flume【源码分析】分析Flume的启动过程
前言
之前一直在用flume收集数据,也做了一些插件开发,但是一直没整理相关的知识,最近感觉老是有一种知其然不知其所以然的感觉,所以从源码入手希望能更透彻一点吧,越来越感觉会用不能掌握啊!别人几个为啥就low了!
1.启动入口
估计没人关注过启动入口在什么地方吧?启动不报错就可以直接去用了吧!
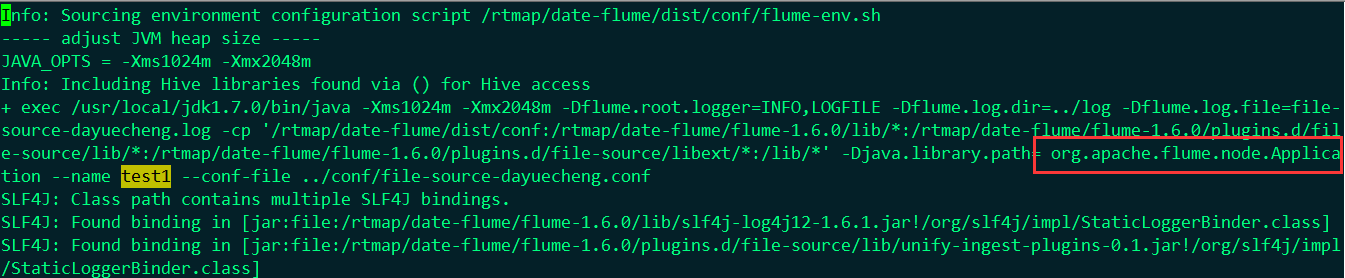
从这里可以看出flume的启动入口是:org.apache.flume.node.Application 注意:记得用maven 安装flume-ng-node 不然你找不到!因为有的开发用不到也就不装了!
下面我们就来看该入口程序是如何来运行的:

try { boolean isZkConfigured = false; Options options = new Options(); Option option = new Option("n", "name", true, "the name of this agent"); option.setRequired(true); options.addOption(option); option = new Option("f", "conf-file", true, "specify a config file (required if -z missing)"); option.setRequired(false); options.addOption(option); option = new Option(null, "no-reload-conf", false, "do not reload config file if changed"); options.addOption(option); // Options for Zookeeper option = new Option("z", "zkConnString", true, "specify the ZooKeeper connection to use (required if -f missing)"); option.setRequired(false); options.addOption(option); option = new Option("p", "zkBasePath", true, "specify the base path in ZooKeeper for agent configs"); option.setRequired(false); options.addOption(option); option = new Option("h", "help", false, "display help text"); options.addOption(option); CommandLineParser parser = new GnuParser(); CommandLine commandLine = parser.parse(options, args); if (commandLine.hasOption('h')) { new HelpFormatter().printHelp("flume-ng agent", options, true); return; } String agentName = commandLine.getOptionValue('n'); boolean reload = !commandLine.hasOption("no-reload-conf"); if (commandLine.hasOption('z') || commandLine.hasOption("zkConnString")) { isZkConfigured = true; } Application application = null; if (isZkConfigured) { // get options String zkConnectionStr = commandLine.getOptionValue('z'); String baseZkPath = commandLine.getOptionValue('p'); if (reload) { EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus"); List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList(); PollingZooKeeperConfigurationProvider zookeeperConfigurationProvider = new PollingZooKeeperConfigurationProvider( agentName, zkConnectionStr, baseZkPath, eventBus); components.add(zookeeperConfigurationProvider); application = new Application(components); eventBus.register(application); } else { StaticZooKeeperConfigurationProvider zookeeperConfigurationProvider = new StaticZooKeeperConfigurationProvider( agentName, zkConnectionStr, baseZkPath); application = new Application(); application.handleConfigurationEvent(zookeeperConfigurationProvider .getConfiguration()); } } else { File configurationFile = new File(commandLine.getOptionValue('f')); /* * The following is to ensure that by default the agent will fail on * startup if the file does not exist. */ if (!configurationFile.exists()) { // If command line invocation, then need to fail fast if (System.getProperty(Constants.SYSPROP_CALLED_FROM_SERVICE) == null) { String path = configurationFile.getPath(); try { path = configurationFile.getCanonicalPath(); } catch (IOException ex) { logger.error("Failed to read canonical path for file: " + path, ex); } throw new ParseException( "The specified configuration file does not exist: " + path); } } List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList(); if (reload) { EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus"); PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider = new PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider( agentName, configurationFile, eventBus, 30); components.add(configurationProvider); application = new Application(components); eventBus.register(application); } else { PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider = new PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider( agentName, configurationFile); application = new Application(); application.handleConfigurationEvent(configurationProvider .getConfiguration()); } } application.start(); final Application appReference = application; Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread("agent-shutdown-hook") { @Override public void run() { appReference.stop(); } }); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("A fatal error occurred while running. Exception follows.", e); } }
附:flume每次启动都会先判断有没有与当前配置的三大组件同名的组件存在,存在的话先停掉该组件,顺序为source,sink,channel
其次是启动所有当前配置的组件,启动顺序为channel,sink,source
以上启动顺序来源如下:
public synchronized void handleConfigurationEvent(MaterializedConfiguration conf) { stopAllComponents(); startAllComponents(conf); }
这个地方说几句:
1.前面一堆就是启动命令中一些参数的解析,如果真想了解自己去看看源码吧!
2.这里面有两种形式配置文件,一种是连接zk读取配置文件的,一种是读取配置文件,反正我经常用的也是读取配置文件的方式-f 那就说配置文件吧!
3.这里有一个机制,如果不带--no-reload-conf这个参数,flume会自动加载配置参数 默认是30秒,现在不用再傻傻的修改完配置文件去重启flume了吧!
if (reload) { EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus"); PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider = new PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider( agentName, configurationFile, eventBus, 30); components.add(configurationProvider); application = new Application(components); eventBus.register(application); } else { PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider = new PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider( agentName, configurationFile); application = new Application(); application.handleConfigurationEvent(configurationProvider .getConfiguration()); }
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider该类是一个轮询操作,每隔30秒会去检查conf配置文件。
这个地方如果不是轮训的方式,那么需要杀掉所有组件,在重启所有组件。调用这两个方法 stopAllComponents(); startAllComponents(conf);
configurationProvider.getConfiguration() 这个是重点好多配置,source 类型,source 和channel对接都在这个里面
1.请注意重点看一下loadxx方法
2.loadSources里面有个 SourceRunner.forSource(source)是指定source类型的:PollableSource,EventDrivenSourceRunner这个需要你在自己开发的时候根据需求自己继承吧!

public static SourceRunner forSource(Source source) { SourceRunner runner = null; if (source instanceof PollableSource) { runner = new PollableSourceRunner(); ((PollableSourceRunner) runner).setSource((PollableSource) source); } else if (source instanceof EventDrivenSource) { runner = new EventDrivenSourceRunner(); ((EventDrivenSourceRunner) runner).setSource((EventDrivenSource) source); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("No known runner type for source " + source); } return runner; }

public MaterializedConfiguration getConfiguration() { MaterializedConfiguration conf = new SimpleMaterializedConfiguration(); FlumeConfiguration fconfig = getFlumeConfiguration(); AgentConfiguration agentConf = fconfig.getConfigurationFor(getAgentName()); if (agentConf != null) { Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap = Maps.newHashMap(); Map<String, SourceRunner> sourceRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap(); Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap(); try { loadChannels(agentConf, channelComponentMap); loadSources(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sourceRunnerMap); loadSinks(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sinkRunnerMap); Set<String> channelNames = new HashSet<String>(channelComponentMap.keySet()); for(String channelName : channelNames) { ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap. get(channelName); if(channelComponent.components.isEmpty()) { LOGGER.warn(String.format("Channel %s has no components connected" + " and has been removed.", channelName)); channelComponentMap.remove(channelName); Map<String, Channel> nameChannelMap = channelCache. get(channelComponent.channel.getClass()); if(nameChannelMap != null) { nameChannelMap.remove(channelName); } } else { LOGGER.info(String.format("Channel %s connected to %s", channelName, channelComponent.components.toString())); conf.addChannel(channelName, channelComponent.channel); } } for(Map.Entry<String, SourceRunner> entry : sourceRunnerMap.entrySet()) { conf.addSourceRunner(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } for(Map.Entry<String, SinkRunner> entry : sinkRunnerMap.entrySet()) { conf.addSinkRunner(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } } catch (InstantiationException ex) { LOGGER.error("Failed to instantiate component", ex); } finally { channelComponentMap.clear(); sourceRunnerMap.clear(); sinkRunnerMap.clear(); } } else { LOGGER.warn("No configuration found for this host:{}", getAgentName()); } return conf; }
这里通过文件修改时间来判断是否配置文件被修改了,然后通过事件总线的post调用EventHandler,也就是被@Subscribe注解的方法:这个地方只需要添加这个注解就可以就会指定调用方法执行了。
@Subscribe public synchronized void handleConfigurationEvent(MaterializedConfiguration conf) { stopAllComponents(); startAllComponents(conf); }
2.前面配置准备完后启动程序
启动程序:application.start();
public synchronized void start() { for(LifecycleAware component : components) { supervisor.supervise(component, new SupervisorPolicy.AlwaysRestartPolicy(), LifecycleState.START); } }
这是对所有组件进行监督supervise,只有在flume启动或者配置发生更改的时候会调用此监督方法
MonitorRunnable monitorRunnable = new MonitorRunnable(); monitorRunnable.lifecycleAware = lifecycleAware; monitorRunnable.supervisoree = process; monitorRunnable.monitorService = monitorService; supervisedProcesses.put(lifecycleAware, process); ScheduledFuture<?> future = monitorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay( monitorRunnable, 0, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); monitorFutures.put(lifecycleAware, future);
方法里将每个组件纳入了生命周期的管理中,每隔3秒会执行以下方法【在停止组件的时候,会调用unsupervisor方法,会给各个组件状态赋值】:
1、判断组件状态
2、如果组件当前状态不是组件预期的状态,那么就要对预期状态按照switch分支来执行相应的逻辑
MonitorRunnable 继承了Runnable接口,重写了run方法!

@Override public void run() { logger.debug("checking process:{} supervisoree:{}", lifecycleAware, supervisoree); long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { if (supervisoree.status.firstSeen == null) { logger.debug("first time seeing {}", lifecycleAware); supervisoree.status.firstSeen = now; } supervisoree.status.lastSeen = now; synchronized (lifecycleAware) { if (supervisoree.status.discard) { // Unsupervise has already been called on this. logger.info("Component has already been stopped {}", lifecycleAware); return; } else if (supervisoree.status.error) { logger.info("Component {} is in error state, and Flume will not" + "attempt to change its state", lifecycleAware); return; } supervisoree.status.lastSeenState = lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState(); if (!lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState().equals( supervisoree.status.desiredState)) { logger.debug("Want to transition {} from {} to {} (failures:{})", new Object[] { lifecycleAware, supervisoree.status.lastSeenState, supervisoree.status.desiredState, supervisoree.status.failures }); switch (supervisoree.status.desiredState) { case START: try { lifecycleAware.start(); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Unable to start " + lifecycleAware + " - Exception follows.", e); if (e instanceof Error) { // This component can never recover, shut it down. supervisoree.status.desiredState = LifecycleState.STOP; try { lifecycleAware.stop(); logger.warn("Component {} stopped, since it could not be" + "successfully started due to missing dependencies", lifecycleAware); } catch (Throwable e1) { logger.error("Unsuccessful attempt to " + "shutdown component: {} due to missing dependencies." + " Please shutdown the agent" + "or disable this component, or the agent will be" + "in an undefined state.", e1); supervisoree.status.error = true; if (e1 instanceof Error) { throw (Error) e1; } // Set the state to stop, so that the conf poller can // proceed. } } supervisoree.status.failures++; } break; case STOP: try { lifecycleAware.stop(); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Unable to stop " + lifecycleAware + " - Exception follows.", e); if (e instanceof Error) { throw (Error) e; } supervisoree.status.failures++; } break; default: logger.warn("I refuse to acknowledge {} as a desired state", supervisoree.status.desiredState); } if (!supervisoree.policy.isValid(lifecycleAware, supervisoree.status)) { logger.error( "Policy {} of {} has been violated - supervisor should exit!", supervisoree.policy, lifecycleAware); } } } } catch(Throwable t) { logger.error("Unexpected error", t); } logger.debug("Status check complete"); }
注意:lifecycleAware.start(); 这个才是所有的核心,当判断状态后开始调用相关的start()方法。


