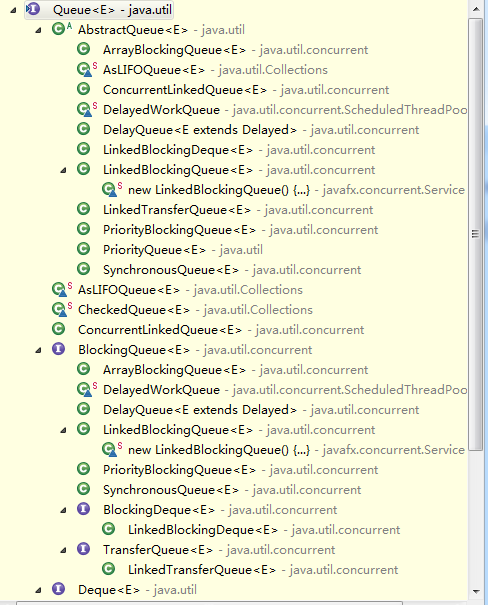
并发队列Queue
队列其实就是一个容器
在并发队列上JDK提供了两套实现,一个是以ConcurrentLinkedQueue为代表的高性能队
列,一个是以BlockingQueue接口为代表的阻塞队列,无论哪种都继承自Queue。
同步容器
Vector容器,HashTable容器,都是线程安全
如果同步容器使用foreach迭代过程中修改了元素的值,则会出现ConcurrentModificationException异常
可以使用iterator迭代器解决,但是在多线程并行情况下,修改容器中数据,会发生阻塞或者报NoSech异常
并发容器,队列
无界限:代表队列当中可以存放N个数据,没有长度限制
有界限:队列当中规定只能存放多少个数据,超过则阻塞
1.ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue : 是一个适用于高并发场景下的队列,通过无锁的方式,实现了高并发状态下的高性能,通常ConcurrentLinkedQueue性能好于BlockingQueue.
它是一个基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列。该队列的元素遵循先进先出的原则。头是最先加入的,尾是最近加入的,该队列不允许null元素。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue重要方法:
add 和offer() 都是加入元素的方法(在ConcurrentLinkedQueue中这俩个方法没有任何区别)
poll() 和peek() 都是取头元素节点,区别在于前者会删除元素,后者不会。
peek和poll当队列当中没有数据时,获取的数据为null,不会产生阻塞
public static void main(String[] args) { //准备队列 ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>(); //存放数据 queue.offer("张三"); queue.offer("李四"); queue.offer("王五"); //获取队列中数据个数 System.out.println("队列中当前有:"+queue.size()+"个数据~"); //获取队列中头数据 poll()方法相当于消费了队列中的数据,队列数据会随之删除 System.out.println("获取队列中的数据:"+queue.poll()); System.out.println("队列中当前有:"+queue.size()+"个数据~"); //获取队列中数据,但是不会删除 System.out.println("获取队列中的数据:"+queue.peek()); System.out.println("获取队列中的数据:"+queue.peek()); System.out.println("队列中当前有:"+queue.size()+"个数据~"); }

2.有边界的阻塞队列BlockingQueue
put方法和take会发生阻塞,add以及offer还有poll和peek不会发生阻塞
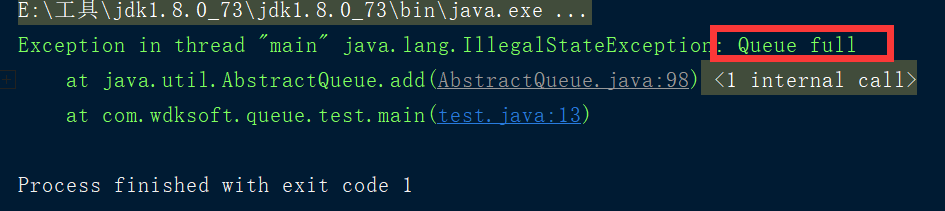
3.1 ArrayBlockingQueue:当队列没有数据时,获取时为null,当队列满时,会报异常或者入队失败
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //ArrayBlockingQueue底层数组实现 ArrayBlockingQueue<String> arrays = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(3); arrays.add("张三"); arrays.add("李四"); arrays.add("王五"); arrays.add("赵六"); }
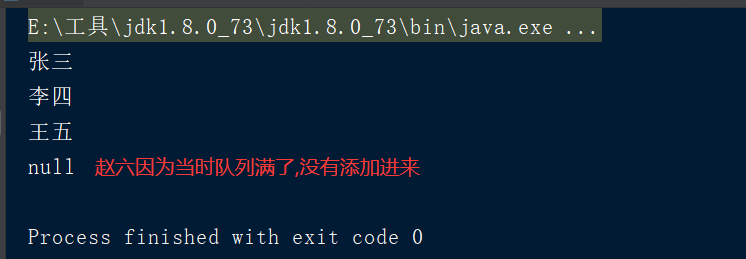
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//ArrayBlockingQueue底层数组实现
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> arrays = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(3);
arrays.add("张三");
arrays.add("李四");
arrays.add("王五");
arrays.offer("赵六",1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println(arrays.poll());
System.out.println(arrays.poll());
System.out.println(arrays.poll());
System.out.println(arrays.poll());
}
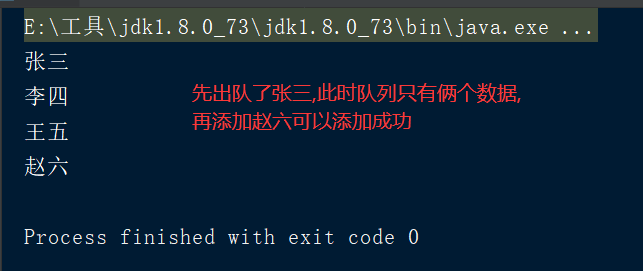
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //ArrayBlockingQueue底层数组实现 ArrayBlockingQueue<String> arrays = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(3); arrays.add("张三"); arrays.add("李四"); arrays.add("王五"); System.out.println(arrays.poll()); arrays.offer("赵六",1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); System.out.println(arrays.poll()); System.out.println(arrays.poll()); System.out.println(arrays.poll()); }
3.LinkedBlockingQueue
初始可以指定队列大小,如果不指定则按照Integer.MaxValue值进行设定
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //ArrayBlockingQueue底层数组实现 LinkedBlockingQueue <String> arrays = new LinkedBlockingQueue<String>(100); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { arrays.put("item"+i); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { try { System.out.println(arrays.take()+i); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); }



