好的用户界面,不易给用户造成反感。如果是一个金融类系统,在用户界面出现一个系统异常的崩溃界面,很有可能直接导致用户流失。
常见的系统异常提示:
1)页面丢失404
2)服务器异常500
二、解决应用启动后404界面

1、引入页面Jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、自定义首页接口
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index(ModelMap modelMap) {
modelMap.addAttribute("name","知了一笑") ;
return "index";
}
}
3、首页界面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${name}"></h1>
</body>
</html>
4、运行效果
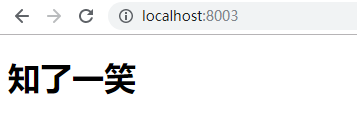
三、SpringBoot2.0中异常处理
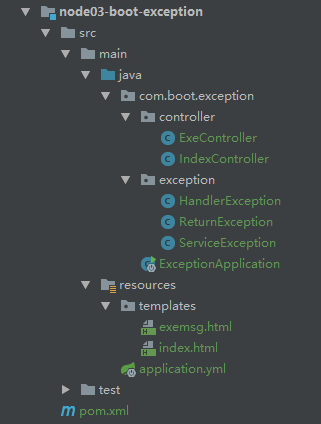
1、项目结构图
2、自定义业务异常类
public class ServiceException extends Exception {
public ServiceException (String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
3、自定义异常描述对象
public class ReturnException {
// 响应码
private Integer code;
// 异常描述
private String msg;
// 请求的Url
private String url;
// 省略 get set 方法
}
4、统一异常处理格式
1)两个基础注解
@ControllerAdvice 定义统一的异常处理类
@ExceptionHandler 定义异常类型对应的处理方式
2)代码实现
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@ControllerAdvice
// 异常以Json格式返回 等同 ExceptionHandler + ResponseBody 注解
// @RestControllerAdvice
public class HandlerException {
/**
* 自定义业务异常映射,返回JSON格式提示
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = ServiceException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ReturnException handler01 (HttpServletRequest request,ServiceException e){
ReturnException returnException = new ReturnException() ;
returnException.setCode(600);
returnException.setMsg(e.getMessage());
returnException.setUrl(String.valueOf(request.getRequestURL()));
return returnException ;
}
/**
* 服务异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public ModelAndView handler02 (HttpServletRequest request,Exception e){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView() ;
modelAndView.addObject("ExeMsg", e.getMessage());
modelAndView.addObject("ReqUrl", request.getRequestURL());
modelAndView.setViewName("/exemsg");
return modelAndView ;
}
}
5、简单的测试接口
@Controller
public class ExeController {
/**
* {
* "code": 600,
* "msg": "业务异常:ID 不能为空",
* "url": "http://localhost:8003/exception01"
* }
*/
@RequestMapping("/exception01")
public String exception01 () throws ServiceException {
throw new ServiceException("业务异常:ID 不能为空");
}
@RequestMapping("/exception02")
public String exception02 () throws Exception {
throw new Exception("出现异常,全体卧倒");
}
}







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix